Mathwords Inscribed Circle

Mathwords Inscribed Circle Inscribed circle incircle. the largest possible circle that can be drawn interior to a plane figure. for a polygon, a circle is not actually inscribed unless each side of the polygon is tangent to the circle. note: all triangles have inscribed circles, and so do all regular polygons. most other polygons do not have inscribed circles. Mathwords . the center a polygon’s inscribed circle . the incenter is located at the point of intersection of the polygon's angle bisectors. note: any triangle has an inscribed circle, called the incircle. all regular polygons have inscribed circles. other polygons with 4 or more sides, however, usually do not.
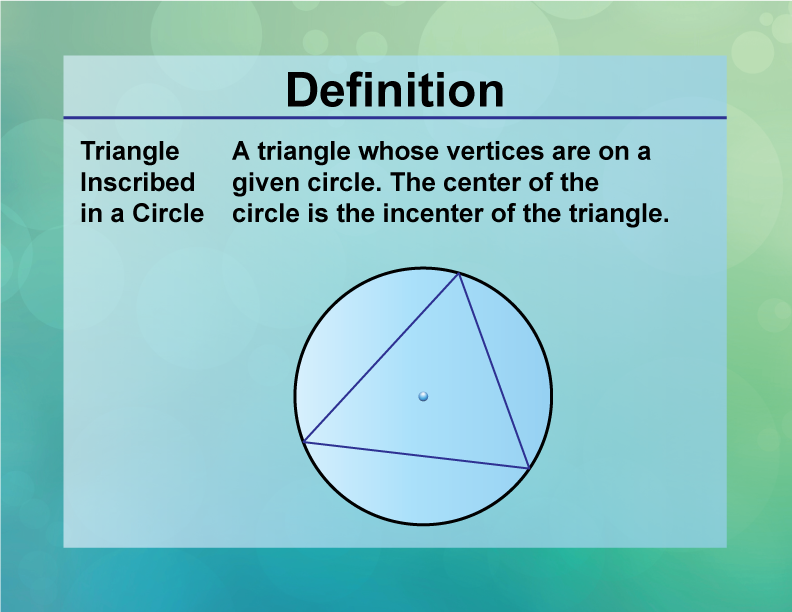
Inscribed Circle Inscribed angle in a circle. an angle in a circle with vertex on the circle itself. this page updated 15 jul 23 mathwords: terms and formulas from algebra i to. In geometry, an inscribed circle, also known as the incircle of a polygon is the largest possible circle that can be drawn inside a regular, cyclic polygon. the inscribed circle will touch each of the three sides of the triangle at exactly one point. the center of such a circle is called the incenter. Theorem 2.5. for any triangle abc, the radius r of its circumscribed circle is given by: 2r = a sina = b sinb = c sinc. note: for a circle of diameter 1, this means a = sina, b = sinb, and c = sin c.) to prove this, let o be the center of the circumscribed circle for a triangle abc. An incircle is an inscribed circle of a polygon, i.e., a circle that is tangent to each of the polygon's sides. the center i of the incircle is called the incenter, and the radius r of the circle is called the inradius. an incircle of a polygon is the two dimensional case of an insphere of a solid. while an incircle does not necessarily exist for arbitrary polygons, it exists and is moreover.
How To Draw A Inscribed Circle Theorem 2.5. for any triangle abc, the radius r of its circumscribed circle is given by: 2r = a sina = b sinb = c sinc. note: for a circle of diameter 1, this means a = sina, b = sinb, and c = sin c.) to prove this, let o be the center of the circumscribed circle for a triangle abc. An incircle is an inscribed circle of a polygon, i.e., a circle that is tangent to each of the polygon's sides. the center i of the incircle is called the incenter, and the radius r of the circle is called the inradius. an incircle of a polygon is the two dimensional case of an insphere of a solid. while an incircle does not necessarily exist for arbitrary polygons, it exists and is moreover. Circumscribed and inscribed circles show up a lot in area problems. circumscribe & inscribe basics 1. this instructional video describes the basic concept of circles, triangles, and squares that circumscribe and inscribe each other. use the incenter, which is where the angle bisectors intersect, to draw a circle that circumscribe a triangle. A circle can be inscribed inside a convex polygon if the bisectors of all its inner angles cross at the same point. the center of an inscribed circle lies at the crossing point of polygon bisectors. the center of an inscribed circle is equidistant from the sides of the polygon. this is true because the radius is normal to the tangent line at.

Mathwords Inscribed Angle In A Circle Circumscribed and inscribed circles show up a lot in area problems. circumscribe & inscribe basics 1. this instructional video describes the basic concept of circles, triangles, and squares that circumscribe and inscribe each other. use the incenter, which is where the angle bisectors intersect, to draw a circle that circumscribe a triangle. A circle can be inscribed inside a convex polygon if the bisectors of all its inner angles cross at the same point. the center of an inscribed circle lies at the crossing point of polygon bisectors. the center of an inscribed circle is equidistant from the sides of the polygon. this is true because the radius is normal to the tangent line at.

Relation Between Angle Inscribed In The Same Segment Of A Circle

Comments are closed.