Myocardial Infarction Heart Attack Ischemia Pathophysiology Ecg Nursing Signs Symptoms Part 1

Myocardial Infarction Mi Signs Symptoms Diagnosis Management Myocardial infarction (mi), colloquially known as “heart attack,” is caused by decreased or complete cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium. myocardial infarction may be “silent” and go undetected, or it could be a catastrophic event leading to hemodynamic deterioration and sudden death.[1] most myocardial infarctions are due to underlying coronary artery disease, the. Myocardial ischemia can lead to serious complications, including: heart attack. if a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, the lack of blood and oxygen can lead to a heart attack that destroys part of the heart muscle. the damage can be serious and sometimes fatal. irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia).

Myocardial Infarction Heart Attack Ischemia Pathophysiology E Acute myocardial infarction (ami) is one of the leading causes of death in the developed world. the prevalence of the disease approaches 3 million people worldwide, with more than 1 million deaths in the united states annually. ami can be divided into 2 categories: non–st segment elevation myocardial infarction (nstemi) and st segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi). unstable angina. Acute myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death in the developed world. the prevalence of the disease approaches three million people worldwide, with more than one million deaths in the united states annually. acute myocardial infarction can be divided into two categories, non st segment elevation mi (nstemi) and st segment elevation mi (stemi). unstable angina is similar to. Myocardial infarction is defined as myocardial necrosis in a clinical setting consistent with myocardial ischemia (1). these conditions can be satisfied by a rise of cardiac biomarkers (preferably cardiac troponin [ctn]) above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit (url) plus at least one of the following: symptoms of ischemia. Other myocardial ischemia symptoms can also include: pain or discomfort in your upper body, including your arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw or stomach. trouble breathing or feeling short of breath. sweating or "cold sweat." feeling full, indigestion, or a choking feeling (may feel like heartburn).

Myocardial Infarction Cardiovascular Medbullets Step 1 Myocardial infarction is defined as myocardial necrosis in a clinical setting consistent with myocardial ischemia (1). these conditions can be satisfied by a rise of cardiac biomarkers (preferably cardiac troponin [ctn]) above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit (url) plus at least one of the following: symptoms of ischemia. Other myocardial ischemia symptoms can also include: pain or discomfort in your upper body, including your arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw or stomach. trouble breathing or feeling short of breath. sweating or "cold sweat." feeling full, indigestion, or a choking feeling (may feel like heartburn). The heart muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen rich blood. the coronary arteries, which branch off the aorta just after it leaves the heart, deliver this blood.an acute coronary syndrome occurs when a sudden blockage in a coronary artery greatly reduces or cuts off the blood supply to an area of the heart muscle (myocardium). Myocardial infarction (mi), colloquially known as “heart attack,” is caused by decreased or complete cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium. myocardial infarction may be “silent” and go undetected, or it could be a catastrophic event leading to hemodynamic deterioration and sudden death. most myocardial infarctions are.
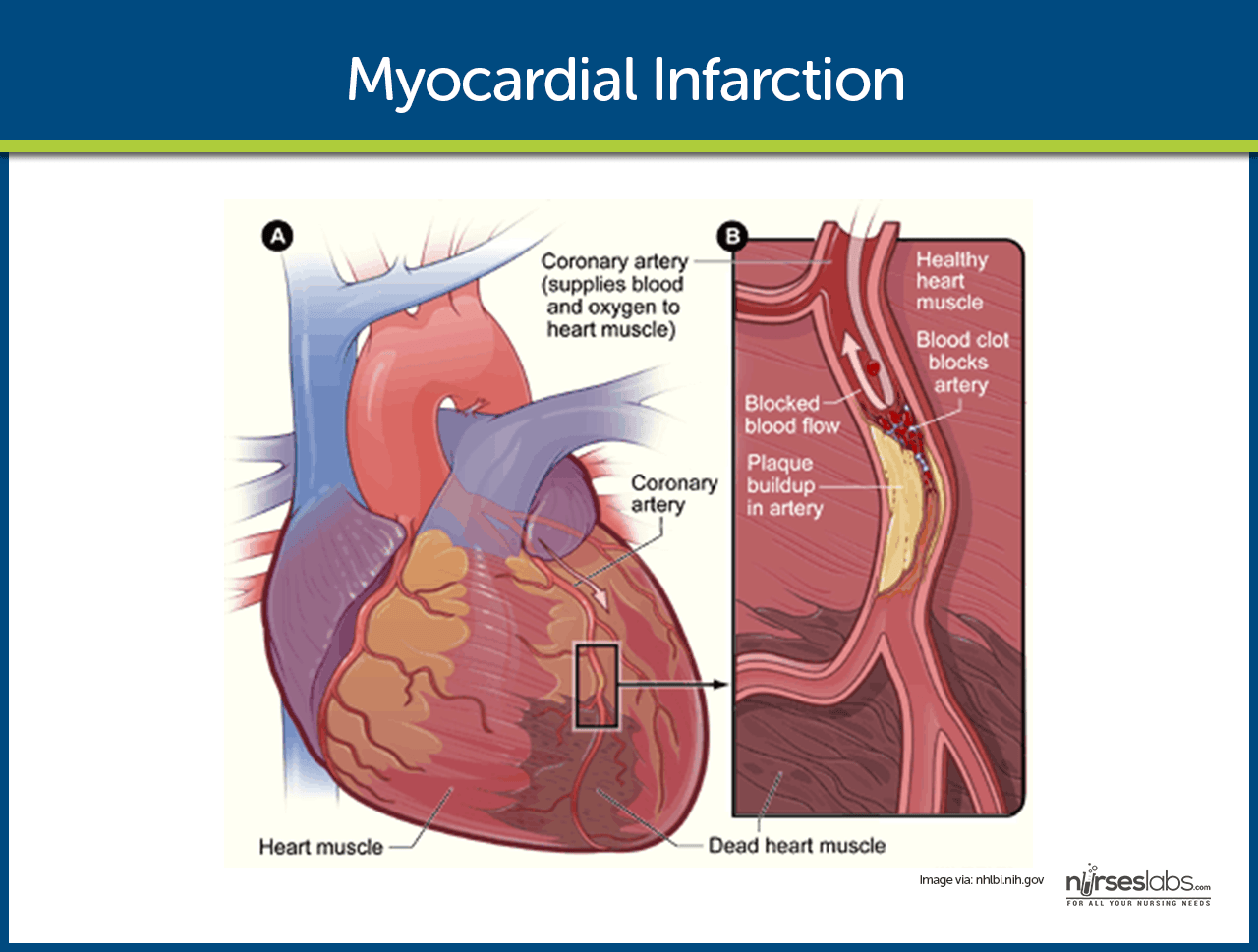
Myocardial Infarction Nursing Care Management And Study Guide The heart muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen rich blood. the coronary arteries, which branch off the aorta just after it leaves the heart, deliver this blood.an acute coronary syndrome occurs when a sudden blockage in a coronary artery greatly reduces or cuts off the blood supply to an area of the heart muscle (myocardium). Myocardial infarction (mi), colloquially known as “heart attack,” is caused by decreased or complete cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium. myocardial infarction may be “silent” and go undetected, or it could be a catastrophic event leading to hemodynamic deterioration and sudden death. most myocardial infarctions are.

Comments are closed.