Marginal Utility Intelligent Economist

Marginal Utility Intelligent Economist To calculate the marginal utility based on these two total utility numbers, find the difference in their total utility. then divide that difference in total utility by the difference in units. here’s how that would look for our example: difference in total utility: $20 – $15 = $5. difference in units (number of sandwiches): 4 – 2 = 2. Marginal analysis. in the field of economics, marginal analysis entails the examination of the final or next unit of cost or of consumption. it involves a cost benefit analysis of business decisions—that is, understanding whether a particular decision provides enough benefits to be worth the cost of that decision.
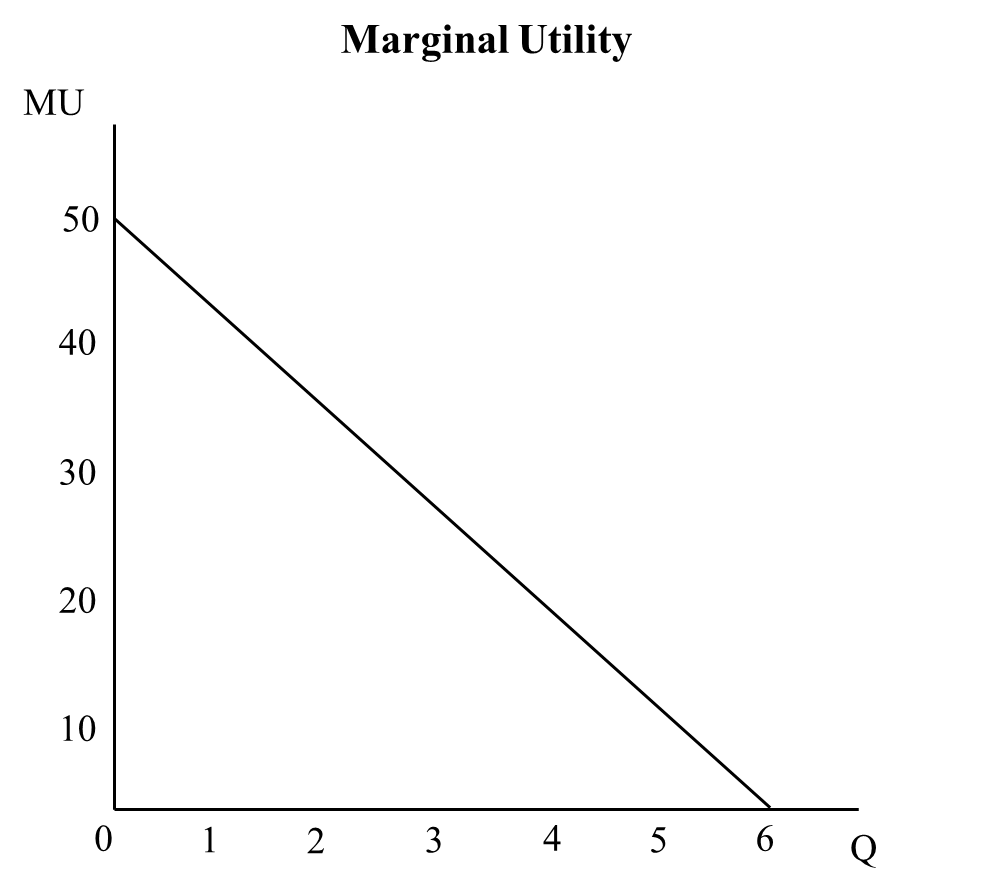
Marginal Utility A Human View Into Behavioural Economics Marginal utility is calculated by subtracting the total utility of the previous consumption level from the total utility of the current consumption level. when total utility reaches maximum, marginal utility (mu) is zero. when total utility declines, marginal utility (mu) becomes negative. table and chart 7.11 provides an illustration of both. Marginal utility. in liberal economics, marginal utility describes the change in utility (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. [1] marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. negative marginal utility implies that every additional unit consumed of a commodity causes more harm than. Summary. marginal utility is the extra benefit derived from consuming one more unit of a specific good or service. the main types of marginal utility include positive marginal utility, zero marginal utility, and negative marginal utility. consumers often experience higher marginal utility when marginal cost is lower. A non linear indifference curve is concave to the origin, and the marginal state of substitution is declining as you move along the indifference curve to the right. assume pizza is on the y axis and movies are on the x axis. as you move to the right, you have more and more movies, and the marginal utility from each additional movie decreases.

Marginal Utility Intelligent Economist Summary. marginal utility is the extra benefit derived from consuming one more unit of a specific good or service. the main types of marginal utility include positive marginal utility, zero marginal utility, and negative marginal utility. consumers often experience higher marginal utility when marginal cost is lower. A non linear indifference curve is concave to the origin, and the marginal state of substitution is declining as you move along the indifference curve to the right. assume pizza is on the y axis and movies are on the x axis. as you move to the right, you have more and more movies, and the marginal utility from each additional movie decreases. Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. the concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an. Marginal utility and allocative efficiency. suppose the consumption was a quantity of 40. at this quantity, the price is £15, but the marginal cost is £6. in this case, the marginal benefit (utility) is greater than the marginal cost – there is a deadweight welfare loss and underconsumption of the good.

How To Get Marginal Utility Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. the concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an. Marginal utility and allocative efficiency. suppose the consumption was a quantity of 40. at this quantity, the price is £15, but the marginal cost is £6. in this case, the marginal benefit (utility) is greater than the marginal cost – there is a deadweight welfare loss and underconsumption of the good.

Comments are closed.