Mastering Prostate Cancer Staging
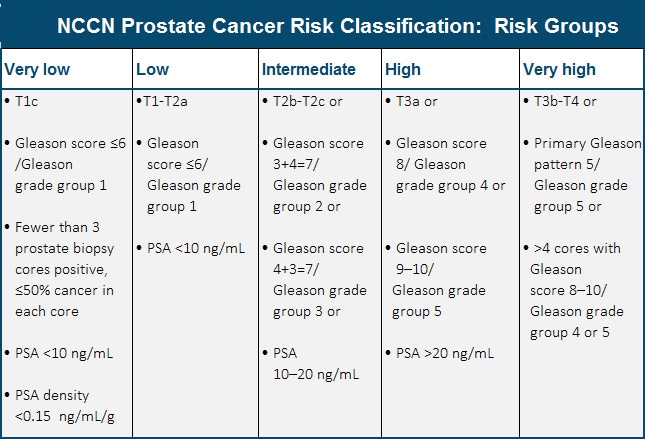
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis And Staging The main stages of prostate cancer range from i (1) through iv (4). some stages are split further (iia, iib, iic, etc.). as a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. a higher number, such as stage iv, means cancer has spread more. and within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Welcome to “mastering prostate cancer staging” – an interactive and in depth guide designed to demystify the complexities of prostate cancer staging and grading systems. whether you’re a patient or someone interested in learning more, this guide offers insights and tools to navigate this crucial aspect of prostate cancer management.
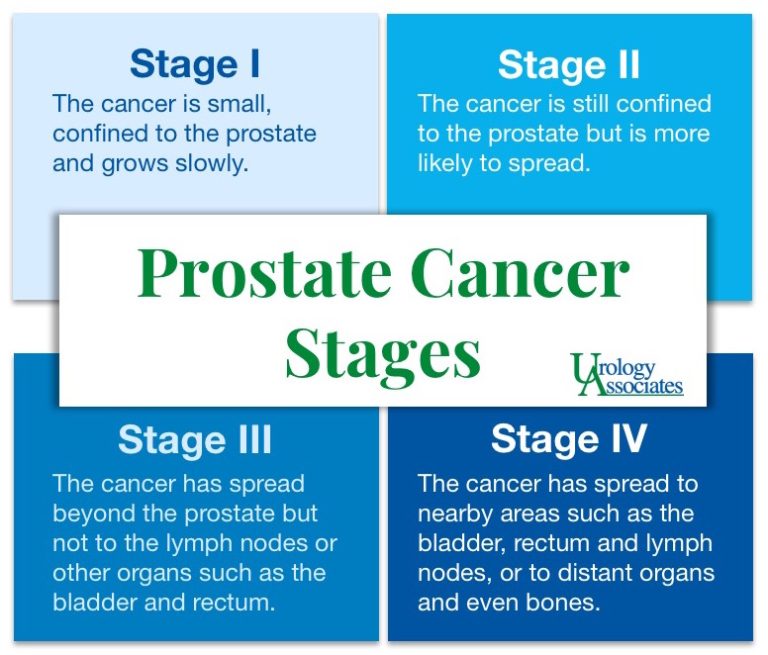
Prostate Cancer Stages Options Urology Associates Co The following clinical stages are used to describe prostate cancer: t1: the tumor cannot be felt during the dre or seen during imaging (e.g., a computed tomography (ct) scan or transrectal ultrasound). it may be found when surgery is done for another medical condition. t1a: the tumor is discovered accidentally during a surgical procedure used. 3. pathological stage: a look at the actual cancer cells and their distribution within the pelvic area. this system assesses how pervasive the cancer cells are within and around the prostate. these stages begin at t2. t2: the tumor is located in the prostate only. t3: the tumor extends outside the prostate. >t3b: the tumor has begun to grow in. Unfavorable intermediate risk group. initial treatment options for men with cancers in this risk group might include: surgery (radical prostatectomy, along with the removal of nearby lymph nodes) external radiation therapy plus hormone therapy. external radiation plus brachytherapy (possibly along with hormone therapy) if surgery is done and it. The stage helps your doctor choose the best course of treatment for you. stage i. the cancer is growing in your prostate but hasn’t spread beyond it. in most cases, the doctor can’t feel the.

Chart Prostate Cancer Stages Zero Prostate Cancer Unfavorable intermediate risk group. initial treatment options for men with cancers in this risk group might include: surgery (radical prostatectomy, along with the removal of nearby lymph nodes) external radiation therapy plus hormone therapy. external radiation plus brachytherapy (possibly along with hormone therapy) if surgery is done and it. The stage helps your doctor choose the best course of treatment for you. stage i. the cancer is growing in your prostate but hasn’t spread beyond it. in most cases, the doctor can’t feel the. After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent of cancer in the body and anticipated response to treatment. signs and symptoms of prostate cancer. tests to diagnose and stage prostate cancer. prostate cancer stages. risk groups and lab tests to help determine risk from localized prostate cancer. The prostate cancer staging system and initial staging evaluation are reviewed here. the initial clinical presentation, indications for prostate biopsy, utility of prostate magnetic resonance imaging (mri), ramifications of risk stratification, and approach to treatment are discussed separately: (see "clinical presentation and diagnosis of.

Prostate Cancer Diagnosis And Staging After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent of cancer in the body and anticipated response to treatment. signs and symptoms of prostate cancer. tests to diagnose and stage prostate cancer. prostate cancer stages. risk groups and lab tests to help determine risk from localized prostate cancer. The prostate cancer staging system and initial staging evaluation are reviewed here. the initial clinical presentation, indications for prostate biopsy, utility of prostate magnetic resonance imaging (mri), ramifications of risk stratification, and approach to treatment are discussed separately: (see "clinical presentation and diagnosis of.

Comments are closed.