Overview Of Periodic Trends
.PNG)
Periodic Trends Presentation Chemistry Exercise 20.2.1 20.2. 1. based on the positions of the group 14 elements c, si, ge, sn, and pb in the periodic table and the general trends outlined in this section, classify these elements as metals, semimetals, or nonmetals. predict which element forms the most stable compounds in the 2 oxidation state. predict which element differs the most. Periodic trends are specific patterns observed among the chemical elements of the periodic table. these observed patterns allude to the changes in atomic structure, including size and radius, as well as properties of the elements. these changes occur within their respective period from left to right and group from top to bottom in the periodic.

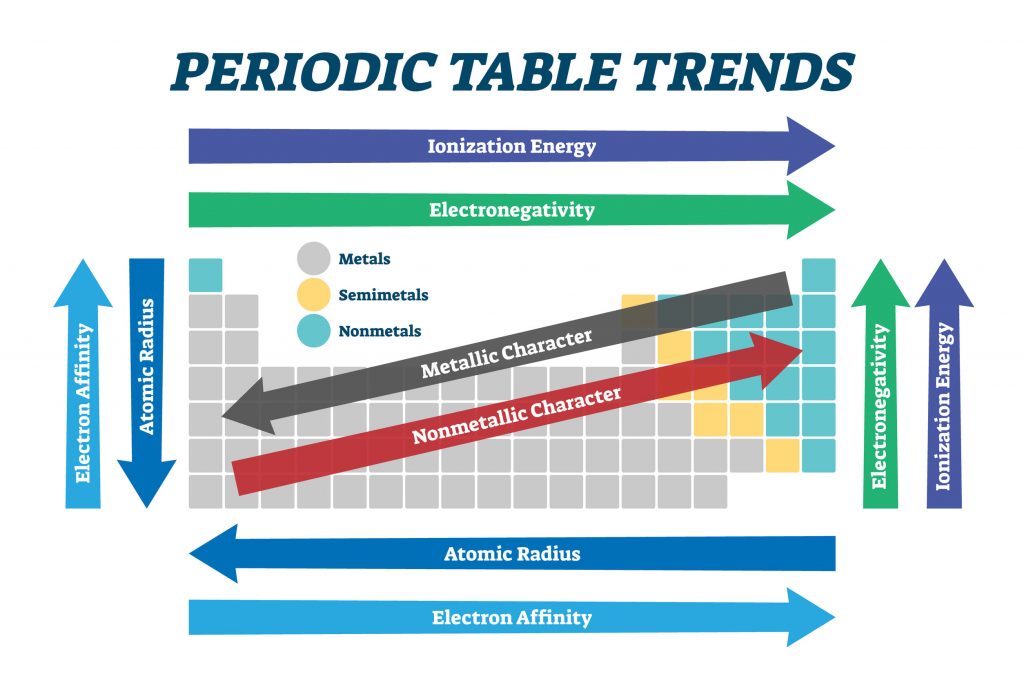
Graphs And Tables Of Period 3 Trends In chemistry, periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of certain elements when grouped by period and or group. they were discovered by the russian chemist dmitri mendeleev in 1863. major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity. The ionization energy and the electronegativity generally increase from left to right in a row and from bottom to top in a column. the atomic size and the metallic character are opposite, i.e., they increase from right to left in a row and from top to bottom in a column. fig. 2.6.6 summarizes the periodic trend in the properties of the elements. Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element, including its size and its electronic properties. major periodic trends include: electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. The organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other. atomic radius increases as you move.
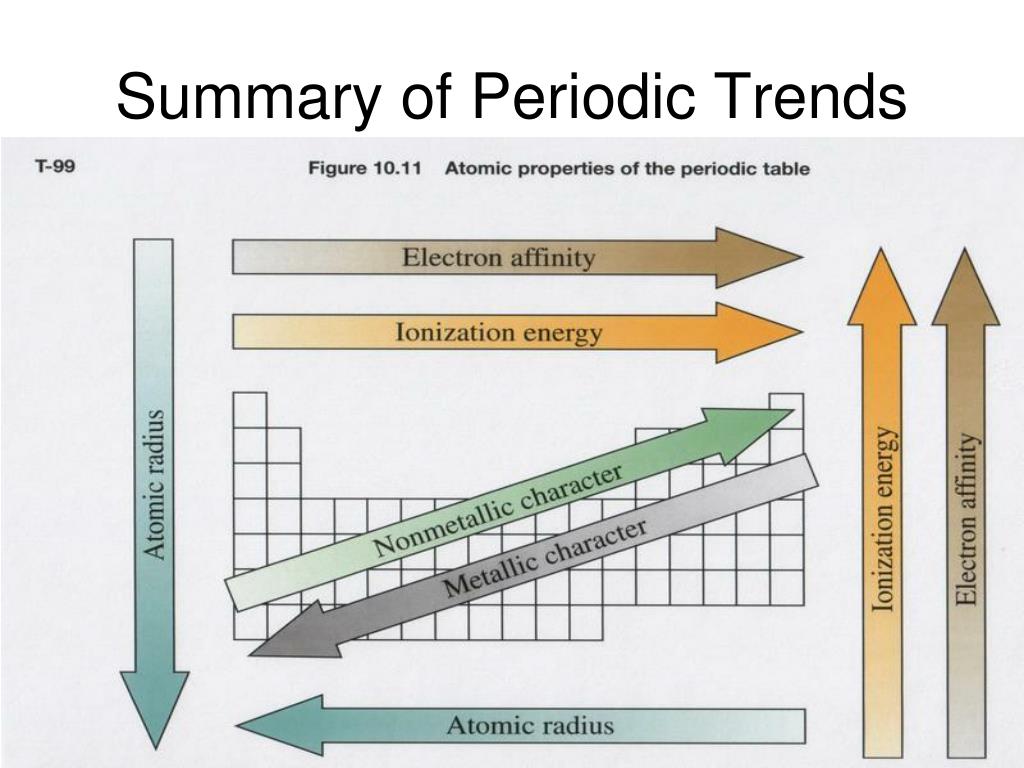
Ppt Ch 6 The Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element, including its size and its electronic properties. major periodic trends include: electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. The organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other. atomic radius increases as you move. Electron electron repulsions: due to their like charges, electron pairs orient themselves as far away as possible from each other, causing the electron cloud to expand (justifies trends across a period). 1. atomic radius. atomic radius increases. atomic radius is the distance from the atom’s nucleus to the outer edge of the electron cloud. Ionization energy (ie) is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase: a (g) → a (g) e− Δh ≡ ie. ie is usually expressed in kj mol of atoms. it is always positive because the removal of an electron always requires that energy be put in (i.e., it is endothermic).

Periodicity Trends In The Periodic Table Compound Interest Electron electron repulsions: due to their like charges, electron pairs orient themselves as far away as possible from each other, causing the electron cloud to expand (justifies trends across a period). 1. atomic radius. atomic radius increases. atomic radius is the distance from the atom’s nucleus to the outer edge of the electron cloud. Ionization energy (ie) is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase: a (g) → a (g) e− Δh ≡ ie. ie is usually expressed in kj mol of atoms. it is always positive because the removal of an electron always requires that energy be put in (i.e., it is endothermic).
The Periodic Table Is Way Of Ordering Chemical Elements

Comments are closed.