Macroeconomics Ch4
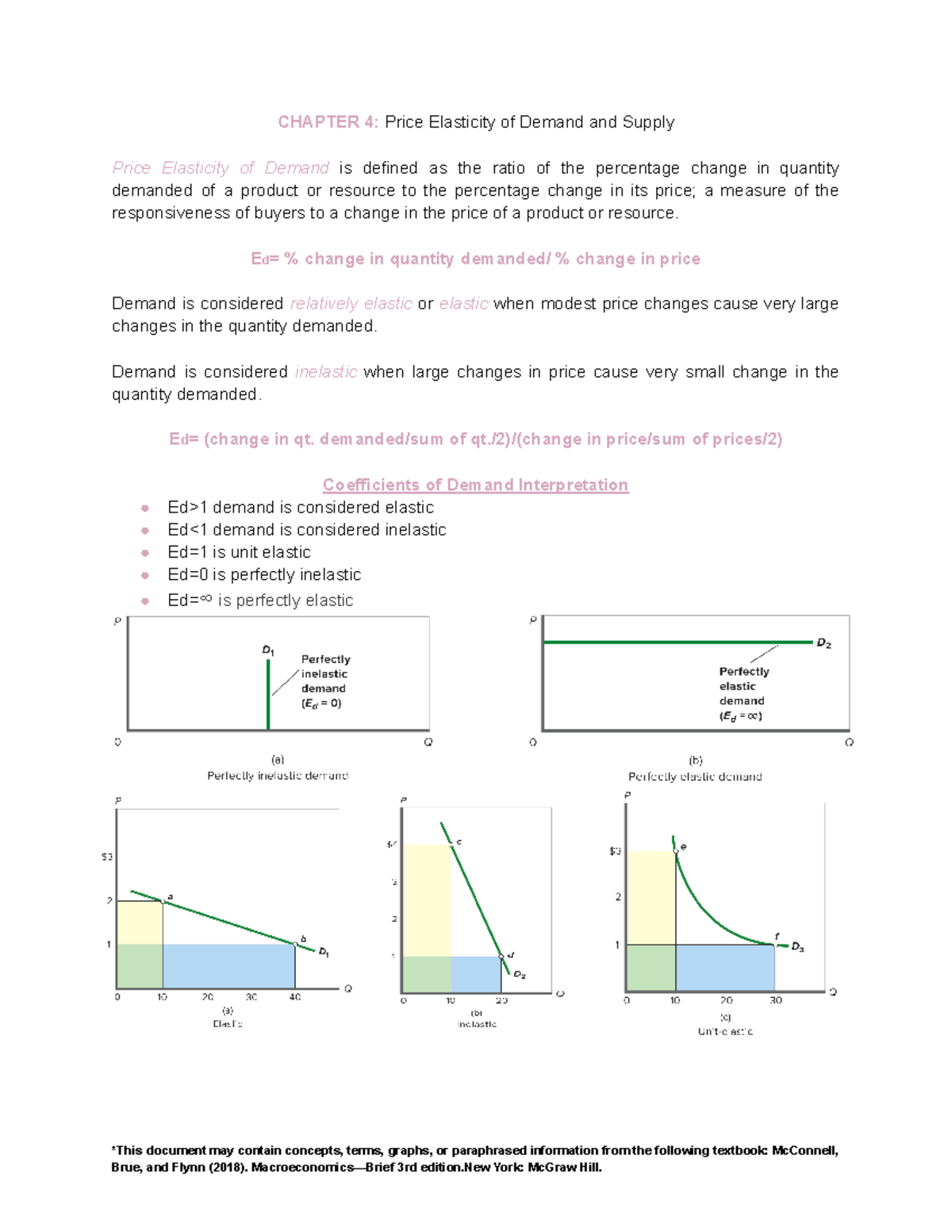
Macroeconomics Ch4 Notes Chapter 4 Price Elasticity Of Demand And Demand curve. shows how the quantity of a good demanded depends on the price. according to the law of demand, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded rises. therefore the demand curve slopes downward. supply and demand. the model that economists use to analyze competitive markets. determinants of how much consumers want to buy. price. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like true or false: market failure implies that the forces of supply and demand have not lead to the best point on the production possibilities curve., true or false: government intervention is not necessary even when the market mix of output equal the optional mix of output., true or false: the existence of public goods and.

Ppt Ch 4 What Macroeconomics Tries To Explain Powerpoint The curve remains unaffected, resulting in a decrease in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of tv screens sold. supply, supply, demand. suppose a technological advance reduces the cost of manufacturing tv screens.show the effect of this technological advancement on the market for tv screens. 11.1 macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply; 11.2 building a model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply; 11.3 shifts in aggregate supply; 11.4 shifts in aggregate demand; 11.5 how the ad as model incorporates growth, unemployment, and inflation; 11.6 keynes’ law and say’s law in the ad as model; key terms; key concepts and. Ncert macroeconomics solutions class 12 chapter 4. 1. what is marginal propensity to consume? how is it related to marginal propensity to save? mpc, or marginal propensity to consume, is a vital component of the keynesian theory of macroeconomics, and it is defined as the increase in consumer spending due to an increase in income. 11.1 macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply; 11.2 building a model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply; 11.3 shifts in aggregate supply; 11.4 shifts in aggregate demand; 11.5 how the ad as model incorporates growth, unemployment, and inflation; 11.6 keynes’ law and say’s law in the ad as model; key terms; key concepts and.

Macroeconomics Ch4 Ppt Ncert macroeconomics solutions class 12 chapter 4. 1. what is marginal propensity to consume? how is it related to marginal propensity to save? mpc, or marginal propensity to consume, is a vital component of the keynesian theory of macroeconomics, and it is defined as the increase in consumer spending due to an increase in income. 11.1 macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply; 11.2 building a model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply; 11.3 shifts in aggregate supply; 11.4 shifts in aggregate demand; 11.5 how the ad as model incorporates growth, unemployment, and inflation; 11.6 keynes’ law and say’s law in the ad as model; key terms; key concepts and. Sandeep garg macroeconomics class 12 solutions chapter 4 free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. firm a sold timber to firm b for rs. 1,000 and firewood to consumers for rs. 500. firm b converted logs into slippers and sold some to firm c and consumers. firm c sold furniture to consumers and the government. 1 price of related goods. 2. taste and preferences. 3. income. 4. expectations. therefore, the price of hot dogs (related goods) and income of consumers will affect the demand curve. the price of hamburger buns does not affect the demand curve, it will affect the supply curve and the price of hamburger does not shift the demand curve, it moves.

Macroeconomics Ch4 Sandeep garg macroeconomics class 12 solutions chapter 4 free download as pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. firm a sold timber to firm b for rs. 1,000 and firewood to consumers for rs. 500. firm b converted logs into slippers and sold some to firm c and consumers. firm c sold furniture to consumers and the government. 1 price of related goods. 2. taste and preferences. 3. income. 4. expectations. therefore, the price of hot dogs (related goods) and income of consumers will affect the demand curve. the price of hamburger buns does not affect the demand curve, it will affect the supply curve and the price of hamburger does not shift the demand curve, it moves.

Macroeconomics Ch4 Ppt

Comments are closed.