Memory Hierarchy Naukri Code 360
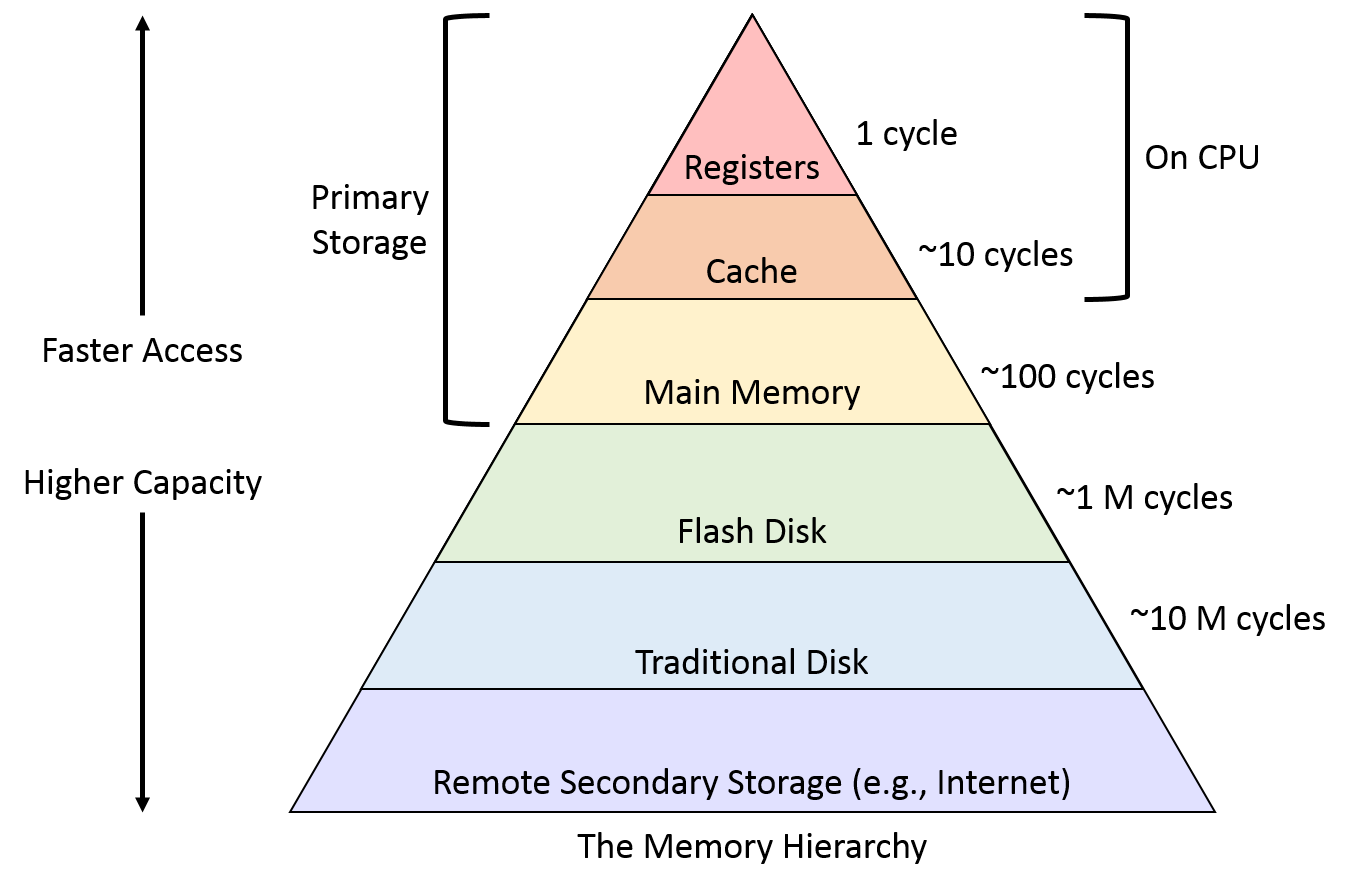
Memory Hierarchy Naukri Code 360 This memory hierarchy design is divided into 2 types: primary internal memory. it consists of cpu registers, cache memory, main memory, and these are directly accessible by the processor. secondary external memory. it consists of a magnetic disk, optical disk, magnetic tape, which are accessible by processor via i o module. Get the tech career you deserve faster with coding ninjas courses. user rating 4.7 5. 1:1 doubt support. 95% placement record. read all the latest information about memory organization. practice free coding problems, learn from a guided path and insightful videos in naukri code 360’s resource section.
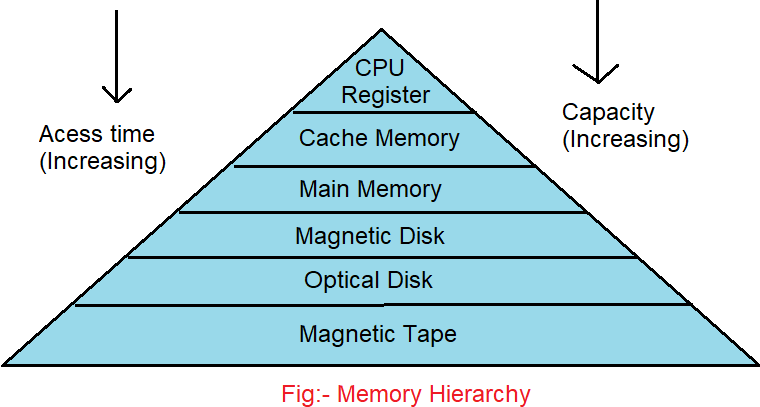
Memory Hierarchy Design And Its Characteristics Naukri Code 360 Auxiliary memory is the lowest cost, highest space, and slowest approach to storage in computer systems. data, programs, and information are preserved for long term storage or not in direct use. the most usual auxiliary memory devices used in computer systems are magnetic disks and magnetic tapes. Memory hierarchy can be simply illustrated as the organization of the memory for saving the access time. because of the nicely written codes or program, memory hierarchy works well. it takes less time in accessing at the current level. 2. explain the types of memory hierarchy. answer: here are the some types of the memory hierarchy: external. But then cache and memory would be inconsistent. write through: also update memory. but makes writes take longer. e.g., if base cpi = 1, 10% of instructions are stores, write to memory takes 100 cycles. effective cpi = 1 0.1×100 = 11. solution: write buffer. holds data waiting to be written to memory. Understanding memory management in operating systems. memory management stands as a pivotal function within an operating system, falling under its primary role of resource management. main memory, commonly known as ram, serves as the backbone for running most applications. for consumers, the ram often becomes a key consideration when purchasing.

Memory Hierarchy Design And Its Characteristics Naukri Code 360 But then cache and memory would be inconsistent. write through: also update memory. but makes writes take longer. e.g., if base cpi = 1, 10% of instructions are stores, write to memory takes 100 cycles. effective cpi = 1 0.1×100 = 11. solution: write buffer. holds data waiting to be written to memory. Understanding memory management in operating systems. memory management stands as a pivotal function within an operating system, falling under its primary role of resource management. main memory, commonly known as ram, serves as the backbone for running most applications. for consumers, the ram often becomes a key consideration when purchasing. The hierarchical memory system tries to hide the disparity in speed by placing the fastest memories near the processor. memory hierarchy design becomes more crucial with recent multi core processors because the aggregate peak bandwidth grows with the number of cores. for example, intel core i7 can generate two references per core per clock. Dive into systems. 11. storage and the memory hierarchy. 11.1. the memory hierarchy. 11.1. the memory hierarchy. as we explore modern computer storage, a common pattern emerges: devices with higher capacities offer lower performance. said another way, systems use devices that are fast and devices that store a large amount of data, but no single.
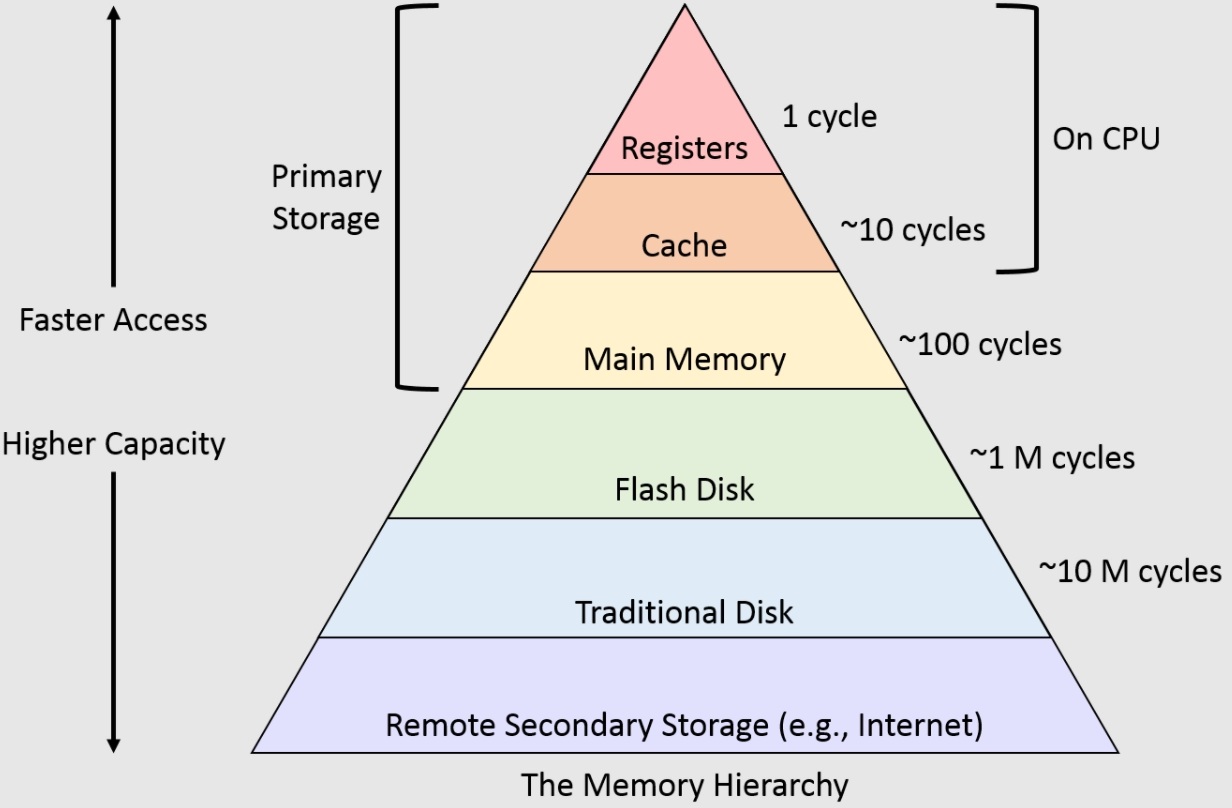
Memory Hierarchy Naukri Code 360 The hierarchical memory system tries to hide the disparity in speed by placing the fastest memories near the processor. memory hierarchy design becomes more crucial with recent multi core processors because the aggregate peak bandwidth grows with the number of cores. for example, intel core i7 can generate two references per core per clock. Dive into systems. 11. storage and the memory hierarchy. 11.1. the memory hierarchy. 11.1. the memory hierarchy. as we explore modern computer storage, a common pattern emerges: devices with higher capacities offer lower performance. said another way, systems use devices that are fast and devices that store a large amount of data, but no single.

Comments are closed.