Microwave Transmission In Wireless Network

Microwave Transmission In Wireless Network Microwave transmission. microwave is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. their frequency ranges from 300 mhz to 300 ghz, which corresponds to wavelengths of 1 mm to 30 cm. sending and receiving information by microwaves is known as microwave transmission. microwaves come under unguided or wireless transmission media. Into wireless networks is a complicated task requiring broad expertise across a number of technologies and disciplines. commscope has been involved in microwave networks since the early 1950s. our microwave antenna solutions connect the world’s networks, much as the early railways connected cities and nations.
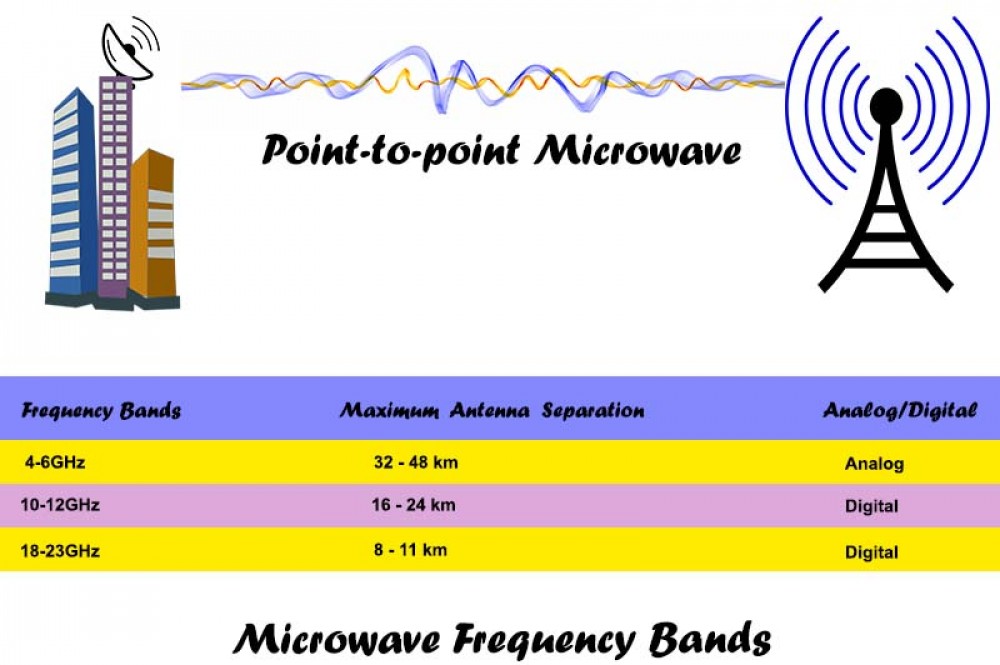
Wireless Transmission And Microwave Transmission In Networking Microwave signals are normally limited to the line of sight, so long distance transmission using these signals requires a series of repeaters forming a microwave relay network. it is possible to use microwave signals in over the horizon communications using tropospheric scatter , but such systems are expensive and generally used only in. Ka band microwaves: its frequency range is 26.5 ghz 40.0 ghz. it is used in satellite communications and broadband internet services. it provides high speed data transmission. v band microwaves (millimeter waves): frequency range of v band microwaves is 40.0 ghz 75.0 ghz. this band is basically used in 5g communication. Wireless metropolitan area networks (wmans)—when it comes to wmans, the microwave spectrum is used in support of broadband fixed wireless access (bfwa) systems, ieee 802.16 wimax standards, the korean wibro specification, etsi's broadband radio access network (bran), hiperman and hiperaccess, flash ofdm, ieee 802.20 mobile fi, iburst personal. Wireless transmission is a form of unguided media. wireless communication involves no physical link established between two or more devices, communicating wirelessly. wireless signals are spread over in the air and are received and interpreted by appropriate antennas. when an antenna is attached to electrical circuit of a computer or wireless.
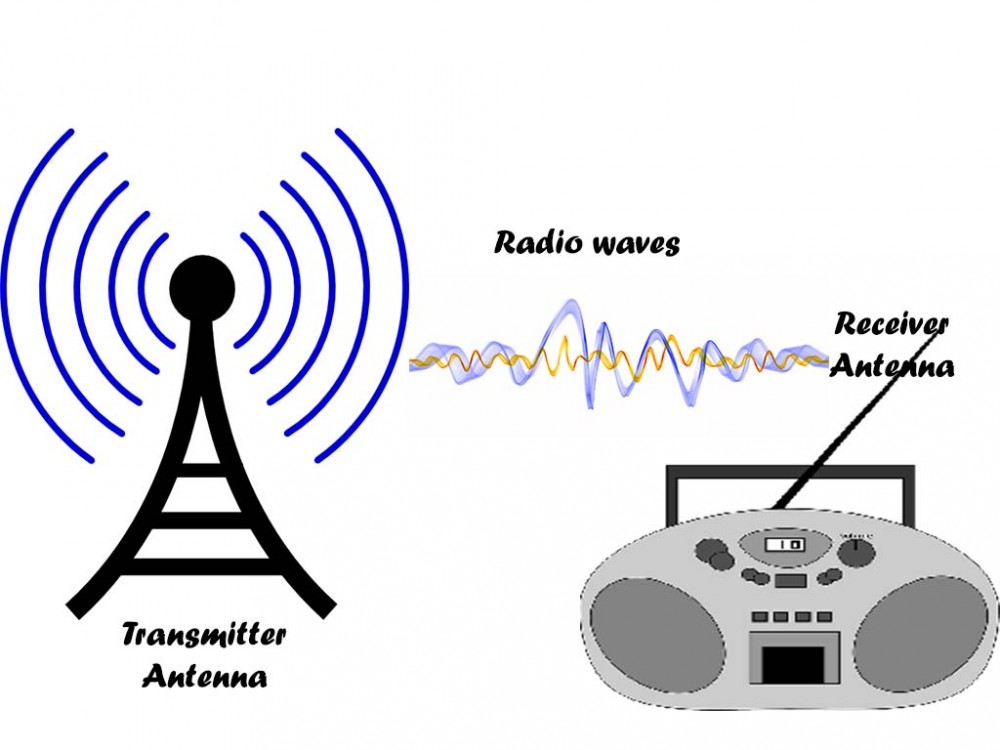
Wireless Transmission And Microwave Transmission In Networking Wireless metropolitan area networks (wmans)—when it comes to wmans, the microwave spectrum is used in support of broadband fixed wireless access (bfwa) systems, ieee 802.16 wimax standards, the korean wibro specification, etsi's broadband radio access network (bran), hiperman and hiperaccess, flash ofdm, ieee 802.20 mobile fi, iburst personal. Wireless transmission is a form of unguided media. wireless communication involves no physical link established between two or more devices, communicating wirelessly. wireless signals are spread over in the air and are received and interpreted by appropriate antennas. when an antenna is attached to electrical circuit of a computer or wireless. In this paper we will focus on challenges wireless companies and their transmission engineers are facing in order to meet the capacity, reliability, performance, speed of deployment, and cost challenges in microwave point to point networks. microwave networks, although very popular in the rest of the word, only recently have become a topic of. It is made with about 200 plus examples for transmission lines, waveguides, passive components, active microwave devices amplifiers oscillators diodes tube based devices, radar systems, satellite communication and conceptual understanding of maxwell equations and prionciples.

Physical And Wireless Transmission Media In this paper we will focus on challenges wireless companies and their transmission engineers are facing in order to meet the capacity, reliability, performance, speed of deployment, and cost challenges in microwave point to point networks. microwave networks, although very popular in the rest of the word, only recently have become a topic of. It is made with about 200 plus examples for transmission lines, waveguides, passive components, active microwave devices amplifiers oscillators diodes tube based devices, radar systems, satellite communication and conceptual understanding of maxwell equations and prionciples.

Comments are closed.