Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica 41ођ

Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica Molecular structure a ball and stick model of molecular structure, showing atoms bonded together. molecules are held together by shared electron pairs, or covalent bonds. such bonds are directional, meaning that the atoms adopt specific positions relative to one another so as to maximize the bond strengths. In another example, dna, which is a very long molecule—in humans, the combined length of all the dna molecules in a single cell stretched end to end would be about 1.8 metres (6 feet), whereas the cell nucleus is about 6 μm (6 10 6 metre) in diameter—has a highly flexible helical structure that allows the molecule to become tightly coiled.

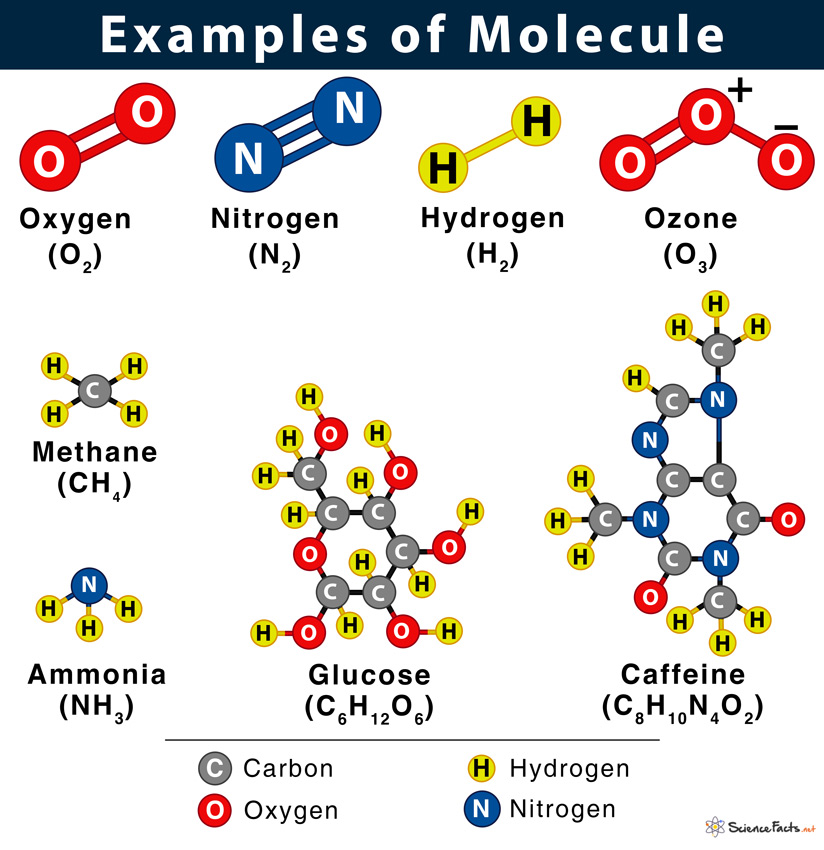
What Is A Molecule Definition And Examples Aldehyde, any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom, a single bond with a hydrogen atom, and a single bond with another atom or group of atoms (designated r in general chemical formulas and structure diagrams). the double bond between carbon and oxygen is characteristic of all aldehydes. Hcl is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule. polyatomic molecule – a polyatomic molecule consists of more than two atoms. glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) and water (h 2 o) are examples of polyatomic molecules. macromolecule – a macromolecule is a very large molecule, often consisting of subunits. proteins and dna are examples of. Molecule definition. a molecule is two or more atoms bonded together to form a single chemical entity. each atom carries a certain number of electrons that orbit around the nucleus. the nucleus consists of protons and neutrons, of different numbers in different elements. the electrons that orbit the nucleus exist in various clouds, or valence. Molecule. all objects that we see around us are made of molecules. from living objects such as a plant or an animal, including humans, inanimate objects like a chair, table, wall, door, windows, books, computer, and mobile phones are all made of molecules. examples. oxygen (o 2), ozone (o 3), methane (ch 4), sodium chloride (nacl), and glucose.

Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica 57 Off Molecule definition. a molecule is two or more atoms bonded together to form a single chemical entity. each atom carries a certain number of electrons that orbit around the nucleus. the nucleus consists of protons and neutrons, of different numbers in different elements. the electrons that orbit the nucleus exist in various clouds, or valence. Molecule. all objects that we see around us are made of molecules. from living objects such as a plant or an animal, including humans, inanimate objects like a chair, table, wall, door, windows, books, computer, and mobile phones are all made of molecules. examples. oxygen (o 2), ozone (o 3), methane (ch 4), sodium chloride (nacl), and glucose. Introduction. a molecule is the smallest unit of a substance that has all the properties of that substance. for instance, a water molecule is the smallest unit that is still water. a water molecule can be divided into tiny parts called atoms. this produces two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Recent news. lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. one type of lipid, the triglycerides, is sequestered as fat in adipose cells, which serve as the energy storage depot for organisms and.

Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica 51 Off Introduction. a molecule is the smallest unit of a substance that has all the properties of that substance. for instance, a water molecule is the smallest unit that is still water. a water molecule can be divided into tiny parts called atoms. this produces two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Recent news. lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. one type of lipid, the triglycerides, is sequestered as fat in adipose cells, which serve as the energy storage depot for organisms and.
Molecule Definition Examples Structures Facts Britannica 51 Off

Comments are closed.