Part 5 From Bells Inequalities To Entangled Qubits A New Quantum Age

Part 5 From Bell S Inequalities To Entangled Qubits A New Part 5 alain aspect from bell's inequalities to entangled qubits: a new quantum age? cleo iqec 2009bells theorem has drawn physicists attention onto th. This work provides quantitative tests of the extent of violation of two inequalities applicable to qubits coupled into bell states, using ibm's publicly accessible quantum computers. violations of the inequalities are well established. our purpose is not to test the inequalities, but rather to determine how.
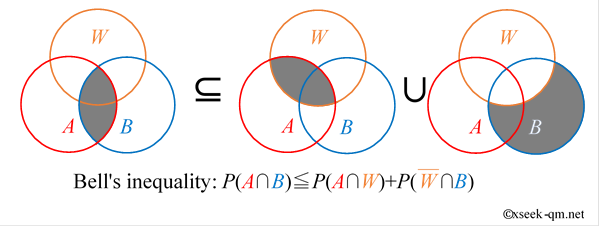
The Meaning Of Bell S Inequality Mysterious World Of Quantum Theory Superconducting qubits cover new distances. superconducting quantum bits, a promising platform for future quantum computers, have been entangled over a separation of 30 metres, with a performance. 5.3 quantum theory, formally (continued) tensor products; 5.4 more qubits, and binary representations; 5.5 separable or entangled? 5.6 controlled not; 5.7 bell states; 5.8 quantum teleportation; 5.9 no cloning, and other no go theorems; 5.10 controlled phase and controlled u; 5.11 universality, revisited; 5.12 phase kick back; 5.13 density. 4.2 the bell inequality 10 4.2.1 three quantum coins 10 4.2.2 quantum entanglement vs. einstein locality 13 4.3 more bell inequalities 17 4.3.1 chsh inequality 17 4.3.2 maximal violation 18 4.3.3 quantum strategies outperform classical strategies 20 4.3.4 all entangled pure states violate bell inequalities 22 4.3.5 photons 24. Bell inequalities have traditionally been used to demonstrate that quantum theory is nonlocal, in the sense that there exist correlations generated from composite quantum states that cannot be explained by means of local hidden variables. with the advent of device independent quantum information protocols, bell inequalities have gained an additional role as certificates of relevant quantum.

Part 4 From Bell S Inequalities To Entangled Qubits A New Qua 4.2 the bell inequality 10 4.2.1 three quantum coins 10 4.2.2 quantum entanglement vs. einstein locality 13 4.3 more bell inequalities 17 4.3.1 chsh inequality 17 4.3.2 maximal violation 18 4.3.3 quantum strategies outperform classical strategies 20 4.3.4 all entangled pure states violate bell inequalities 22 4.3.5 photons 24. Bell inequalities have traditionally been used to demonstrate that quantum theory is nonlocal, in the sense that there exist correlations generated from composite quantum states that cannot be explained by means of local hidden variables. with the advent of device independent quantum information protocols, bell inequalities have gained an additional role as certificates of relevant quantum. Tion of the bell’s inequality may not reveal the general structure of entanglement of a quantum state, the relation between the entanglement, measured in terms of the con currence [5], and the violation of the bell’s inequality was shown in two qubit systems [6, 7]. the generalization for higher qubit systems is still unclear. We use seven qubit quantum states as an example to estimate intensity of quantum entanglement in the maximally entangled state through bell’s inequality [[11], [18]]. a ground state of a toric code model [[3], [4]] on a disk manifold can be shown be occurred at a critical point of quantum entanglement in our quantum states through an upper.
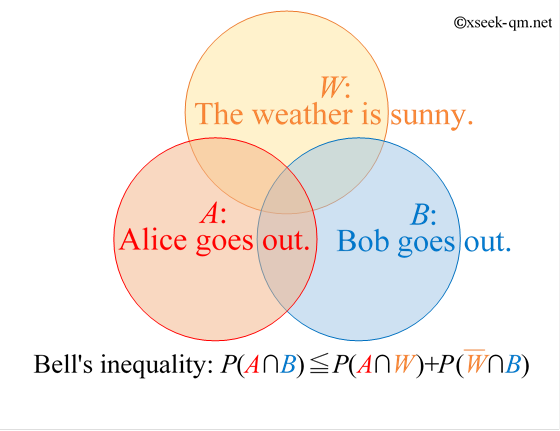
The Meaning Of Bell S Inequality Mysterious World Of Quantum Theory Tion of the bell’s inequality may not reveal the general structure of entanglement of a quantum state, the relation between the entanglement, measured in terms of the con currence [5], and the violation of the bell’s inequality was shown in two qubit systems [6, 7]. the generalization for higher qubit systems is still unclear. We use seven qubit quantum states as an example to estimate intensity of quantum entanglement in the maximally entangled state through bell’s inequality [[11], [18]]. a ground state of a toric code model [[3], [4]] on a disk manifold can be shown be occurred at a critical point of quantum entanglement in our quantum states through an upper.

Part 3 From Bell S Inequalities To Entangled Qubits A New Qua

Comments are closed.