Metastases Prostate Carcinoma Image Radiopaedia Org
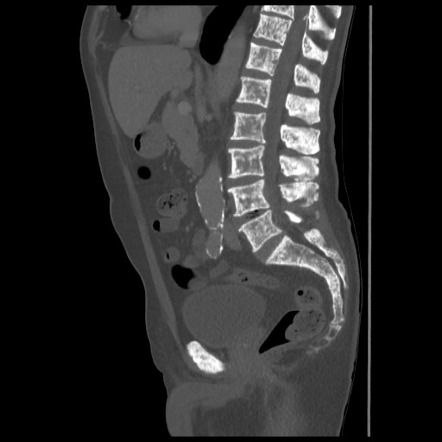
Diffuse Osteoblastic Metastases Prostate Cancer Image Radiopaedia O This was the patient's presentation with and resultant diagnosis of metastatic prostate carcinoma. always check the periphery of the images for clues. in this case, pathological nodes indicating in this age and gender prostate carcinoma as the likely primary. his psa level was subsequently measured and was 2534 ng ml. Terminology. the aim of prostate mri is to detect clinically significant prostate cancer, as insignificant prostate cancer is common 35. however, this term is without a consensus definition 35,36 (c. 2024) and has been defined as one or more of the following (noting variability within criterion) 31 35: prostate specific antigen (psa) >10 ng ml.

Prostate Carcinoma Bone Metastases Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Bickle i, prostate carcinoma bony metastases. case study, radiopaedia.org (accessed on 22 nov 2023) doi.org 10.53347 rid 34629. Prostate cancer staging takes into account a tnm staging system (primary site, nodal and distant metastases), pretreatment psa and histological grading. the gleason score is used to determine the grade group. a superseded staging system is the whitmore jewett staging system. additionally, there is some overlap with prebiopsy imaging assessment. Pathology. 95% of prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop from the acini of the prostatic ducts 15. they arise in the posterior peripheral (70%) prostate gland more commonly than in the anterior gland and central zone (30%) 21. prostate cancer can spread by local invasion (typically into the bladder and seminal vesicles; urethral and. Gender: male. mri. extensive low t2 signal in the right lobe of prostate involving both the transitional and peripheral zones. corresponding b1400 change and avid adc restriction. this extends from the apex to base with extracapsular extension involving the neurovascular bundle and base of the right seminal vesicle. (pirads 5).

Metastases Prostate Carcinoma Image Radiopaedia Org Pathology. 95% of prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop from the acini of the prostatic ducts 15. they arise in the posterior peripheral (70%) prostate gland more commonly than in the anterior gland and central zone (30%) 21. prostate cancer can spread by local invasion (typically into the bladder and seminal vesicles; urethral and. Gender: male. mri. extensive low t2 signal in the right lobe of prostate involving both the transitional and peripheral zones. corresponding b1400 change and avid adc restriction. this extends from the apex to base with extracapsular extension involving the neurovascular bundle and base of the right seminal vesicle. (pirads 5). On preoperative imaging, the suggestion of extraprostatic extension is important for surgical planning and counseling as resection of the neurovascular bundle may be required. extraprostatic extension is associated with a higher risk of recurrence and metastasis and lower cancer specific survival after radical prostatectomy 1. The mandible is an uncommon site for metastatic disease. prostate carcinoma is a tumour well known for its predisposition to metastasise to the bone, but it virtually always sclerotic in nature, as with the diffuse metastases elsewhere in this patient, with the exception on the bilateral mandibular lesions which are lytic in nature. a double.
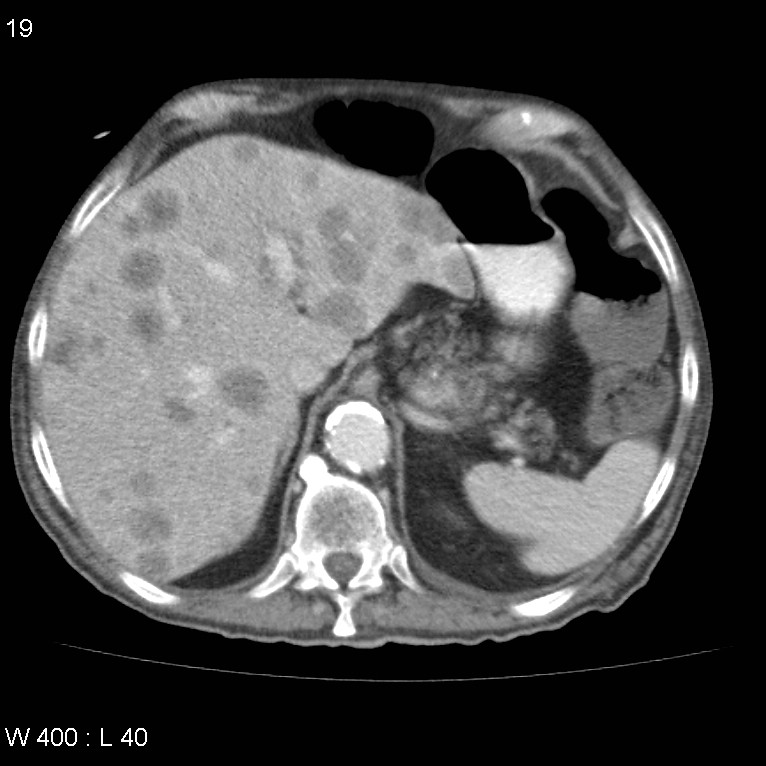
Prostate Metastases Widespread Image Radiopaedia Org On preoperative imaging, the suggestion of extraprostatic extension is important for surgical planning and counseling as resection of the neurovascular bundle may be required. extraprostatic extension is associated with a higher risk of recurrence and metastasis and lower cancer specific survival after radical prostatectomy 1. The mandible is an uncommon site for metastatic disease. prostate carcinoma is a tumour well known for its predisposition to metastasise to the bone, but it virtually always sclerotic in nature, as with the diffuse metastases elsewhere in this patient, with the exception on the bilateral mandibular lesions which are lytic in nature. a double.

Comments are closed.