Modelling Motion Using Vectors Part 1 Mr Mathematics Youtube

Modelling Motion Using Vectors Part 1 Mr Mathematics Youtube Advanced kinematics: lesson 1 of 8: modelling motion using vectorswatch part 2: youtu.be c 4kuqkbi8link to lesson mr mathematics product. Advanced kinematics: lesson 2 of 8: modelling motion using vectorswatch part 1: youtu.be dkchyf9y5velink to lesson mr mathematics product.
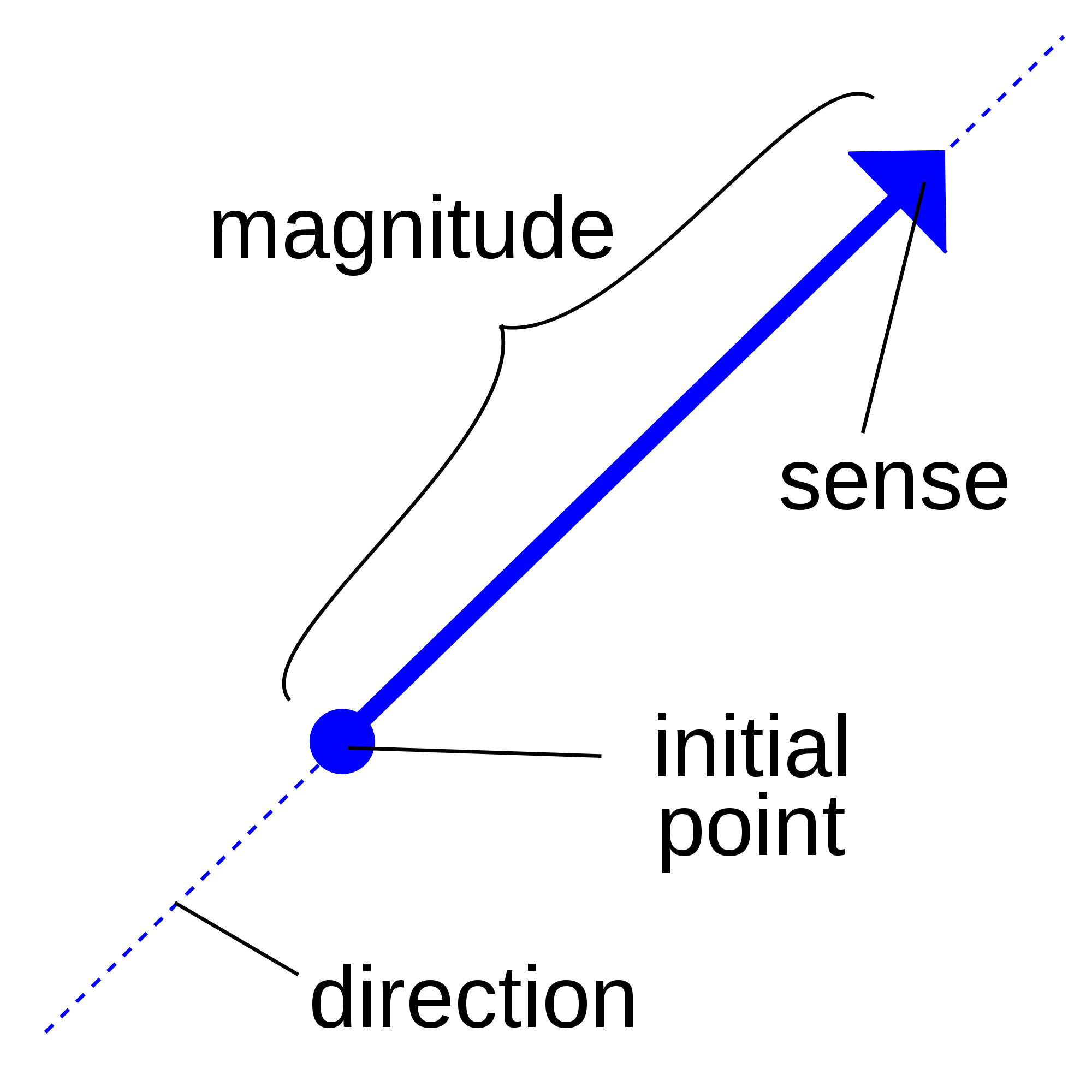
Vector Math Facts For Kids Cool Kid Facts Modelling in mechanics: lesson 2 of 3 modelling motion and forces with vectorsvisit mr mathematics for the complete lesson including powerpoint. Mr mathematics a levle maths tutorial on modelling with vectors for a level maths year 1 pure. mr mathematics 100s of mathematics lessons and wo. Students learn to model motion using vector notation. they start by understanding how to express an object's final position as the sum of its initial position and the product of velocity and time. as learning progresses, students apply these concepts in specific examples. Use kinematic equations in vector form for objects moving with constant acceleration, specifically. \vec {v} = \vec {u} \vec {a}t \; and \; \vec {r} = \vec {u}t \frac {1} {2}\vec {a}t^2. understand the relationships between velocity, acceleration, and displacement vectors over time. differentiate position vectors with respect to time to.

Modelling Motion Using Vectors Mr Mathematics Students learn to model motion using vector notation. they start by understanding how to express an object's final position as the sum of its initial position and the product of velocity and time. as learning progresses, students apply these concepts in specific examples. Use kinematic equations in vector form for objects moving with constant acceleration, specifically. \vec {v} = \vec {u} \vec {a}t \; and \; \vec {r} = \vec {u}t \frac {1} {2}\vec {a}t^2. understand the relationships between velocity, acceleration, and displacement vectors over time. differentiate position vectors with respect to time to. Grasp the concept of projectile motion as a form of two dimensional motion. recognize that projectile motion can be analyzed by separating it into horizontal and vertical components. equations of motion: be able to use the formula for the horizontal motion, understanding that the horizontal velocity is constant since a = 0. Vectors in kinematics february 13, 2024. vectors and motion form a critical part of the applied section of a level mathematics curriculum. in the final chapter of mechanics 2 students combine their understanding of vectors and calculus from the pure curriculum with advanced kinematics.

Comments are closed.