Microscopes вђ General Microbiology

Velab Ve B2 Binocular Microscope With Led Illumination And Quadruple The bright field microscope is your standard microscope that you could purchase for your niece or nephew at any toy store. here is a website on the basic parts of a bright field compound microscope, in case you are not enrolled in the general microbiology lab. the specimen is illuminated by a light source at the base of the microscope and then. There are 1000 millimeters (mm) in one meter. 1 mm = 10 3 meter. there are 1000 micrometers (microns, or µm) in one millimeter. 1 µm = 10 6 meter. there are 1000 nanometers in one micrometer. 1 nm = 10 9 meter. figure 1: resolving power of microscopes. the microscope is one of the microbiologist's greatest tools.
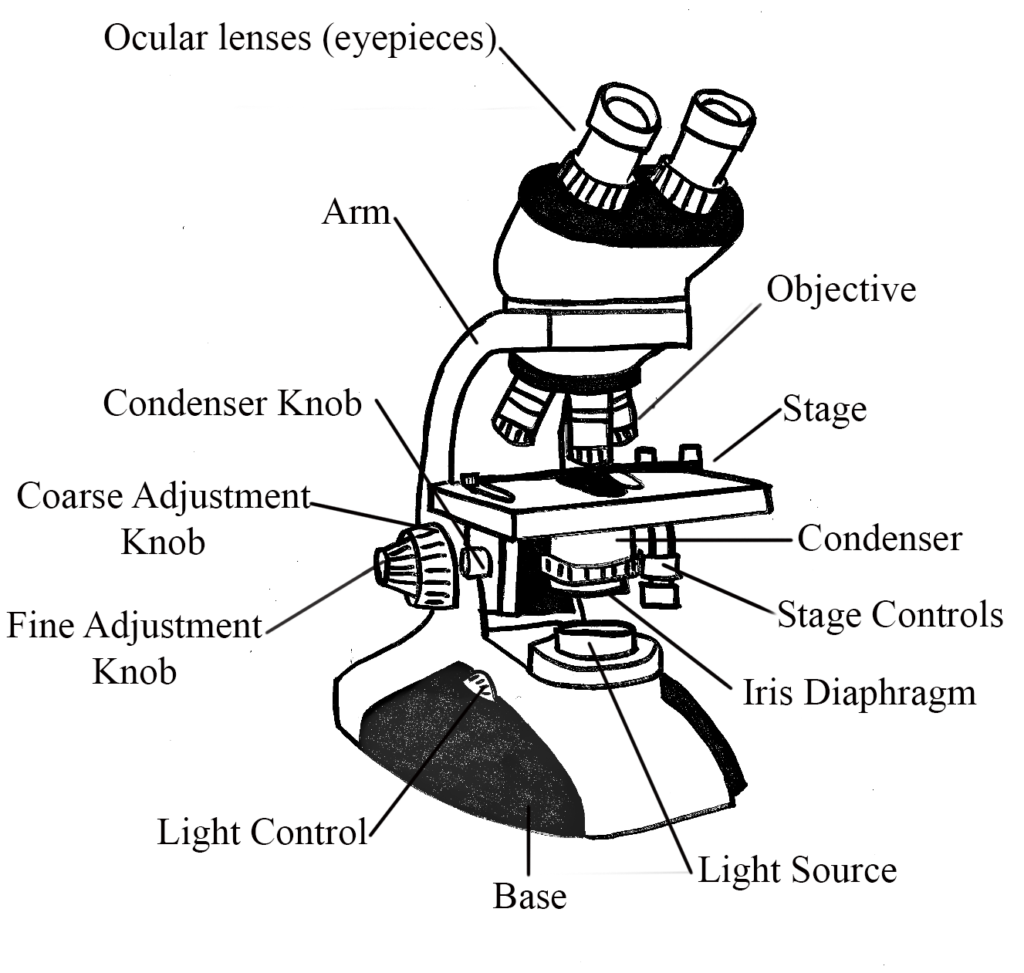
Microscopes вђ General Microbiology It projects the details of surface atoms and molecules. it includes scanning tunneling microscopes, atomic force microscopes, fluid field microscopes, scanning electrochemical microscopy, scanning thermal microscopes, etc. atomic force field and scanning tunneling microscope are mostly used type. History of microscope. in the 1 st century ad, the romans invented the glass and used them to magnify objects. in the early 14 th century ad, eyeglasses were made by italian spectacle makers. in 1590, two dutch spectacle makers, hans, and zacharias jansen created the first microscope. it was a simple tube with 2 lenses system and had 9x. The bright field microscope is your standard microscope that you could purchase for your niece or nephew at any toy store. here is a website on the basic parts of a bright field compound microscope, in case you are not enrolled in the general microbiology lab. the specimen is illuminated by a light source at the base of the microscope and then. There are two fundamental types of microscope: light microscope. electron microscope. light microscope involves the use of series of glass lenses to focus light in order to create an image whereas, electron microscope uses electromagnetic lenses to focus beam of electrons. light microscopes have ability to magnify objects up to a maximum of.

Microscope Types Parts History Diagram Facts Britannica The bright field microscope is your standard microscope that you could purchase for your niece or nephew at any toy store. here is a website on the basic parts of a bright field compound microscope, in case you are not enrolled in the general microbiology lab. the specimen is illuminated by a light source at the base of the microscope and then. There are two fundamental types of microscope: light microscope. electron microscope. light microscope involves the use of series of glass lenses to focus light in order to create an image whereas, electron microscope uses electromagnetic lenses to focus beam of electrons. light microscopes have ability to magnify objects up to a maximum of. Electron microscope. the electron microscope makes use of beams of electrons instead of a beam of light (as is the case in other types of microscopes previously described) to form or produce the image of living microorganisms. in electron microscopy, electromagnets instead of lenses are used to focus specimens or living organisms. Figure 14.2.1 14.2. 1: (a) the amplitude is the height of a wave, whereas the wavelength is the distance between one peak and the next. (b) these waves have different frequencies, or rates of vibration. the wave at the top has the lowest frequency, since it has the fewest peaks per unit time.

Parts Of A Microscope With Functions And Labeled Diagram Electron microscope. the electron microscope makes use of beams of electrons instead of a beam of light (as is the case in other types of microscopes previously described) to form or produce the image of living microorganisms. in electron microscopy, electromagnets instead of lenses are used to focus specimens or living organisms. Figure 14.2.1 14.2. 1: (a) the amplitude is the height of a wave, whereas the wavelength is the distance between one peak and the next. (b) these waves have different frequencies, or rates of vibration. the wave at the top has the lowest frequency, since it has the fewest peaks per unit time.

Comments are closed.