Perpendicular Bisector Theorem Proofs Solved Examples

Perpendicular Bisector Theorem Proofs Solved Examples Solved examples on perpendicular bisector theorem. example 1: in a pyramid, line segment ad is the perpendicular bisector of triangle abc on line segment bc. if ab = 20 feet and bd= 7 feet, find the length of side ac. solution. it is given that ad is the perpendicular bisector on the line segment bc. so, by perpendicular bisector theorem, any. Solution: according to the perpendicular bisector theorem, any point on the perpendicular bisector is equidistant from both the endpoints of the line segment on which it is drawn. we have ab = ac. 2x 10 = 18. 2x = 18 – 10. 2x = 8. x = 8 2 = 4. find the value of x if ap is the perpendicular bisector of the side bc.

Perpendicular Bisector Theorem Proofs Solved Examples Behold the awesome power of the two words, "perpendicular bisector," because with only a line segment, hm, and its perpendicular bisector, wa, we can prove this theorem. perpendicular bisector theorem proof sas. we are given line segment hm and we have bisected it (divided it exactly in two) by a line wa. that line bisected hm at 90° because. Perpendicular bisector theorem can also be used along with other theorems to solve for lengths of a triangle. consider an example of a weather monitoring tower that is erected at a $90^{o}$ angle in the center of a piece of land. Perpendicular bisector theorem. a perpendicular bisector is a line that intersects a line segment at its midpoint and is perpendicular to that line segment, as shown in the construction below. figure 4.20.1 4.20. 1. one important property related to perpendicular bisectors is that if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then. With this definition in mind, the perpendicular bisector theorem can be summarized as follows. a point, p, is in the perpendicular bisector of a segment of line, a b, if and only if it is.

Perpendicular Bisector Theorem Proofs Solved Examples Perpendicular bisector theorem. a perpendicular bisector is a line that intersects a line segment at its midpoint and is perpendicular to that line segment, as shown in the construction below. figure 4.20.1 4.20. 1. one important property related to perpendicular bisectors is that if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then. With this definition in mind, the perpendicular bisector theorem can be summarized as follows. a point, p, is in the perpendicular bisector of a segment of line, a b, if and only if it is. A line that splits another line segment (or an angle) into two equal parts is called a "bisector." if the intersection between the two line segment is at a right angle, then the two lines are perpendicular, and the bisector is called a "perpendicular bisector". the perpendicular bisector theorem states that a point on the perpendicular bisector. Step 3 find the slope of the perpendicular bisector. 1 slope of pq — =. 1 3 2. − −. — 4 ( 2) = — 6 = − − − — 3 because the slopes of perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals, the slope of the perpendicular bisector is 3. step 4 write an equation. the perpendicular bisector of pq — has slope 3 and passes.
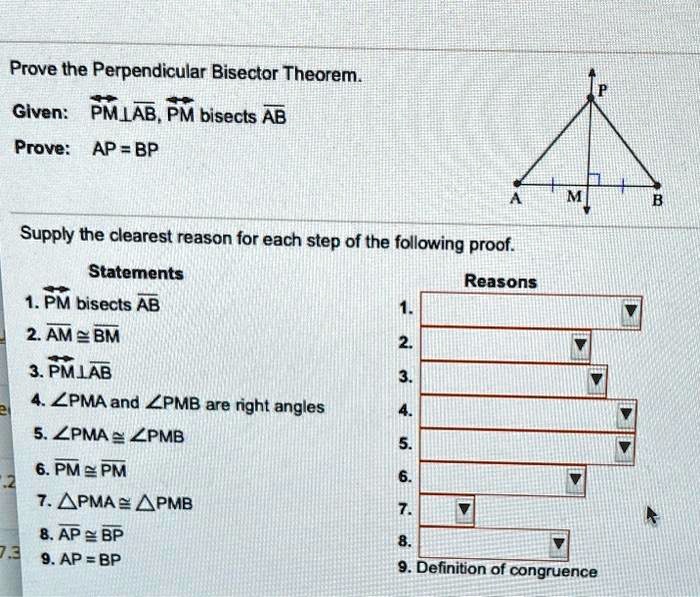
Solved Prove The Perpendicular Bisector Theorem Given Pmlab Pm A line that splits another line segment (or an angle) into two equal parts is called a "bisector." if the intersection between the two line segment is at a right angle, then the two lines are perpendicular, and the bisector is called a "perpendicular bisector". the perpendicular bisector theorem states that a point on the perpendicular bisector. Step 3 find the slope of the perpendicular bisector. 1 slope of pq — =. 1 3 2. − −. — 4 ( 2) = — 6 = − − − — 3 because the slopes of perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals, the slope of the perpendicular bisector is 3. step 4 write an equation. the perpendicular bisector of pq — has slope 3 and passes.

Comments are closed.