Left Ventricular Aneurysm вђў Litfl вђў Ecg Library Diagnosis
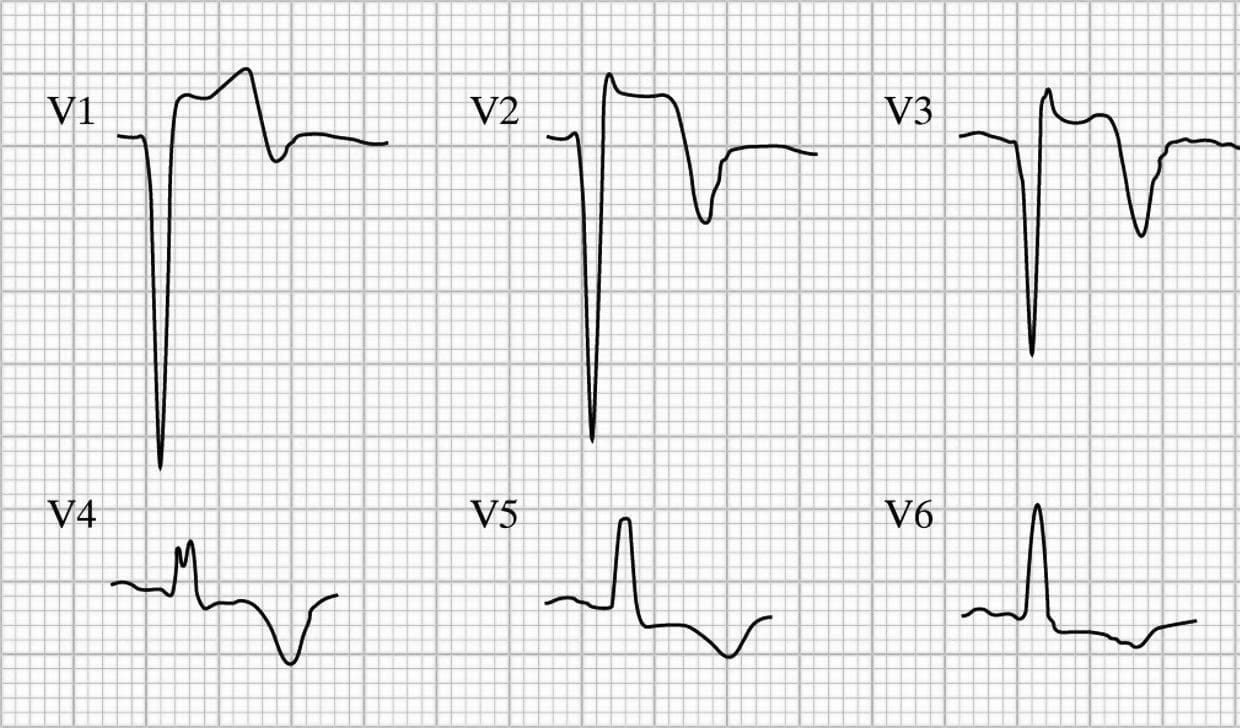
Left Ventricular Aneurysm вђў Litfl вђў Ecg Library Diagnosis Left ventricular aneurysm formation following acute stemi causes persistent st elevation on the ecg. ecg features of left ventricular aneurysm. st elevation seen > 2 weeks following an acute myocardial infarction. most commonly seen in the precordial leads. may exhibit concave or convex morphology. usually associated with well formed q or qs. Ecg library homepage. ecg diagnostic criteria. there are numerous voltage criteria for diagnosing lvh, summarised below. the most commonly used are the sokolov lyon criteria: s wave depth in v1 tallest r wave height in v5 v6 > 35 mm. voltage criteria must be accompanied by non voltage criteria to be considered diagnostic of lvh.

Left Ventricular Aneurysm вђў Litfl вђў Ecg Library Diagnosis Ecg library function. litfl ecg library is a free educational resource covering over 100 ecg topics relevant to emergency medicine and critical care. all our ecgs are free to reproduce for educational purposes, provided: the image is credited to litfl . the teaching activity is on a not for profit basis. About 1.5 million patients develop acute myocardial infarction per year in the united states.[1] several complications, such as ischemic, mechanical, arrhythmic, embolic, or inflammatory complications, are associated with acute myocardial infarction. the development of mechanical complications after acute myocardial infarction is associated with significantly reduced short term and long term. Left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. the two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. the major conditions associated with lv volume. Pathology. the wall of the true aneurysm is thinner than the wall of the rest of the left ventricle and is usually composed of fibrous tissue as well as necrotic muscle, sometimes mixed with viable myocardium. a true aneurysmal sac contains an endocardium, epicardium, and thinned fibrous tissue (scar) which is a remnant of the left ventricular.
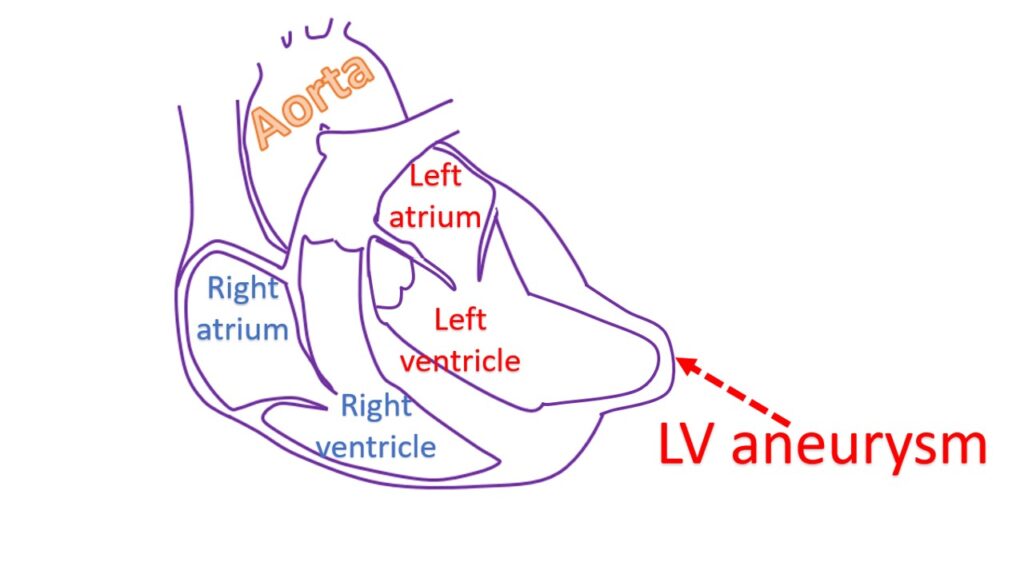
What Is Left Ventricular Aneurysm вђ All About Heart And Blood Vessels Left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. the two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. the major conditions associated with lv volume. Pathology. the wall of the true aneurysm is thinner than the wall of the rest of the left ventricle and is usually composed of fibrous tissue as well as necrotic muscle, sometimes mixed with viable myocardium. a true aneurysmal sac contains an endocardium, epicardium, and thinned fibrous tissue (scar) which is a remnant of the left ventricular. Chapter content. figure 1. ecg changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) and right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh). the electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in lvh, which results in large r waves in left sided leads (v5, v6, avl and i) and deep s waves in right sided chest leads (v1, v2). right ventricular hypertrophy causes. The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. during left ventricular hypertrophy, the thickened heart wall can become stiff. blood pressure in the heart increases. the changes make it harder for the heart to effectively pump blood. eventually, the heart may fail to pump with as much force as needed.

Comments are closed.