Leveling Effect And Differentiating Effect Of Solvents

Leveling Solvent Vs Differentiating Solvent Tabular Form Functional This is called the leveling effect. strong bases are leveling solvents for acids, weak bases are differentiating solvents for acids. because of the leveling effect of common solvents, studies on super acids are conducted in solvents that are very weakly basic such as sulfur dioxide (liquefied) and so 2 clf. [3]. The leveling effect is the ability of a solvent to enhance the strength of weak acids or bases to that of strong ones. leveling solvent is the solvent in which total proton transfer happens or the solute is entirely ionized. water (h 2 o) is a popular example of a leveling solvent. a strong acid’s strength is limited (“leveled”) by the.

Levelling And Differentiating Effect Of Solvents Acid Base Chemistry In a leveling solvent, many acids are completely dissociated and are thus of the same strength. all acids tend to become indistinguishable in strength when dissolved in strongly basic solvents owing to the greater affinity of strong bases for protons. this is called the leveling effect. [citation needed] in a differentiating solvent on the other. The solvent in which the complete proton transfer occurs or the solute is completely ionized is called leveling solvent. one of the most common examples of leveling solvents is water (h 2 o). in such a solvent, several acids are completely dissociated and are thus of the same strength. strong bases are leveling solvents for acids. Leveling effect. in acid base chemistry, the leveling effect refers to the limitation imposed by the solvent on the strength of acids and bases in solution. when a base stronger than the solvent's conjugate base is used, it deprotonates the solvent until the base is entirely consumed, making it ineffective against weaker acids. conversely, an. The leveling effect can also occur in basic solutions. the strongest brønsted base, \(\ce{b}\), that can exist in a solvent is determined by the relative acidity of the solvent, and the base's conjugate acid, \(\ce{bh^{ }}\), determines whether the base will remain unprotonated and able to act as a base in that solvent.

Leveling And Differentiating Effect Of Non Aqueous Solvents Ph Leveling effect. in acid base chemistry, the leveling effect refers to the limitation imposed by the solvent on the strength of acids and bases in solution. when a base stronger than the solvent's conjugate base is used, it deprotonates the solvent until the base is entirely consumed, making it ineffective against weaker acids. conversely, an. The leveling effect can also occur in basic solutions. the strongest brønsted base, \(\ce{b}\), that can exist in a solvent is determined by the relative acidity of the solvent, and the base's conjugate acid, \(\ce{bh^{ }}\), determines whether the base will remain unprotonated and able to act as a base in that solvent. The leveling effect of water on a strong base. to visualize the leveling effect of solvent on strong bases, consider an aqueous solution of acetylene reacting with sodium amide. in this example, acetylene (p ka =25) is a weaker acid than the solvent, water (p ka =15.7), as evident from the inverse relationship between acidity and p ka value. Leveling effects another role that solvents play is to level the strength of an acid or base. this effect is a function of the solvent auto dissociation: this leveling effect means that each solvent has an acid base window. the acidity of the solution can only be changed within that window. outside of the window, solvent leveling will take over.
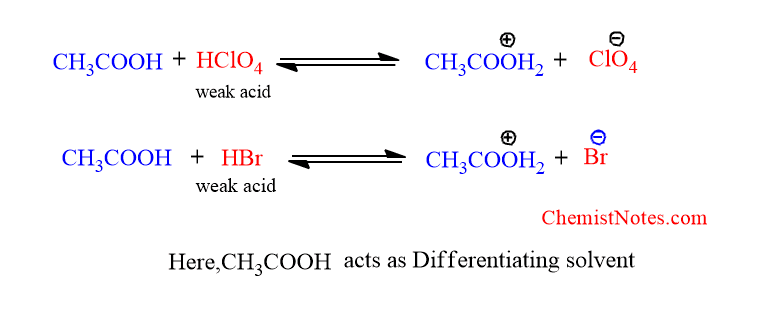
Solvent Leveling Effect Definition Example Chemistry Notes The leveling effect of water on a strong base. to visualize the leveling effect of solvent on strong bases, consider an aqueous solution of acetylene reacting with sodium amide. in this example, acetylene (p ka =25) is a weaker acid than the solvent, water (p ka =15.7), as evident from the inverse relationship between acidity and p ka value. Leveling effects another role that solvents play is to level the strength of an acid or base. this effect is a function of the solvent auto dissociation: this leveling effect means that each solvent has an acid base window. the acidity of the solution can only be changed within that window. outside of the window, solvent leveling will take over.

Leveling Effect Leveling Solvent Differentiating Solvent Leve

Comments are closed.