Particle Size Analysis Clinical Gate

Particle Size Analysis Clinical Gate For instance: • coarse powder: majority of particles > 350 µm. • medium fine powder: 100–350 µm. • very fine powder: 10–50 µm. • micronized powder: < 10 µm (majority < 5 µm). pharmacopoeial definitions of grades of powders, and the methods employed to separate particles, by size, are discussed in detail in chapter 10. The samples measured by static image analysis typically rest on a slide that is moved by an automated stage. with the psa300 static image analysis system a microscope and digital camera collect images of the particles as the slide is scanned. samples prepared on slides can include powders, suspensions, or creams.
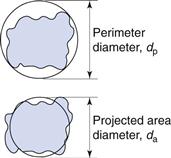
Particle Size Analysis Clinical Gate Absorption rates. other industries where particle size plays an important role include . nanotechnology, proteins, cosmetics, polymers, soils, abrasives, fertilizers, and many more. why is . particle size. imp. ortant? particle size is critical within . a vast number of industries. for example, it determines: appearance and gloss of paint. Respect of particle size) to 1.0 (for a highly polydisperse sample with multiple particle size populations). values of 0.2 and below are most commonly deemed acceptable in practice for. Therefore, the particle size of a suspension can be reported in two different ways. for example, consider a particulate mixture containing four particles of 100 nm, four particles of 200 nm and four particles of 300 nm. the particle size based on the number and volume distribution is shown in fig. 21.2. when represented as a number distribution. 3.3 particle size analysis. particle size may influence many physical and chemical properties of particulate materials and it is a valuable indicator of quality and performance. the size of the particles controls flow and compaction properties. smaller particles dissolve faster and lead to high viscosity.
Particle Size Analysis Clinical Gate Therefore, the particle size of a suspension can be reported in two different ways. for example, consider a particulate mixture containing four particles of 100 nm, four particles of 200 nm and four particles of 300 nm. the particle size based on the number and volume distribution is shown in fig. 21.2. when represented as a number distribution. 3.3 particle size analysis. particle size may influence many physical and chemical properties of particulate materials and it is a valuable indicator of quality and performance. the size of the particles controls flow and compaction properties. smaller particles dissolve faster and lead to high viscosity. Pdf | on jun 20, 2016, mohamad taleuzzaman and others published particle size role, importance and strategy of hplc analysis an update | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate. Particle size analysis, particle size measurement, or simply particle sizing, is the collective name of the technical procedures, or laboratory techniques which determines the size range, and or the average, or mean size of the particles in a powder or liquid sample. particle size analysis is part of particle science, and it is generally.

Comments are closed.