Metric Vs Customary Measurement Do Your Students Understand The

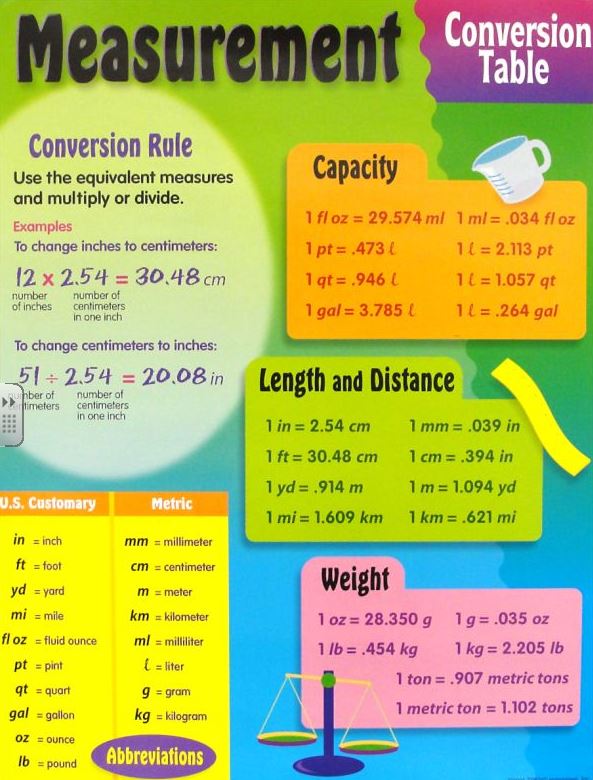
Metric Vs Customary Measurement Do Your Students Understand The To determine whether the parcel is a heavy shipment or not, you need to convert the total weight of the plant containers to pounds. compute for the total weight. total weight = 24 × 1.3 kg = 31.2 kg total weight = 24 × 1.3 kg = 31.2 kg. convert the total weight to pounds. use the metric to us customary units’ equivalence: 1 kg = 2.2 lbs. The united states follows the customary units of measurement, which uses units like feet, quarts, and ounces for measurement. let’s understand some important formulas for converting metric units of length to customary units. 1 meter $= 39.4$ inches $= 1.09$ yards $= 3.2$ feet; 1 centimeter $= 0.39$ inches; 1 inch $= 2.54$ cm.

Customary Vs Metric Chart Teaching the metric system to u.s. upper elementary students can be challenging! you can help your upper elementary students understand the metric system by following the steps and tips below. start with the basics by introducing the metric system as a way to measure things, just like the customary system your students are already familiar […]. Now, because you are going from a customary unit to a metric unit, you will need to multiply the given value by the metric equivalent from the table. keep in mind that 3.79 is approximately 3.75, and 4 times 3.75 is equal to 15. 4×3.79≈15. the answer is there are approximately 15 liters in 4 gallons. After students become proficient using the metric system and are comfortable applying si measurements, they may encounter applications that require making mathematical conversions between si and non si units. 8. connect to life and careers. make the si relevant. let’s face it, measuring stuff is a practical life skill. 7 m×100=700 cm 7 m × 100 = 700 cm. metric units of mass. the metric system for mass is based around grams (g). (g). for example, covert 4 4 kilograms (kg) (kg) to grams (g). (g). looking at the diagram above, kilograms can be converted to grams by multiplying by 1000. 1000. 4 kg×1000=4000 g 4 kg × 1000 = 4000 g. metric units of capacity.
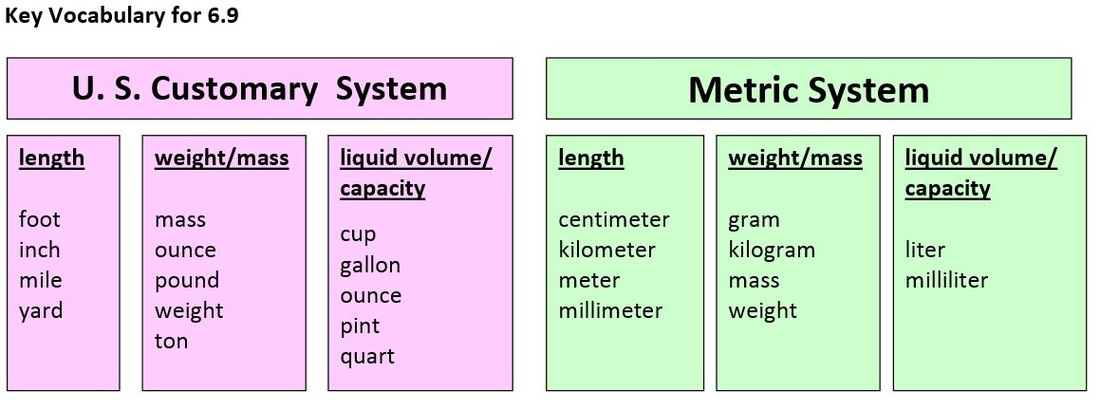
Compare The Customary And Metric Systems Bull Run Middle School Math 6 After students become proficient using the metric system and are comfortable applying si measurements, they may encounter applications that require making mathematical conversions between si and non si units. 8. connect to life and careers. make the si relevant. let’s face it, measuring stuff is a practical life skill. 7 m×100=700 cm 7 m × 100 = 700 cm. metric units of mass. the metric system for mass is based around grams (g). (g). for example, covert 4 4 kilograms (kg) (kg) to grams (g). (g). looking at the diagram above, kilograms can be converted to grams by multiplying by 1000. 1000. 4 kg×1000=4000 g 4 kg × 1000 = 4000 g. metric units of capacity. The customary system, on the other hand, has a much wider variety of units. it is not a decimal based system and does not use multiples of 10. in this way, measurements using the customary system can be a bit harder to understand. so, let’s go over each of the customary units and put things into perspective. Understanding how metric units of measure relate to each other is essential to understanding the metric system: the metric unit for distance is the meter (m). a person’s height might be written as 1.8 meters (1.8 m). a meter slightly longer than a yard (3 feet), while a centimeter is slightly less than half an inch.
Compare The Customary And Metric Systems Bull Run Middle School Math 6 The customary system, on the other hand, has a much wider variety of units. it is not a decimal based system and does not use multiples of 10. in this way, measurements using the customary system can be a bit harder to understand. so, let’s go over each of the customary units and put things into perspective. Understanding how metric units of measure relate to each other is essential to understanding the metric system: the metric unit for distance is the meter (m). a person’s height might be written as 1.8 meters (1.8 m). a meter slightly longer than a yard (3 feet), while a centimeter is slightly less than half an inch.

Comments are closed.