Obstetrics Intrapartum Care Physiomi

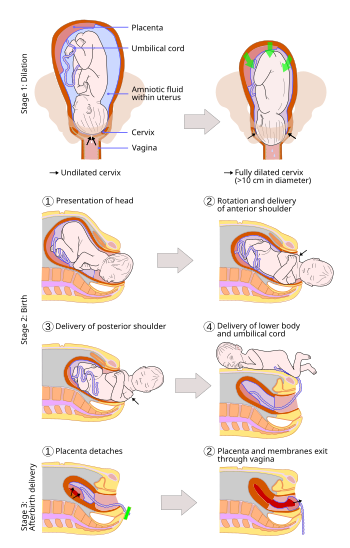
Obstetrics Intrapartum Care вђ Physiomi Review record for any medical obstetric fetal complications & history; review routine screening tests e.g. gbs ; fetal check: external doppler or bedside ultrasound for fetal viability; leopold’s maneuvers vaginal exam bedside ultrasound to get fetal presentation & estimated fetal weight; maternal check: pelvis exam – adequacy of pelvis. Stages & phases of labor stage 1: from onset of true labor to full cervical dilation (10cm). it has 2 phases: latent phase: from onset of labor to period of rapid dilation (1 2cm h). active phase: from the period of rapid dilation (typically at 6cm dilation is when it speeds up ~1 2cm h;…. read more. physiomi medical.

Obstetrics Intrapartum Care вђ Physiomi 3.1 care throughout labour and birth 19 3.2 first stage of labour 35 3.3 second stage of labour 120 3.4 third stage of labour 159 3.5 care of the newborn 162 3.6 care of the woman after birth 165 4. implementation of this guideline: introducing the who intrapartum care model 168 5. research implications 171 6. dissemination 173 7. This guide has been prepared by the awhonn task force to revise the awhonn education guide, basic, high risk, and critical care intrapartum nursing: clinical competencies and education guide. education guides are reviewed periodically. this guide is not intended to be exhaustive; other sources of information and guidance are available and should be consulted. this guide is intended to. Quality of care is a focus area for improvement to reduce avoidable mortality and morbidity in mothers and newborn babies. according to the who quality of care framework for maternal and newborn health, evidence based practice is a key quality of care component . two entities underpin the implementation of evidence based care; firstly, is the. The recommendations below are new in the 2023 update of this guideline. before this recommendation was introduced, information on the impact of body mass index (bmi) to guide a woman’s choice of place of birth was limited. choosing place of birth is an important part of a woman’s birth plan. parity, obstetric history, and medical or.
Obstetrics Intrapartum Care вђ Physiomi Quality of care is a focus area for improvement to reduce avoidable mortality and morbidity in mothers and newborn babies. according to the who quality of care framework for maternal and newborn health, evidence based practice is a key quality of care component . two entities underpin the implementation of evidence based care; firstly, is the. The recommendations below are new in the 2023 update of this guideline. before this recommendation was introduced, information on the impact of body mass index (bmi) to guide a woman’s choice of place of birth was limited. choosing place of birth is an important part of a woman’s birth plan. parity, obstetric history, and medical or. The guideline highlights the importance of woman centred care to optimize the experience of labour and childbirth for women and their babies through a holistic, human rights based approach. it introduces a global model of intrapartum care, which takes into account the complexity and diverse nature of prevailing models of care and contemporary. Temperature of 38°c or above on a single reading, or 37.5°c or above on 2 consecutive readings 1 hour apart; for advice about intrapartum antibiotics, see the section on intrapartum antibiotics in nice's guideline on neonatal infection. fresh red bleeding or blood stained liquor.
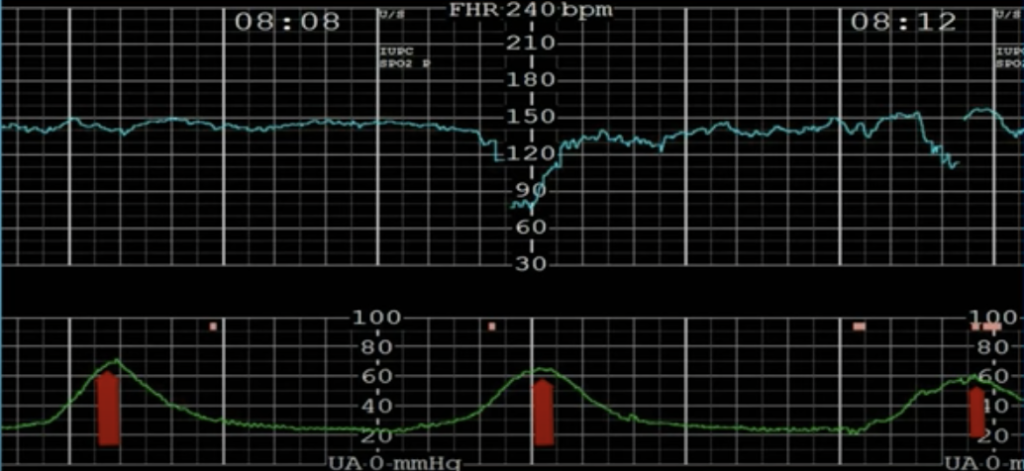
Obstetrics Intrapartum Care вђ Physiomi The guideline highlights the importance of woman centred care to optimize the experience of labour and childbirth for women and their babies through a holistic, human rights based approach. it introduces a global model of intrapartum care, which takes into account the complexity and diverse nature of prevailing models of care and contemporary. Temperature of 38°c or above on a single reading, or 37.5°c or above on 2 consecutive readings 1 hour apart; for advice about intrapartum antibiotics, see the section on intrapartum antibiotics in nice's guideline on neonatal infection. fresh red bleeding or blood stained liquor.

Comments are closed.