Mumps Pathology Clinical Presentations Complications Diagnosis
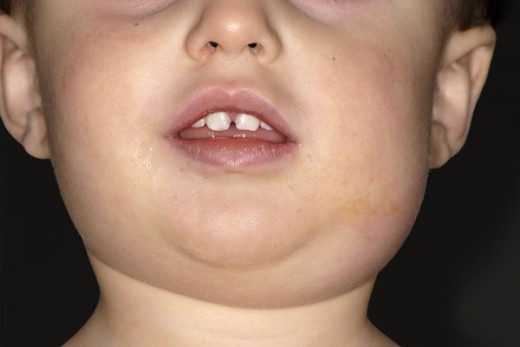
Mumps Pathology Clinical Presentations Complications Diagnosis Differential diagnosis. mumps is the most common cause of childhood parotitis. a classic presentation of parotitis during a mumps outbreak may be presumptively diagnosed based on clinical presentation. however, clinicians should consider other potential etiologies when symptoms are atypical or when the patient has not recently been exposed to. Mumps is a contagious viral illness that is largely preventable via vaccination [1]. typically, it begins with a few days of fever, headache, myalgia, fatigue, and anorexia, followed by parotitis; the illness is usually self limited. the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mumps are discussed here.

Mumps Pathology Clinical Presentations Complications Diagnosis The hallmark of mumps is salivary gland swelling, typically the parotid glands, which forms the basis of a clinical diagnosis. parotitis is usually bilateral, developing 2–3 weeks after exposure and lasting for 2–3 days, but it may persist for a week or more in some cases [ 37 , 50 , 51 ]. Mumps is confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rt pcr) or viral culture from buccal oral or urine specimens. a negative rt pcr or viral culture in a person with clinically compatible mumps symptoms does not rule out mumps as a diagnosis. acute mumps infection can be detected by the presence of serum mumps igm. Key points. mumps disease is caused by a paramyxovirus and can be prevented by vaccination. common clinical features include parotitis (swollen salivary glands in cheek and jaw area) and fever. mumps spreads through direct contact with saliva or respiratory droplets. isolate infected patients until 5 days after the onset of parotitis. Mumps should be suspected in all patients with parotitis or mumps complications, regardless of age, vaccination status, and travel history. differential diagnosis. mumps infection is most often confused with swelling of the lymph nodes of the neck. lymph node swelling can be differentiated by: the well defined borders of the lymph nodes.

Mumps Clinical Features Effects Complications Diagnosis Key points. mumps disease is caused by a paramyxovirus and can be prevented by vaccination. common clinical features include parotitis (swollen salivary glands in cheek and jaw area) and fever. mumps spreads through direct contact with saliva or respiratory droplets. isolate infected patients until 5 days after the onset of parotitis. Mumps should be suspected in all patients with parotitis or mumps complications, regardless of age, vaccination status, and travel history. differential diagnosis. mumps infection is most often confused with swelling of the lymph nodes of the neck. lymph node swelling can be differentiated by: the well defined borders of the lymph nodes. The clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of hbv infection are described in detail separately. hepatitis c virus (hcv) infection is often associated with extrahepatic symptoms ,… a time when there may be no other clinical manifestations of hepatitis. women have a higher incidence of joint disease than men.…. Mumps is a common childhood infection caused by the mumps virus. the hallmark of infection is swelling of the parotid gland. aseptic meningitis and encephalitis are common complications of mumps together with orchitis and oophoritis, which can arise in adult men and women, respectively; other complications include deafness and pancreatitis. clinical diagnosis can be based on the classic.

Mumps Virus Characteristics Pathology And Pathogenesis The clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of hbv infection are described in detail separately. hepatitis c virus (hcv) infection is often associated with extrahepatic symptoms ,… a time when there may be no other clinical manifestations of hepatitis. women have a higher incidence of joint disease than men.…. Mumps is a common childhood infection caused by the mumps virus. the hallmark of infection is swelling of the parotid gland. aseptic meningitis and encephalitis are common complications of mumps together with orchitis and oophoritis, which can arise in adult men and women, respectively; other complications include deafness and pancreatitis. clinical diagnosis can be based on the classic.

Comments are closed.