Luteal Phase Defect A Short Summary
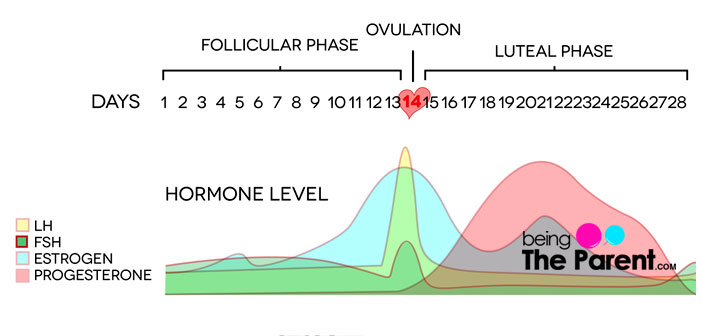
Luteal Phase Defects How It Impacts Fertility And Ways To Treat It The luteal phase is the part of your cycle that prepares your uterus for a potential pregnancy. it begins after ovulation and lasts until you get your period. in most people, the luteal phase lasts between 12 and 14 days. right before the start of the luteal phase, an egg leaves your ovary and travels through your fallopian tube. Luteal phase deficiency (lpd) was first described in 1949 (4) and lpd broadly refers to an abnormal luteal phase. given the importance of the luteal phase in the establishment of a normal pregnancy, a defect in the luteal phase (i.e., lpd) has been suggested as a cause of pregnancy, and most notably, recurrent pregnancy loss.
Luteal Phase Defect A Short Summary However, there's debate about whether luteal phase defect is a direct cause of infertility, and there's no way to test if it is. in most people, the luteal phase lasts 12 to 14 days. When the luteal phase lasts for 10 days or less, it is known as a short luteal phase or a luteal phase defect. a woman with a short luteal phase may have a harder time getting or staying pregnant. Luteal phase deficiency (lpd) is a clinical diagnosis associated with an abnormal luteal phase length of ≤10 days. potential etiologies of lpd include inadequate progesterone duration, inadequate progesterone levels, or endometrial progesterone resistance. lpd has not only been described in association with medical conditions but also in fertile, normally menstruating women. although. Given the above limitations of describing the short luteal phase, it may be reasonable to consider lpd when clinically indicated in the presence of a luteal phase of<10 days. how ever, the above findings also suggest that a shortened luteal phase length is relatively common and not associated with decreased fecundity over 12 months.
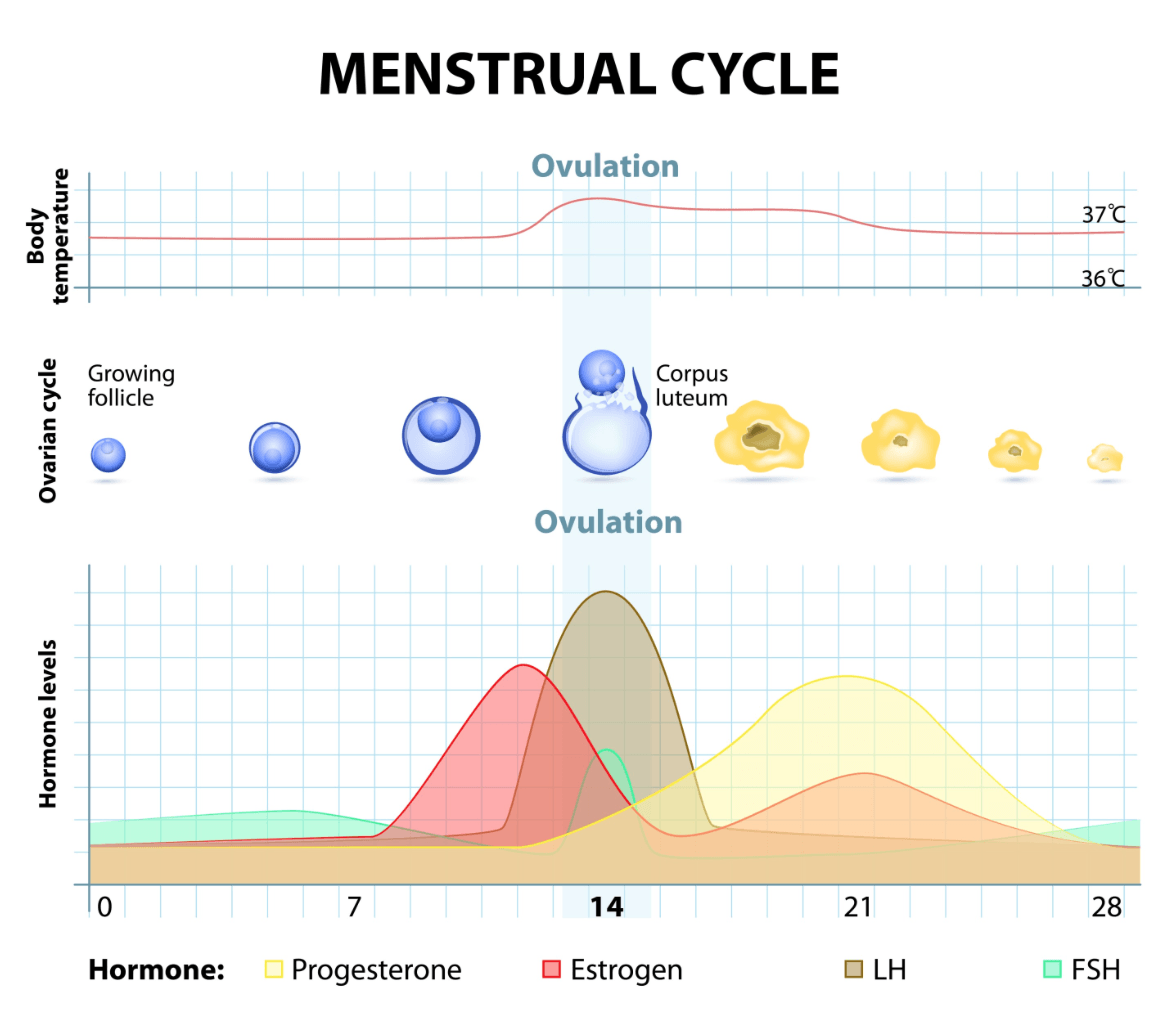
Luteal Phase Defect Understanding A Common Hormone Imbalance Luteal phase deficiency (lpd) is a clinical diagnosis associated with an abnormal luteal phase length of ≤10 days. potential etiologies of lpd include inadequate progesterone duration, inadequate progesterone levels, or endometrial progesterone resistance. lpd has not only been described in association with medical conditions but also in fertile, normally menstruating women. although. Given the above limitations of describing the short luteal phase, it may be reasonable to consider lpd when clinically indicated in the presence of a luteal phase of<10 days. how ever, the above findings also suggest that a shortened luteal phase length is relatively common and not associated with decreased fecundity over 12 months. A luteal phase defect is when your uterine lining doesn’t grow or thicken enough to support a pregnancy. lpd can cause infertility or miscarriage. long luteal phase. a long luteal phase is the opposite of a short luteal phase. it means your period comes 18 days or later after ovulation. people with a long luteal phase may have a hormonal. Luteal phase deficiency (lpd) was first described in 1949 (4) and lpd broadly refers to an abnormal luteal phase. given the importance of the luteal phase in the establishment of a normal pregnancy, a defect in the luteal phase (i.e., lpd) has been suggested as a cause of pregnancy, and most notably, recurrent pregnancy loss.

Comments are closed.