Marginal Utilities Definition Types Examples And History Saxa Fund
Marginal Utilities Definition Types Examples And History Saxa Fund Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. the concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an. Definition of marginal utilities. for example, let’s say a person consumes one slice of pizza and derives a certain level of satisfaction from it. if they consume a second slice of pizza and their satisfaction increases, the change in total utility between consuming the first and second slice is the marginal utility of the second slice. types.
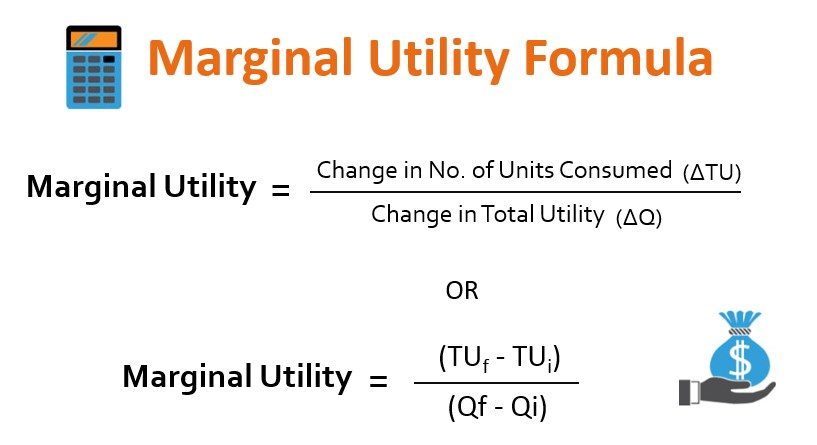
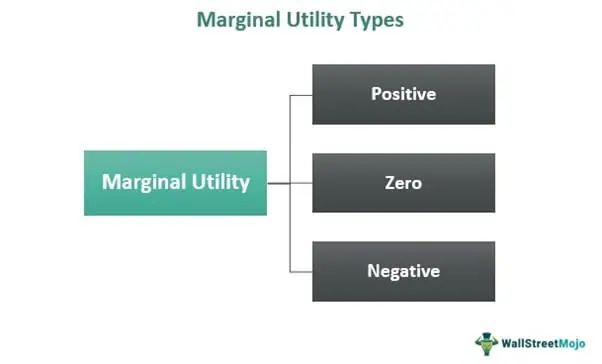
Marginal Utility Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template Definition of marginal utilities. marginal utility refers to the incremental satisfaction or benefit gained from consuming or using one additional unit of a particular good or service. it is an essential concept in economics, as it helps explain how individuals make rational choices based on their preferences and constraints. For example, in the united states, the tax rates range from 10% to 37% based on income brackets. wealth tax: a wealth tax is another example of ability to pay taxation. this type of tax is levied on an individual’s net worth, which includes assets such as real estate, investments, and personal property. the tax rate is typically a percentage. Summary. marginal utility is the extra benefit derived from consuming one more unit of a specific good or service. the main types of marginal utility include positive marginal utility, zero marginal utility, and negative marginal utility. consumers often experience higher marginal utility when marginal cost is lower. Economics. marginal utility, in economics, the additional satisfaction or benefit (utility) that a consumer derives from buying an additional unit of a commodity or service. the concept implies that the utility or benefit to a consumer of an additional unit of a product is inversely related to the number of units of that product he already owns.
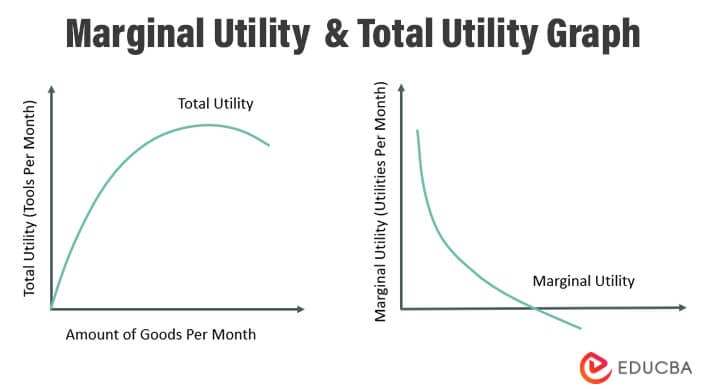
Marginal Utility Meaning Types Curve Formula Examples Summary. marginal utility is the extra benefit derived from consuming one more unit of a specific good or service. the main types of marginal utility include positive marginal utility, zero marginal utility, and negative marginal utility. consumers often experience higher marginal utility when marginal cost is lower. Economics. marginal utility, in economics, the additional satisfaction or benefit (utility) that a consumer derives from buying an additional unit of a commodity or service. the concept implies that the utility or benefit to a consumer of an additional unit of a product is inversely related to the number of units of that product he already owns. Marginal utility. in liberal economics, marginal utility describes the change in utility (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. [1] marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. negative marginal utility implies that every additional unit consumed of a commodity causes more harm than. Marginal utility (or mu) is a concept in economics. it is a measure of additional satisfaction or benefits that a user gets from consuming one extra unit of a commodity or a service. economists primarily use this concept to determine how many units a user could purchase of a particular item. mu isn’t constant; it can be positive, negative, or.

Comments are closed.