Periodic Trends Atomic Radius
Periodic Table Showing Atomic Radius Explain why the atomic radius of hydrogen is so much smaller than the atomic radius of potassium. this page titled 6.15: periodic trends atomic radius is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. Learn the definition and measurement of atomic radius, and how it varies across the periodic table. see the graph, examples, and practice problems on atomic radius trends.
.PNG)
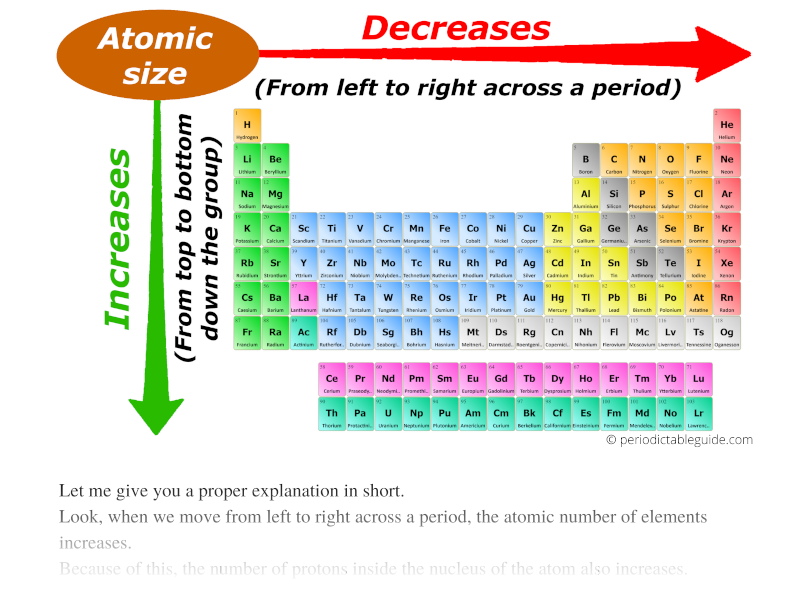
Untitled On Emaze Explanation: periodic trends indicate that atomic radius increases up a group and from left to right across a period. therefore, oxygen has a smaller atomic radius sulfur. 10. answer: b.) false explanation: the reasoning behind this lies in the fact that a metal usually loses an electron in becoming an ion while a non metal gains an electron. Atomic radius trend 1: atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. the first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. within a period of elements, each new electron is added to the same shell. when an electron is added, a new proton is also added to the nucleus, which. Many periodic trends are general. there may be a few points where an opposite trend is seen, but there is an overall trend when considered across a whole row or down a whole column of the periodic table. the first periodic trend we will consider is atomic radius. the atomic radius is an indication of the size of an atom. although the concept of. What are periodic trends. periodic trends are specific patterns observed among the chemical elements of the periodic table. these observed patterns allude to the changes in atomic structure, including size and radius, as well as properties of the elements. these changes occur within their respective period from left to right and group from top.
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Electronegativity Periodic Table Timeline Many periodic trends are general. there may be a few points where an opposite trend is seen, but there is an overall trend when considered across a whole row or down a whole column of the periodic table. the first periodic trend we will consider is atomic radius. the atomic radius is an indication of the size of an atom. although the concept of. What are periodic trends. periodic trends are specific patterns observed among the chemical elements of the periodic table. these observed patterns allude to the changes in atomic structure, including size and radius, as well as properties of the elements. these changes occur within their respective period from left to right and group from top. In chemistry, periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of certain elements when grouped by period and or group. they were discovered by the russian chemist dmitri mendeleev in 1863. major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity. Periodic table trends. the organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other.
.png)
Periodic Table Of The Elements Atomic Radius Vrogue Co In chemistry, periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of certain elements when grouped by period and or group. they were discovered by the russian chemist dmitri mendeleev in 1863. major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity. Periodic table trends. the organization of the periodic table shows the periodic trends of six different physical properties of the elements: atomic radius, electron affinity, electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic nonmetallic character. atomic radius is half the distance between two identical atoms touching each other.

Comments are closed.