Oce Ccboss Cu Cckeys Cuocaeoceuoaµ µeyou Ccprime Cu 2 Uu Aeµuuoo Uƒ Ocithuaoa Oiith Th I Ccthe World Cu C
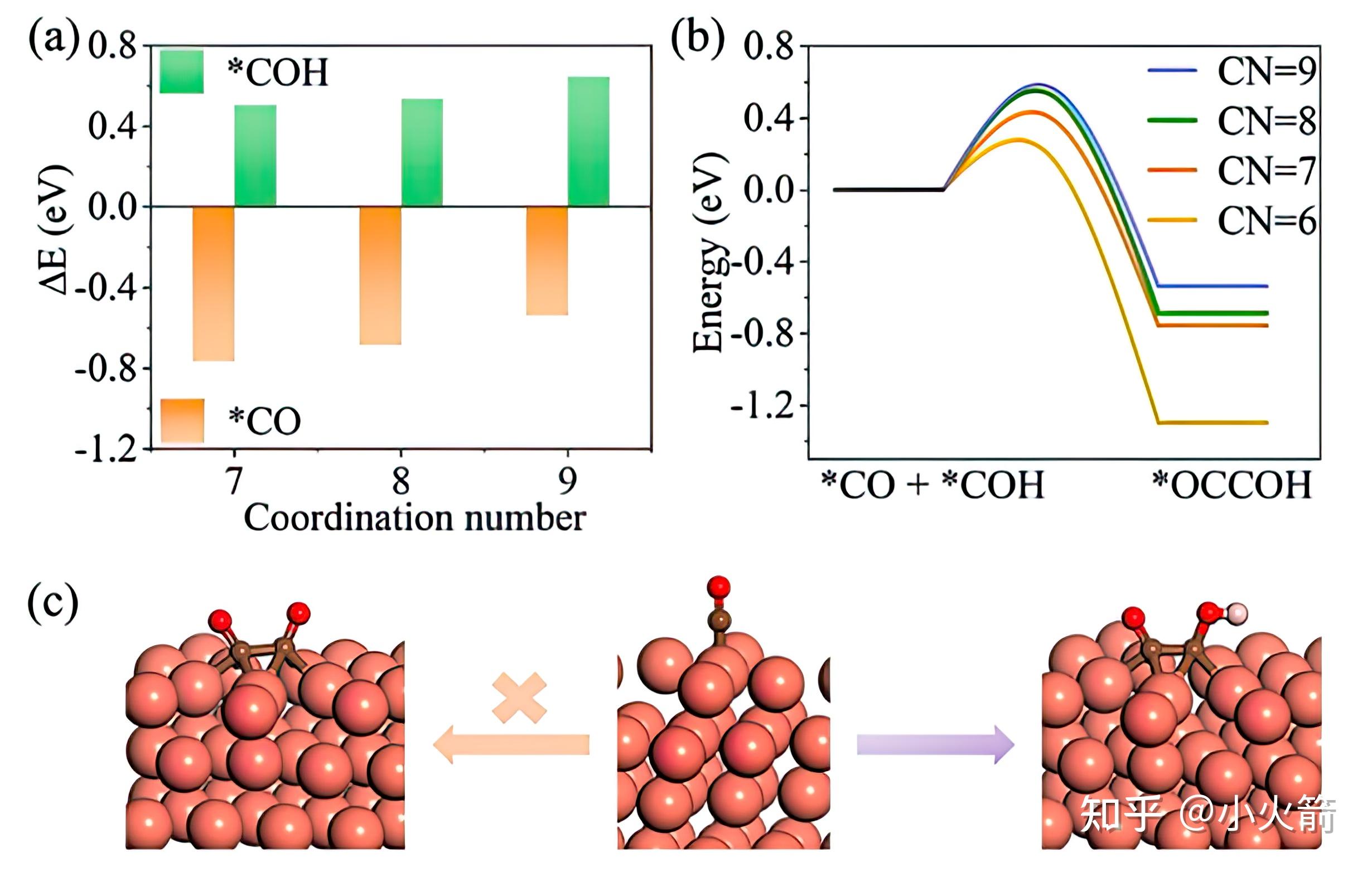
碎片化 Cu 催化co2还原的oc Coh耦合机理 低配位 Cu 有助于oc Coh耦合 知乎 For 1.4 cu 1 w 18 o 49 sample, apart from co production, it exhibited ch 4 and c 2 h 4 production rates of 5.7 and 0.33 µmol g −1 h −1, respectively, with a low selectivity of 6.7% for c 2 h 4 product. at an optimal doping concentration of cu single atoms, c 2 h 4 production reaches the maximum over 3.6 cu 1 w 18 o 49 photocatalyst. The copper 2p 3 2 peak was used to align the spectra to the binding energy of cu cu 2 o (e bin = 932.67 ev) 51. the copper lmm auger line was used to distinguish cu from cu species.

C2 B5 Starwars The high resolution xps spectrum of cu 2p of cuo 500 (figure 2b) exhibited two peaks at 933.57 and 953.48 ev, which were attributed to cu 2p 3 2 and cu 2p 1 2 of cu ( 2). the peaks at binding energies of 941.35 and 943.78 ev can be recognized as the characteristic satellite peaks corresponding to cu ( 2). C, cu mass dissolution rate. 0.05 m khco 3 saturated with co 2 was used as the electrolyte. dmphen was added to the electrolyte (0.1 mm) to prolong the lifetime of the cu intermediate species. it. Although the current density of 10 cycle cu was significantly boosted, the c 1 and c 2 product distribution did not show a significant enhancement from polished cu. the highest c 2 selectivity. A cu@cu–n–c composite electrocatalyst was fabricated from cu(oh) 2 @zif 8, wherein the encapsulated cu(oh) 2 gradually transforms into the final cu 2 o with the increasing temperature. the cu@cu–n–c catalyst shows a hollow polyhedral morphology which is created by carbothermal reduction of in situ formed cu 2 o and zno with carbon.

Co2 Reduction On Pure Cu Produces Only H2 After Subsurface O Is Although the current density of 10 cycle cu was significantly boosted, the c 1 and c 2 product distribution did not show a significant enhancement from polished cu. the highest c 2 selectivity. A cu@cu–n–c composite electrocatalyst was fabricated from cu(oh) 2 @zif 8, wherein the encapsulated cu(oh) 2 gradually transforms into the final cu 2 o with the increasing temperature. the cu@cu–n–c catalyst shows a hollow polyhedral morphology which is created by carbothermal reduction of in situ formed cu 2 o and zno with carbon. This paper describes an emerging synthetic route for the production of ethanol (with a yield of ∼83%) via syngas using cu sio 2 catalysts. the remarkable stability and efficiency of the catalysts are ascribed to the unique lamellar structure and the cooperative effect between surface cu 0 and cu obtained by an ammonia evaporation hydrothermal method. Hence, methanol synthesis over cu appears to be a structure sensitive reaction. single crystal studies (9–11) report turnover frequencies (tof) for methanol synthesis ranging from as low as 1.3 × 10 −6 to 6 × 10 −3 s −1 per site. zno functions as a physical spacer between cu nps and helps disperse the cu phase in the course of.
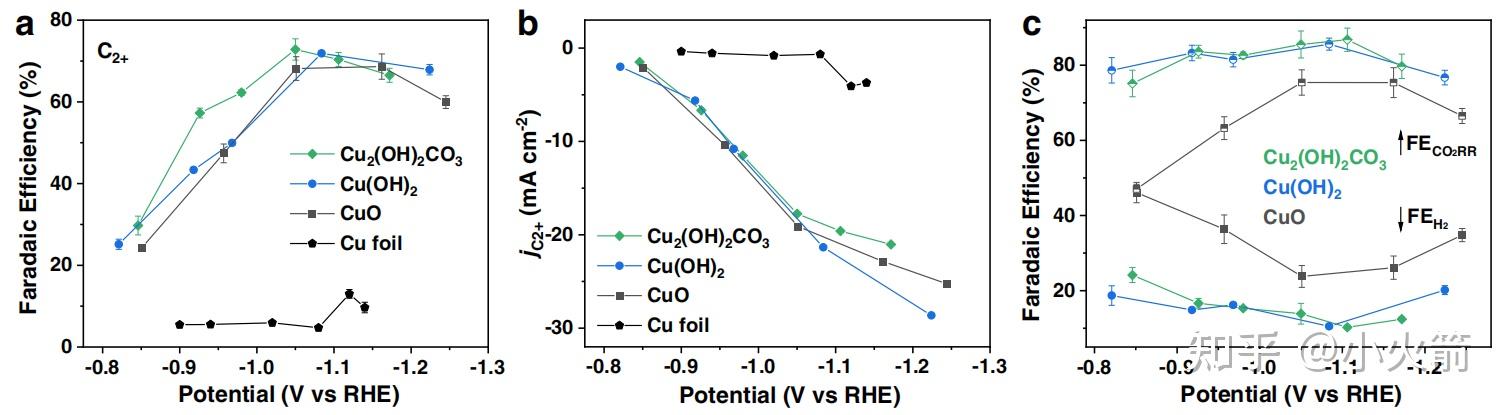
Cu 衍生物的结构演化和催化co2还原 Cu 被还原成0价 C2 法拉第效率73 知乎 This paper describes an emerging synthetic route for the production of ethanol (with a yield of ∼83%) via syngas using cu sio 2 catalysts. the remarkable stability and efficiency of the catalysts are ascribed to the unique lamellar structure and the cooperative effect between surface cu 0 and cu obtained by an ammonia evaporation hydrothermal method. Hence, methanol synthesis over cu appears to be a structure sensitive reaction. single crystal studies (9–11) report turnover frequencies (tof) for methanol synthesis ranging from as low as 1.3 × 10 −6 to 6 × 10 −3 s −1 per site. zno functions as a physical spacer between cu nps and helps disperse the cu phase in the course of.

Catalysts Free Full Text Recent Advances In Heterogeneous

Comments are closed.