Ph Of Weak Acids And Bases Percent Ionization Ka Kb

Ph Of Weak Acids And Bases Percent Ionization Ka Kb Youtube This chemistry video explains how to calculate the ph of a weak acid and a weak base. it explains how to calculate the percent ionization of a weak acid usi. Use the relationships pk = −log k and k = 10 −pk (equations and ) to convert between and or and . solution: we are given the for butyric acid and asked to calculate the and the for its conjugate base, the butyrate ion. because the value cited is for a temperature of 25°c, we can use equation : = pk w = 14.00.
How To Calculate Percent Ionization Of A Weak Acid Or Base Chemistry 🌡️ to calculate the ph from ka, use the formula ph = log[h3o ], and for kb, calculate the hydroxide ion concentration first and then find the poh and subsequently the ph. 📐 the process of finding the ph of a salt solution involves recognizing the weak acid or base components and using the appropriate equilibrium constant (ka or kb). Solution: we are given the pka for butyric acid and asked to calculate the kb and the pkb for its conjugate base, the butyrate ion. because the pka value cited is for a temperature of 25°c, we can use equation 16.5.16: pk a pk b = pkw = 14.00. substituting the pk a and solving for the pk b, 4.83 pk b=14.00. Solution. boric acid is sufficiently weak that we can use the approximation of eq 1 22 to calculate a: = (5.8e–10 .1) ½ = 7.5e 5; multiply by 100 to get .0075 % diss. for the more dilute acid, a similar calculation yields 7.6e–4, or 0.76%. A table of ionization constants for weak bases appears is here. as for acids, the relative strength of a base is also reflected in its percent ionization, computed as $$\text{% ionization}=\frac{[oh^ ] {eq}}{[b] 0}\times 100\text{%}$$ but will vary depending on the base ionization constant and the initial concentration of the solution.
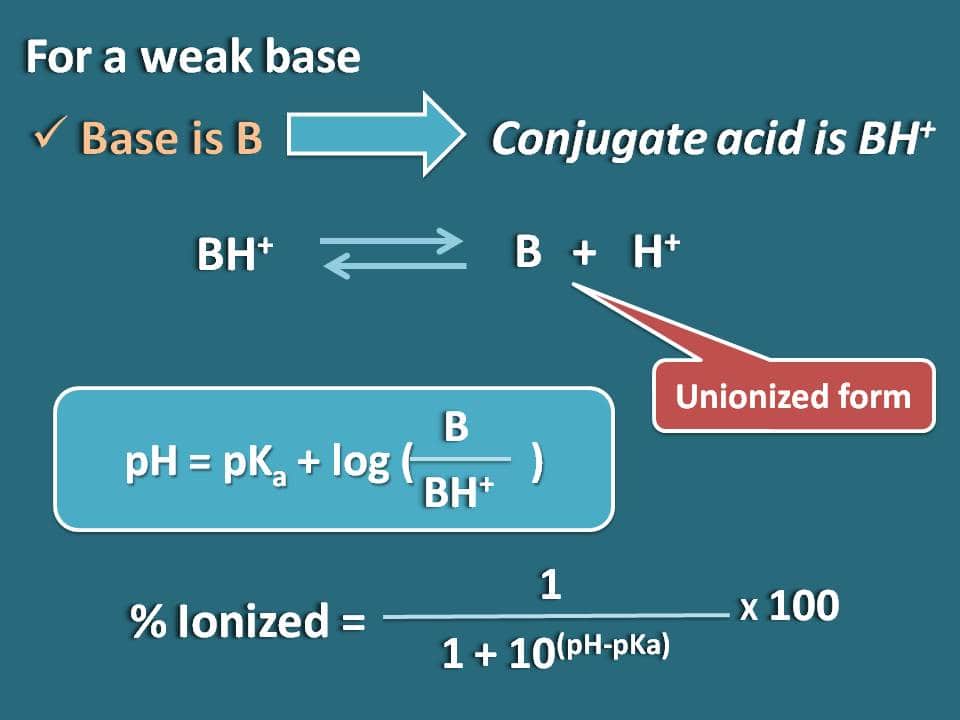
Calculation Of Percentage Ionization Of Weak Electrolytes Solution. boric acid is sufficiently weak that we can use the approximation of eq 1 22 to calculate a: = (5.8e–10 .1) ½ = 7.5e 5; multiply by 100 to get .0075 % diss. for the more dilute acid, a similar calculation yields 7.6e–4, or 0.76%. A table of ionization constants for weak bases appears is here. as for acids, the relative strength of a base is also reflected in its percent ionization, computed as $$\text{% ionization}=\frac{[oh^ ] {eq}}{[b] 0}\times 100\text{%}$$ but will vary depending on the base ionization constant and the initial concentration of the solution. Understanding ph and percent ionization. ph: ph is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. it is calculated using the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. . the ph scale ranges from 0 to 14, with values below 7 indicating acidity, values above 7 indicating basicity, and a ph of 7 being neut. Strong and weak bases and base ionization constant, k b. as with acids, bases can either be strong or weak, depending on their extent of ionization. a strong base is a base, which ionizes completely in an aqueous solution. the most common strong bases are soluble metal hydroxide compounds such as potassium hydroxide.

Comments are closed.