Memory Hierarchy Interfacing
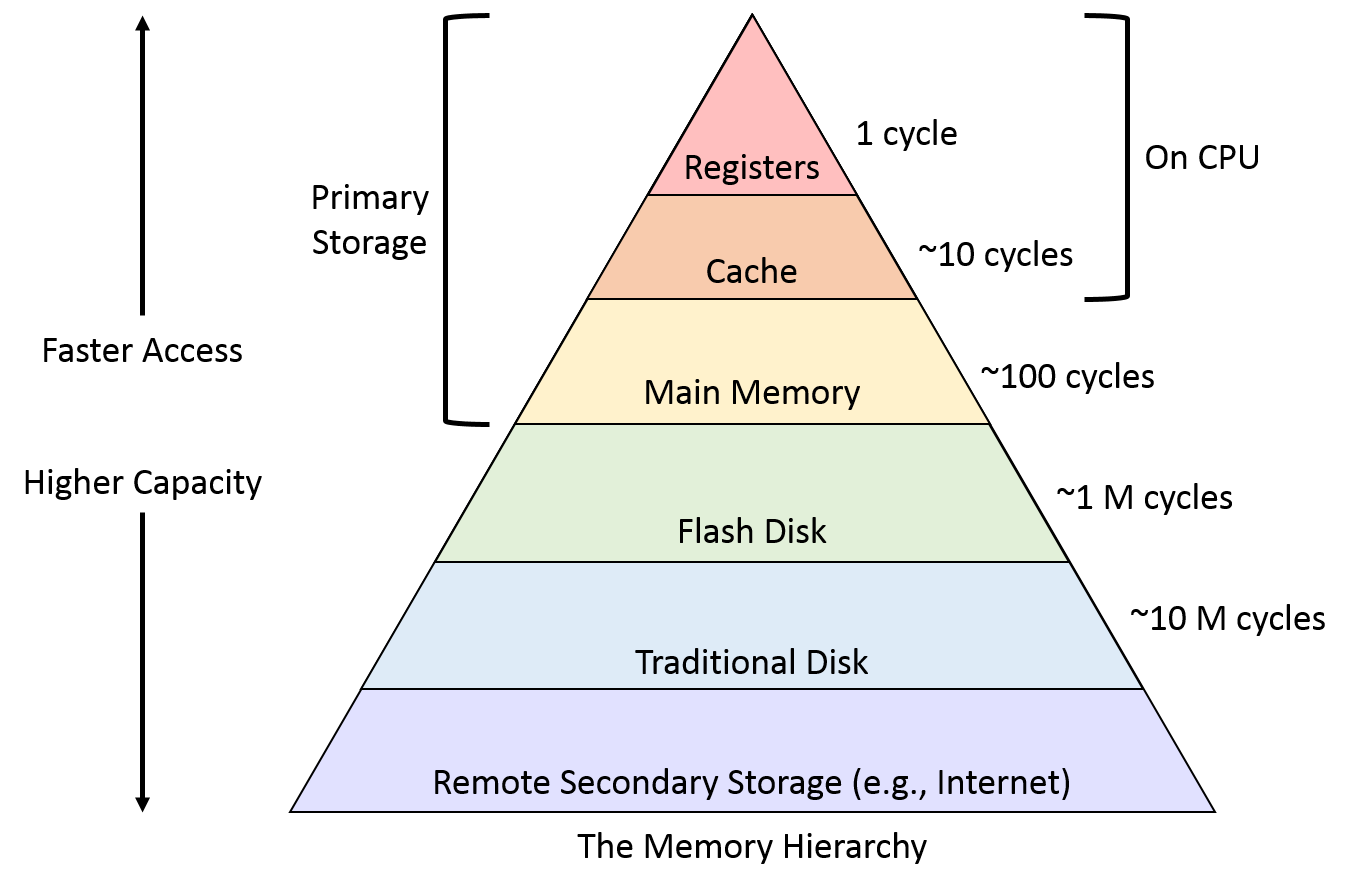
Memory Hierarchy Design And Its Characteristics Coding Ninjas Codestudio Characteristics of memory hierarchy. capacity: it is the global volume of information the memory can store. as we move from top to bottom in the hierarchy, the capacity increases. access time: it is the time interval between the read write request and the availability of the data. The memory interfacing design should consider these aspects based on the system’s requirements. memory hierarchy: modern computer systems often use a memory hierarchy to optimize performance. this hierarchy includes multiple levels of memory, such as cache, main memory, and secondary storage, with varying access speeds and capacities.
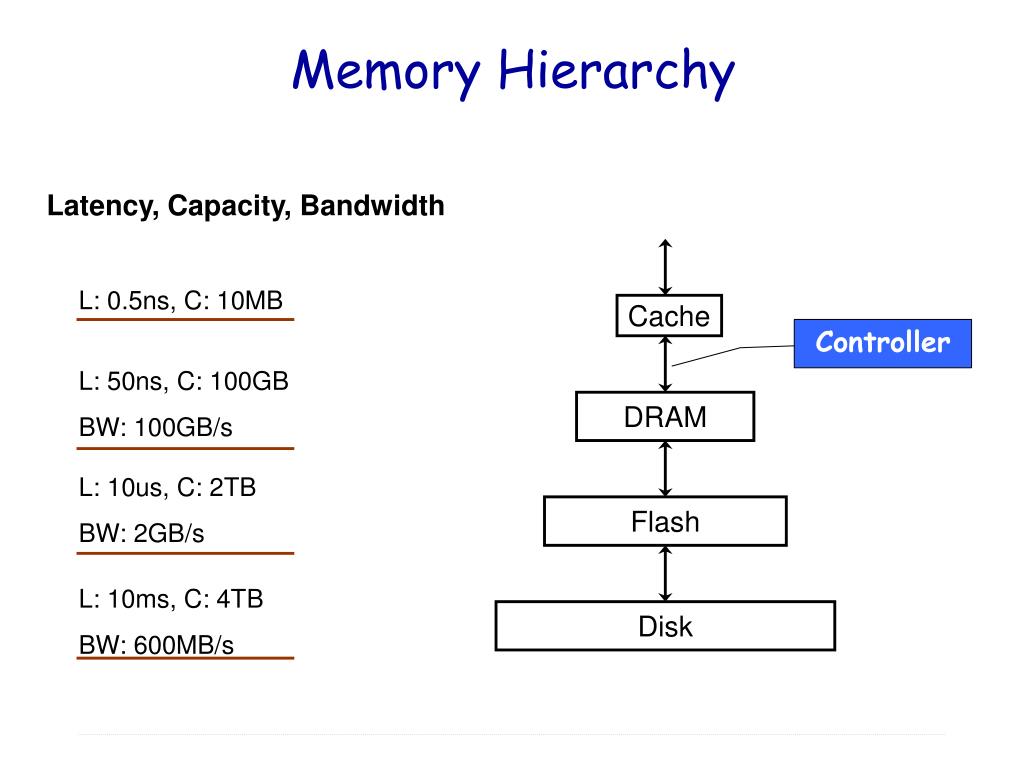
Ppt Memory Hierarchy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3197851 Coa: memory hierarchy & interfacingtopics discussed:1. hierarchy and its examples.2. memory hierarchy.3. memory interfacing and levels of memory: i. paral. The hierarchical memory system tries to hide the disparity in speed by placing the fastest memories near the processor. memory hierarchy design becomes more crucial with recent multi core processors because the aggregate peak bandwidth grows with the number of cores. for example, intel core i7 can generate two references per core per clock. Memory hierarchy interface approach 1: expose hierarchy §registers, sram, dram, flash, hard disk each available as storage alternatives §tell programmers: “use them cleverly” approach 2: hide hierarchy §programming model: single memory, single address space §machine transparently stores data in fast or slow memory, depending on usage. Each cell stores bit with a six transistor circuit. retains value indefinitely, as long as it is kept powered. relatively insensitive to disturbances such as electrical noise. faster and more expensive than dram. each cell stores bit with a capacitor and transistor. value must be refreshed every 10 100 ms.
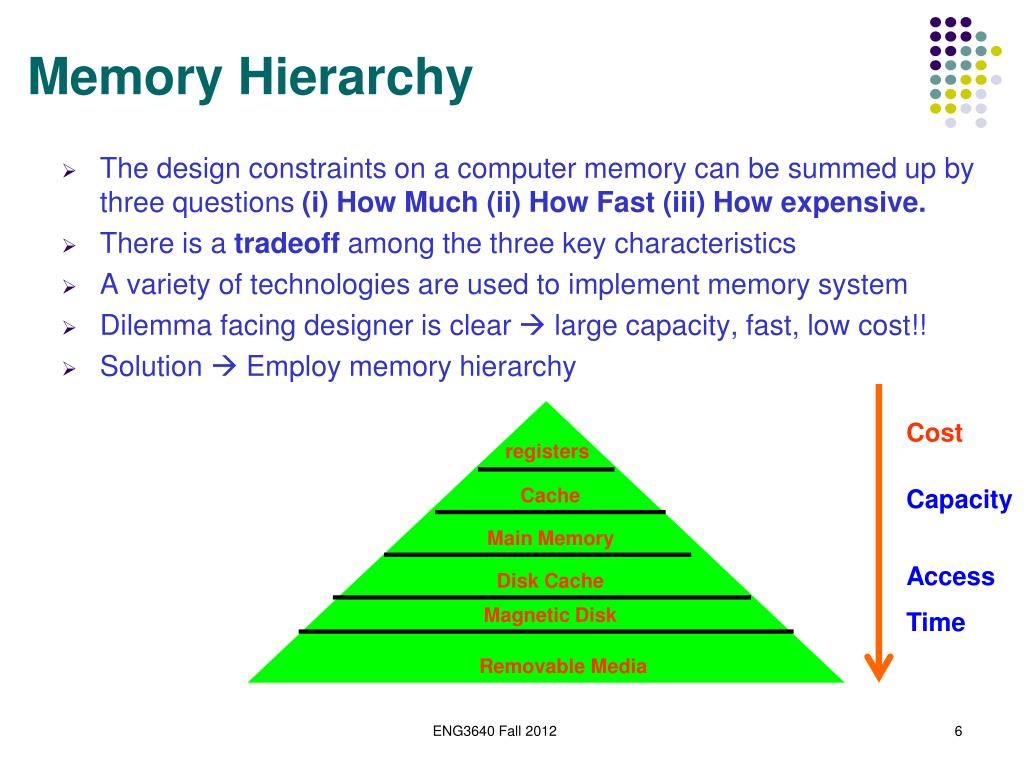
Ppt Week 11 Memory Interfacing Powerpoint Presentation Free Memory hierarchy interface approach 1: expose hierarchy §registers, sram, dram, flash, hard disk each available as storage alternatives §tell programmers: “use them cleverly” approach 2: hide hierarchy §programming model: single memory, single address space §machine transparently stores data in fast or slow memory, depending on usage. Each cell stores bit with a six transistor circuit. retains value indefinitely, as long as it is kept powered. relatively insensitive to disturbances such as electrical noise. faster and more expensive than dram. each cell stores bit with a capacitor and transistor. value must be refreshed every 10 100 ms. Memory hierarchy design. memory hierarchy design becomes more crucial with recent multi core processors: aggregate peak bandwidth grows with # cores: intel core i7 can generate two references per core per clock. four cores and 3.2 ghz clock. . 25.6 billion 64 bit data references second . . The cpu–main memory interface cont'd. additional points: •if b<w, main memory must make w b b bit transfers. •some cpus allow reading and writing of word sizes <w. example: intel 8088: m=20, w=16,s=b=8. 8 and 16 bit values can be read and written •if memory is sufficiently fast, or if its response is predictable, then complete may be.

Memory Hierarchy Interfacing Youtube Memory hierarchy design. memory hierarchy design becomes more crucial with recent multi core processors: aggregate peak bandwidth grows with # cores: intel core i7 can generate two references per core per clock. four cores and 3.2 ghz clock. . 25.6 billion 64 bit data references second . . The cpu–main memory interface cont'd. additional points: •if b<w, main memory must make w b b bit transfers. •some cpus allow reading and writing of word sizes <w. example: intel 8088: m=20, w=16,s=b=8. 8 and 16 bit values can be read and written •if memory is sufficiently fast, or if its response is predictable, then complete may be.

Comments are closed.