Permeability Of Soil Types

Permeability Of Soil Types 6–20 inches of water move through the soil per hour. rapid permeability includes textures of loamy sand and sand and soils with greater than 15 % gravel. soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. The soil permeability is a measure indicating the capacity of the soil or rock to allow fluids to pass through it. it is often represented by the permeability coefficient (k) through the darcy’s equation: v=ki. where v is the apparent fluid velocity through the medium i is the hydraulic gradient , and k is the coefficient of permeability.
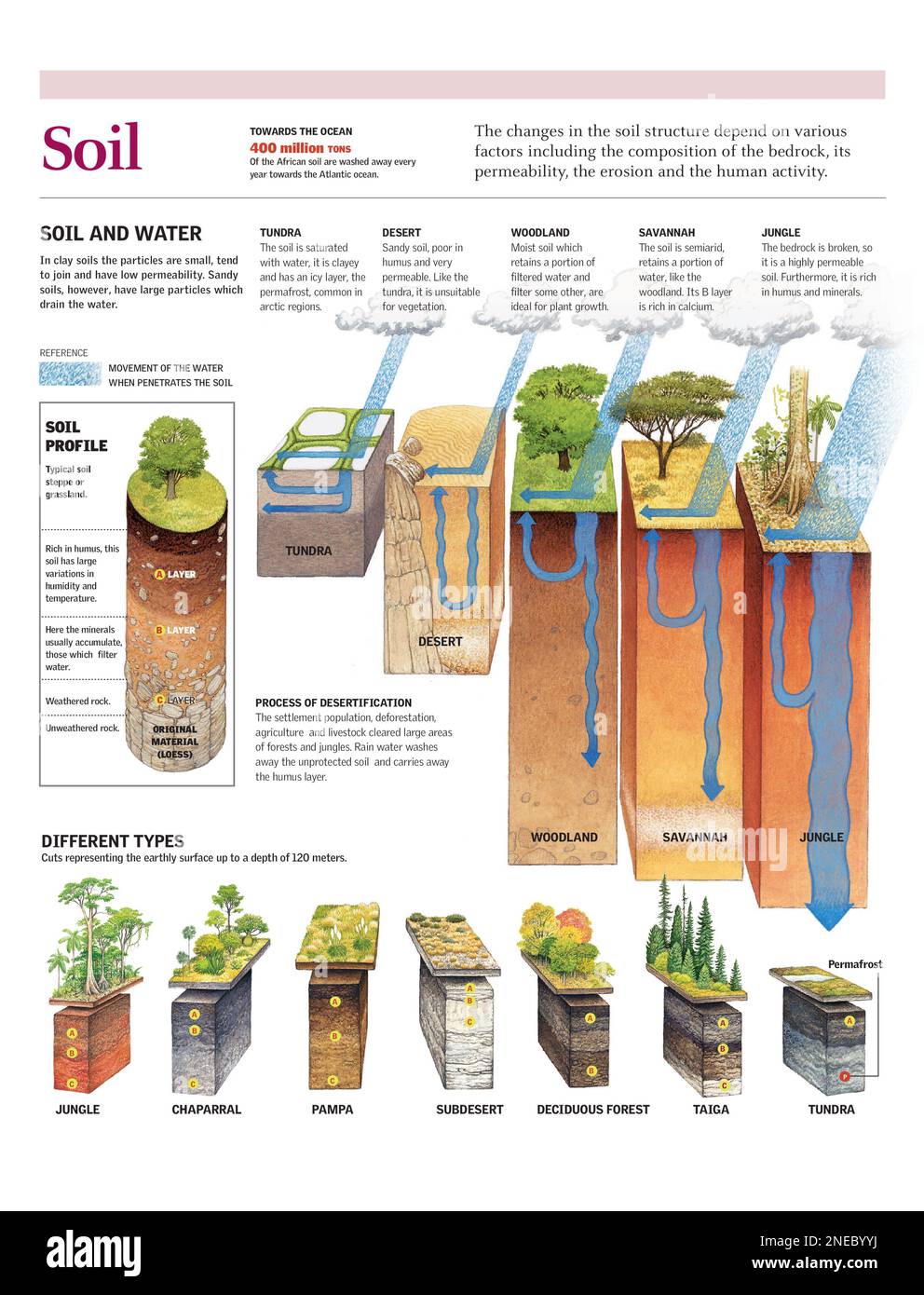
Infographics Of The Different Soil Types According To Their Table 2: typical values of optimum moisture content and suggested relative compactions (based on standard proctor test) permeability. soil permeability describes the rate at which fluids flow through the porous matrix of soil, playing a critical role in numerous geotechnical and environmental applications. There have been attempts to correlate permeability with e2, e2 1 e, e3 1 e. one can intuitively see that larger the d10 or e, larger the void volume and thus larger the permeability. typical permeability values for the common soil types, and what these mean when it comes to drainage characteristics, are summarized in table 7.1 (terzaghi et al. For a given soil, the greater the void ratio, the higher the value of the coefficient of permeability. here 'e' is the void ratio. based on other concepts it has been established that the permeability of a soil varies as e2 or e3 (1 e). whatever may be the exact relationship, all soils have e versus log k plot as a straight line. The permeability of a soil type, which determines how easily water can flow through it, can vary significantly based on factors like compaction and saturation in its natural setting. the coefficient of permeability (k) measured under standard laboratory test conditions does enable a hierarchy of soil types to be made.
Soil Permeability Definition Tests And Formulae Tensar For a given soil, the greater the void ratio, the higher the value of the coefficient of permeability. here 'e' is the void ratio. based on other concepts it has been established that the permeability of a soil varies as e2 or e3 (1 e). whatever may be the exact relationship, all soils have e versus log k plot as a straight line. The permeability of a soil type, which determines how easily water can flow through it, can vary significantly based on factors like compaction and saturation in its natural setting. the coefficient of permeability (k) measured under standard laboratory test conditions does enable a hierarchy of soil types to be made. To determine the permeability of a type of soil, we are going to base ourselves on the experiments carried out by darcy to define darcy’s law. basically, a constant (k) is going to be defined, which means the soil permeability value, by measuring the flow (q) and the hydraulic gradient (Δh Δl), with the help of a permeameter. The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when under a unit hydraulic gradient. low soil permeability can lead to water ponding and weakening of the subgrade.
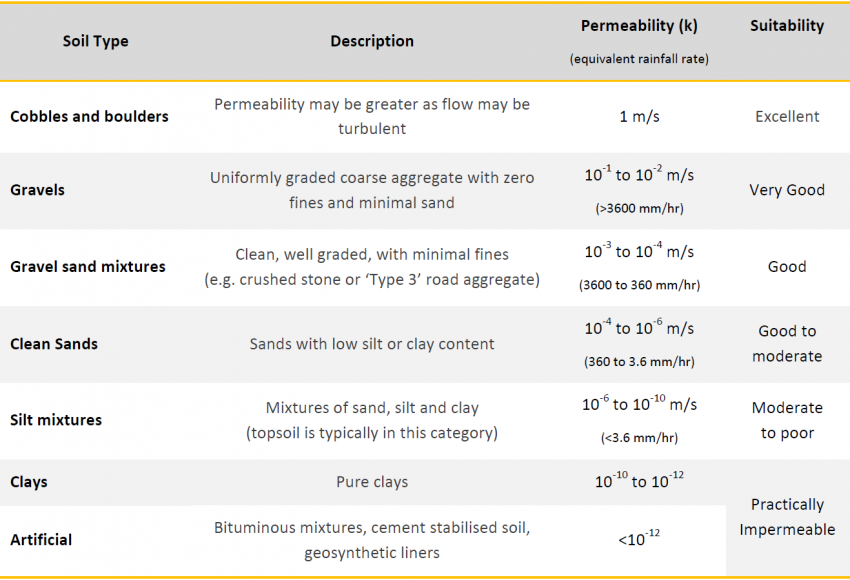
Soil Permeability Abg Geosynthetics Technical Soil Properties Notes To determine the permeability of a type of soil, we are going to base ourselves on the experiments carried out by darcy to define darcy’s law. basically, a constant (k) is going to be defined, which means the soil permeability value, by measuring the flow (q) and the hydraulic gradient (Δh Δl), with the help of a permeameter. The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when under a unit hydraulic gradient. low soil permeability can lead to water ponding and weakening of the subgrade.

Comments are closed.