Normal Inferior Giffen Goods

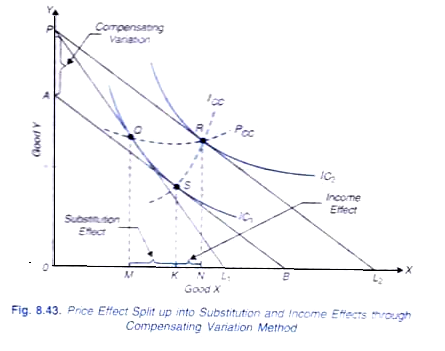
P 3 Type Of Goods Mcq Veblen Goods Bandwagon Snob Effect Inferior The price demand relationship in case of a giffen good is illustrated in fig. 8.46. with a certain given price income situation depicted by the budget line pl 1, the consumer is initially in equilibrium at q on indifference curve ic 1. with a fall in price of the good, the consumer shifts to point r on indifference curve ic 2. Normal goods, inferior goods, and giffen goods are three types of goods with different effects on the demand for the commodity when the income of the consumer or the price of the commodity changes. what are normal goods? the goods whose demand increases when there is an increase in the income of consumer are known as normal goods. these include.

Indifference Curves And Budget Lines Economics Help In the above example of a normal good, income rises (500 700) 40%, demand rises 100 800 – 12.5% yed – 12.5 40 = 0.3125; note: a luxury good is also a normal good, but a normal good isn’t necessarily a luxury good. inferior good. an inferior good means an increase in income causes a fall in demand. it is a good with a negative income. Giffen goods violate the law of demand, whereas inferior goods is a part of consumer goods and services, a determinant of demand. giffen goods have no close substitutes. on the other hand, inferior goods have alternatives of better quality. when there is a fall in price, the overall price effect in the case of giffen goods will be negative. Inferior goods are the opposite of normal goods, whose demand increases when incomes increase. giffen goods are rare forms of inferior goods that have no ready substitute or alternative, such. While both giffen goods and inferior goods exhibit a decrease in demand as income increases, the factors influencing their demand differ. for giffen goods, the primary factor is the lack of available substitutes due to financial constraints. as the price of a giffen good increases, consumers are unable to switch to other goods, leading to an.
Price Demand Relationship Normal Inferior And Giffen Goods Inferior goods are the opposite of normal goods, whose demand increases when incomes increase. giffen goods are rare forms of inferior goods that have no ready substitute or alternative, such. While both giffen goods and inferior goods exhibit a decrease in demand as income increases, the factors influencing their demand differ. for giffen goods, the primary factor is the lack of available substitutes due to financial constraints. as the price of a giffen good increases, consumers are unable to switch to other goods, leading to an. Income effect. when the price of a giffen good increases, consumers allocate a larger share of their income towards it, leading to a decrease in their income. the decrease in consumer’s income leads to an increase in demand for the giffen good as consumers cannot afford more expensive substitutes. 3. substitution effect. A giffen good (1) is when after a decrease in price of good (1) the demand for (1) decreases but the demand of some other good (2) increases. or is def 1 just the definition of a giffen good, which is a special type of inferior good? for a giffen good the income effect is strong enough to outweigh the substitution effect.
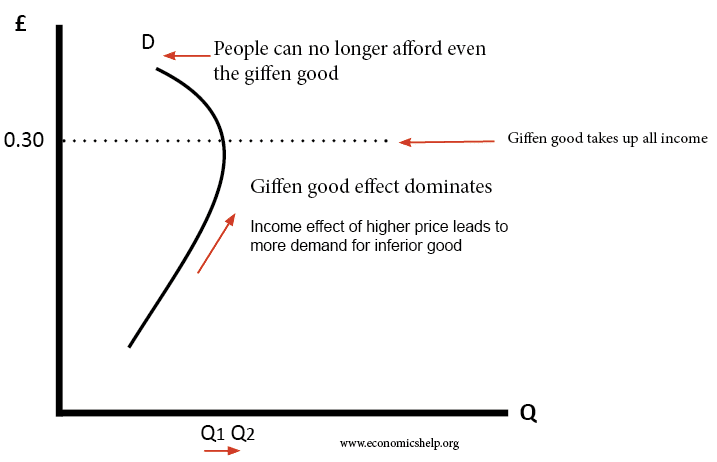
1 Economics Help Income effect. when the price of a giffen good increases, consumers allocate a larger share of their income towards it, leading to a decrease in their income. the decrease in consumer’s income leads to an increase in demand for the giffen good as consumers cannot afford more expensive substitutes. 3. substitution effect. A giffen good (1) is when after a decrease in price of good (1) the demand for (1) decreases but the demand of some other good (2) increases. or is def 1 just the definition of a giffen good, which is a special type of inferior good? for a giffen good the income effect is strong enough to outweigh the substitution effect.

Comments are closed.