Marginal Propensity To Consume And Change In Income Due To Change In
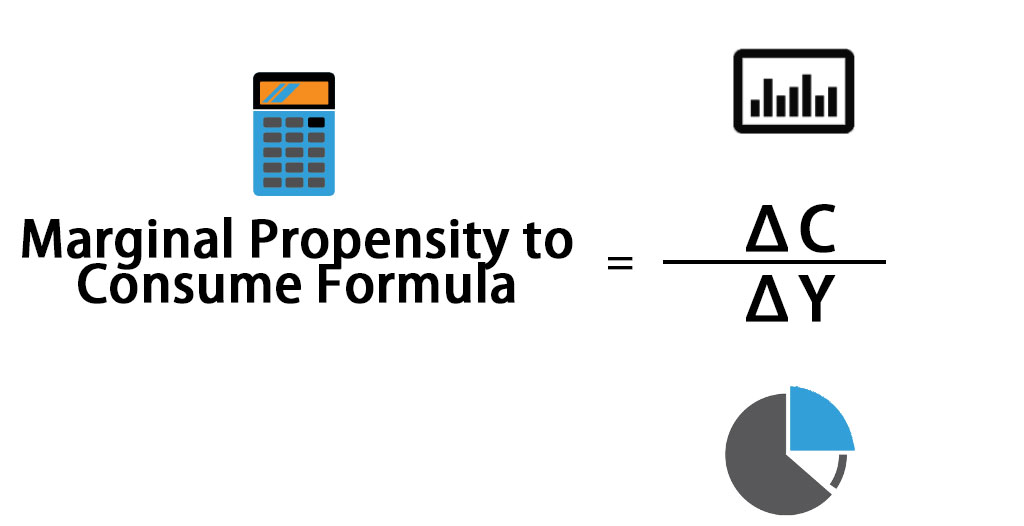
Marginal Propensity To Consume Formula Calculator Excel Template After the salary rose to $75,000, they spent $65,000 on goods and services. the change in consumption is $5,000 ($65,000 minus $60,000). to calculate the marginal propensity to consume, insert. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) measures the proportion of extra income that is spent on consumption. for example, if an individual gains an extra £10, and spends £7.50, then the marginal propensity to consume will be £7.5 10 = 0.75. the mpc will invariably be between 0 and 1. the marginal propensity to consume measures the change.

Marginal Propensity To Consume And Change In Income Due To Change In Anthony’s consumption function is given by the following equation: c = $2,000 0.8 × y d.tom’s marginal propensity to save (mps) is 0.25. mark’s mpc is the ratio of change in consumption (∆c) to change in income (∆y): mpc m c y $300 $500 0.6. anothy’s mpc is 0.8 which is the slope of his consumption function. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to Δc Δy, where Δc is the change in consumption, and Δy is the change in income. if consumption increases by 80 cents for each additional dollar. In short, the marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is the amount by which consumption changes when disposable income increases by one dollar. it is easy to see that the mpc is always between zero and one: an additional dollar of income increases consumption somewhere between nothing and one dollar. in other words, when households gain an extra. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) refers to how sensitive consumption in a given economy is to unitized changes in income levels. mpc as a concept works similar to price elasticity, where novel insights can be drawn by looking at the magnitude of change in consumption as a result of income fluctuations.

Comments are closed.