Organoids And 3d Cell Culture Systems Developmental Biology Study
Organoids And 3d Cell Culture Systems Developmental Biology Study Learn how human organoids, stem cell derived 3d culture systems, can model human development and disease and reduce animal experiments. Organoids are three dimensional (3d) miniature structures cultured in vitro produced from either human pluripotent stem cells (hpscs) or adult stem cells (adscs) derived from healthy individuals.
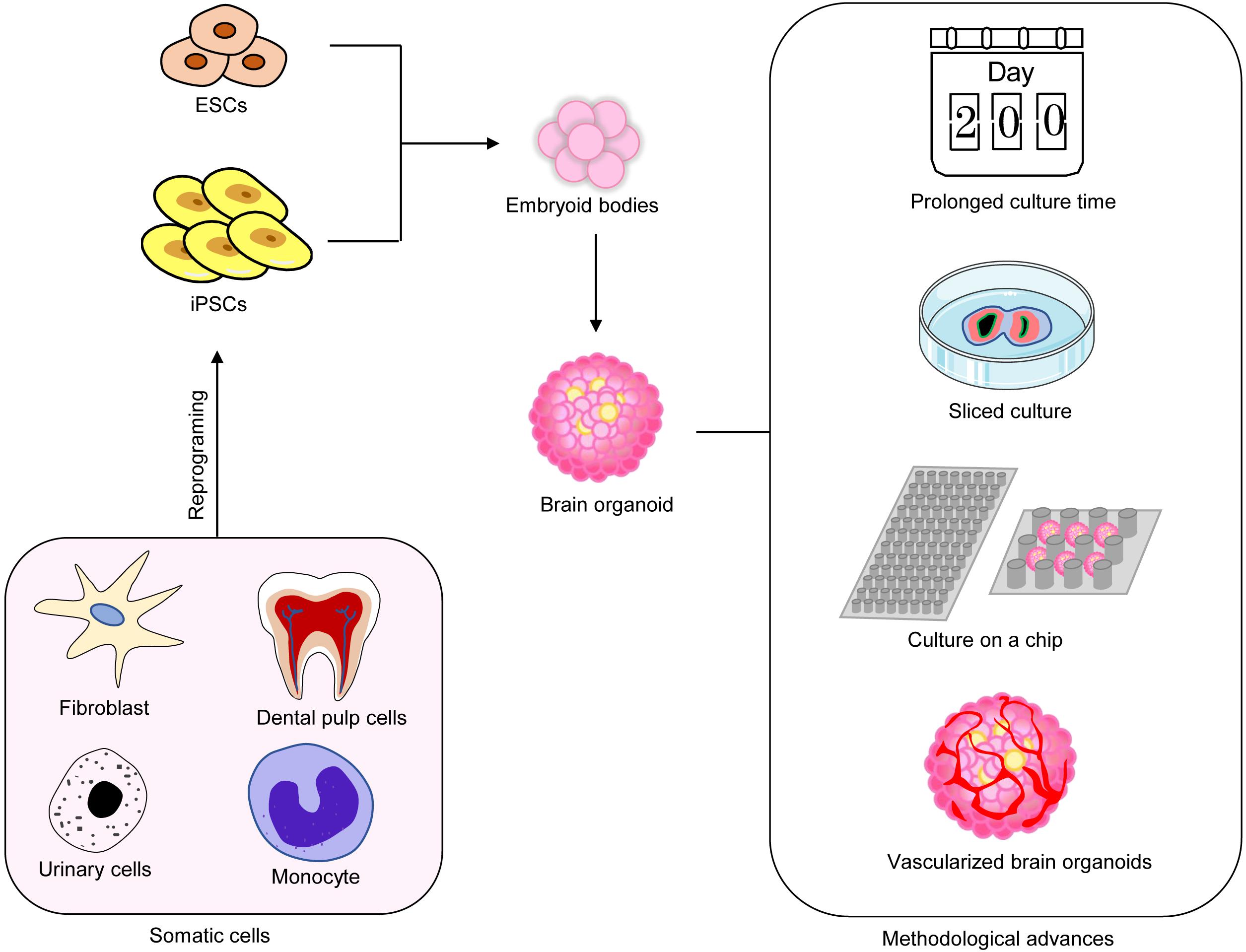
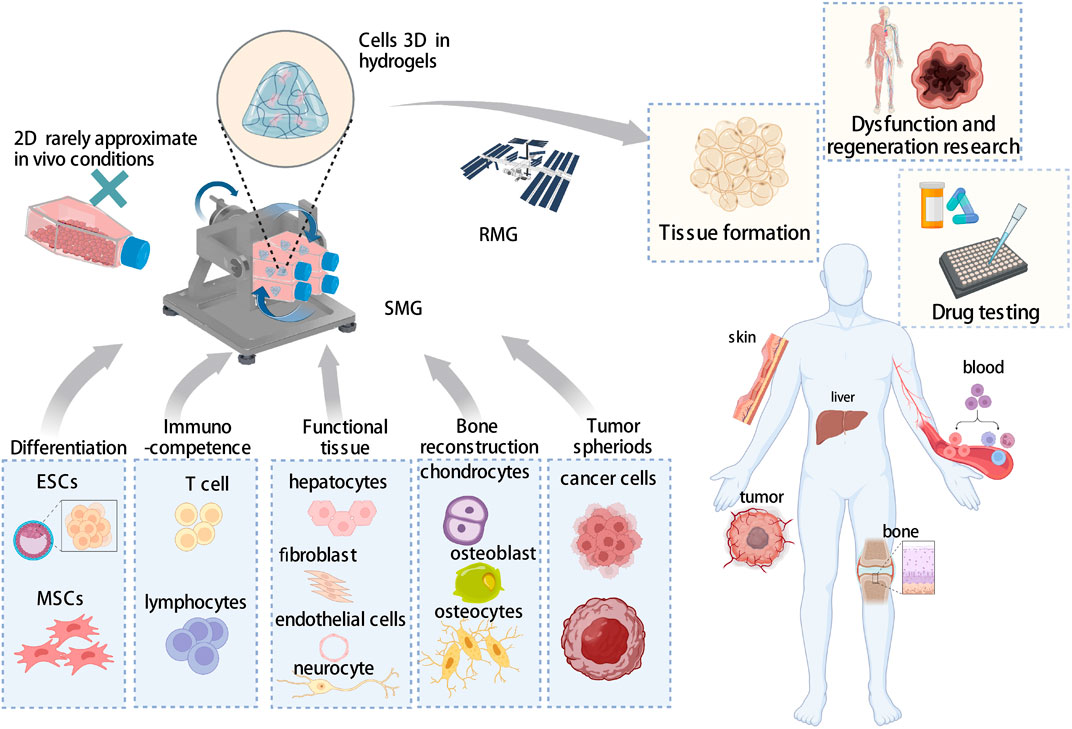
Organoids And 3d Cell Culture Systems Developmental Biology Study Organoid technology has emerged as an essential tool for both fundamental and biomedical research, providing developmental biologists with means for ex vivo modeling of tissue morphogenesis and organogenesis. here, kretzschmar and clevers discuss how organoid cultures have been established and utilized as a model system for stem cell research and developmental biology. Supportive 3d co culture conditions including various cell types and ecm, provide proper niche, enhance organoid condensation, and improve vascularization and maturation of organoids. application of co culture systems for the study of developmental biology is still in its infancy, and further studies are needed to uncover the signaling pathways. As such, 3d cell culture models are more representative of in vivo tissue biology and may serve as a physiological model to study human diseases. one such 3d cell culture technique is organoid culture. organoids may be defined as cellular aggregates derived from primary tissues or stem cells that can self organize into organotypic structures. 2d cell culture and animal models have allowed us to accumulate knowledge in cellular and molecular biology, but questions inherent to human cell physiology remain unanswered. 3d cell culture models, more specifically, organoids, can recreate human 3d tissue architecture and spatially and temporally recapitulate morphogenetic events due to human stem cell differentiation (kim et al., 2020.
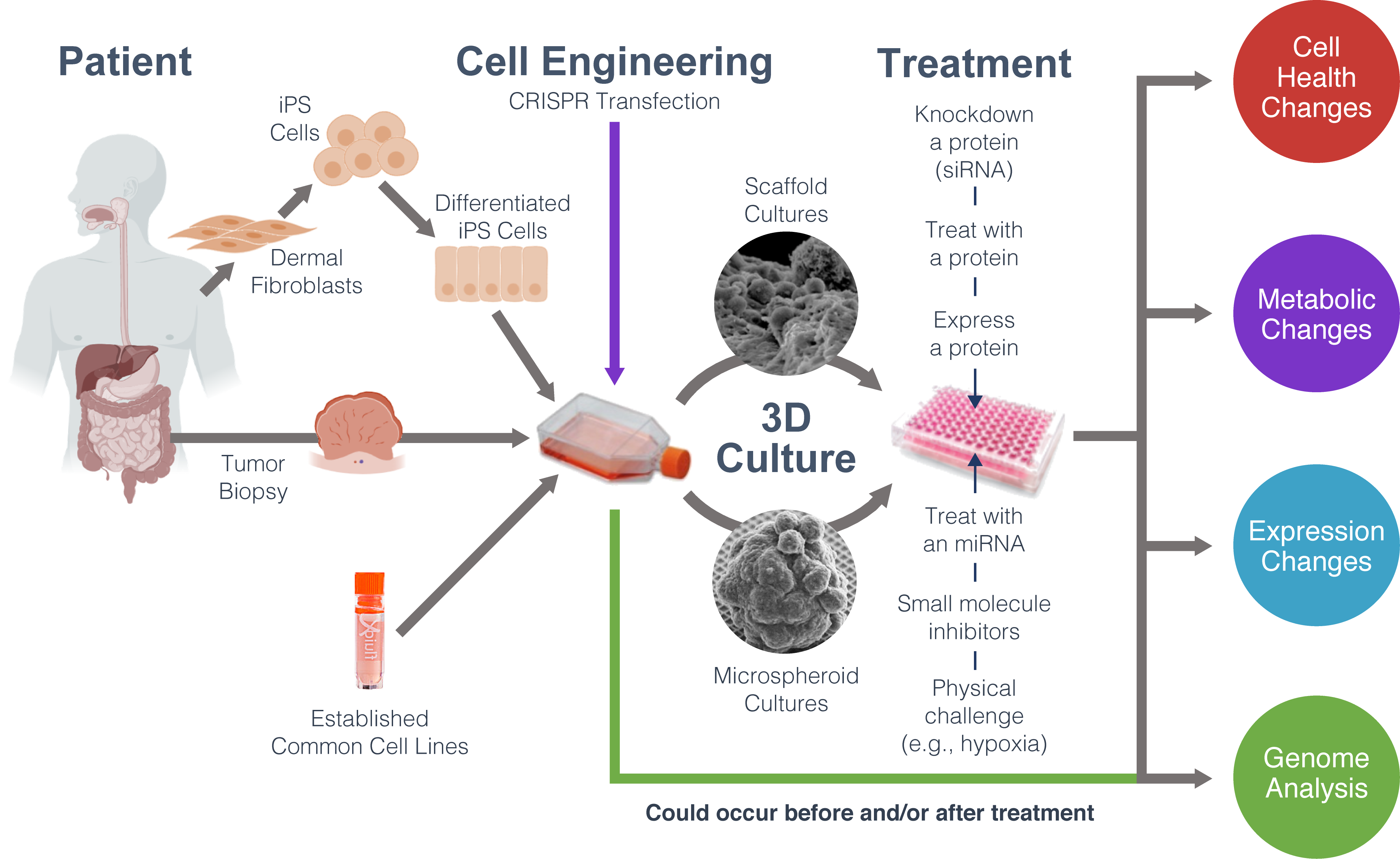
Introduction To 3d Cell Culture As such, 3d cell culture models are more representative of in vivo tissue biology and may serve as a physiological model to study human diseases. one such 3d cell culture technique is organoid culture. organoids may be defined as cellular aggregates derived from primary tissues or stem cells that can self organize into organotypic structures. 2d cell culture and animal models have allowed us to accumulate knowledge in cellular and molecular biology, but questions inherent to human cell physiology remain unanswered. 3d cell culture models, more specifically, organoids, can recreate human 3d tissue architecture and spatially and temporally recapitulate morphogenetic events due to human stem cell differentiation (kim et al., 2020. Organoid formation and the process of organogenesis share common developmental pathways; thus, our knowledge of developmental biology can help model the complexity of different organs to refine organoids into a more sophisticated platform. the developmental process is strongly dependent on complex networks and communication of cell cell and. Abstract. organoids are in vitro miniaturized and simplified model systems of organs that have gained enormous interest for modelling tissue development and disease, and for personalized medicine.

Comments are closed.