Phase Diagram Chemistry Dictionary Glossary

Phase Diagram Chemistry Dictionary Glossary Phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour liquid, liquid solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution. the figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. the stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the temperature and the. Introduction. a phase diagram is a representation of different phases of a system consists of a substance or many substances at two different thermodynamic conditions such as temperature and pressure. phase diagram can also be drawn between other thermodynamic conditions such as between temperature and volume or temperature and solubility etc.
.PNG)
How To Read Phase Diagrams Chemistry Chemistry glossary. phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour liquid, liquid solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution. the figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. the stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the. Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. a typical phase diagram has pressure on the y axis and temperature on the x axis. as we cross the lines or curves on the phase diagram, a phase change occurs. in addition, two states of the substance coexist. One component phase diagram. figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. the curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. at the point tt vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. in the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one phase exists. A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in figure 3.4.1 3.4. 1. figure 3.4.1 3.4. 1: the physical state of a substance and its phase transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. a graph is shown where the x axis is labeled “temperature” and the y axis is labeled “pressure.”.

Phase Diagram Definition Explanation And Diagram One component phase diagram. figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. the curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. at the point tt vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. in the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one phase exists. A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in figure 3.4.1 3.4. 1. figure 3.4.1 3.4. 1: the physical state of a substance and its phase transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. a graph is shown where the x axis is labeled “temperature” and the y axis is labeled “pressure.”. Phase diagram. a phase diagram represents the various physical states or phases of matter at different pressures and temperatures. in other words, it summarizes the effect of pressure and temperature on the nature of a substance. a phase diagram is divided into three areas representing the substances’ solid, liquid, and gaseous phases [1 4]. A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in figure 11.5.1. figure 11.5.1. the physical state of a substance and its phase transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. to illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in figure 11.5.2.
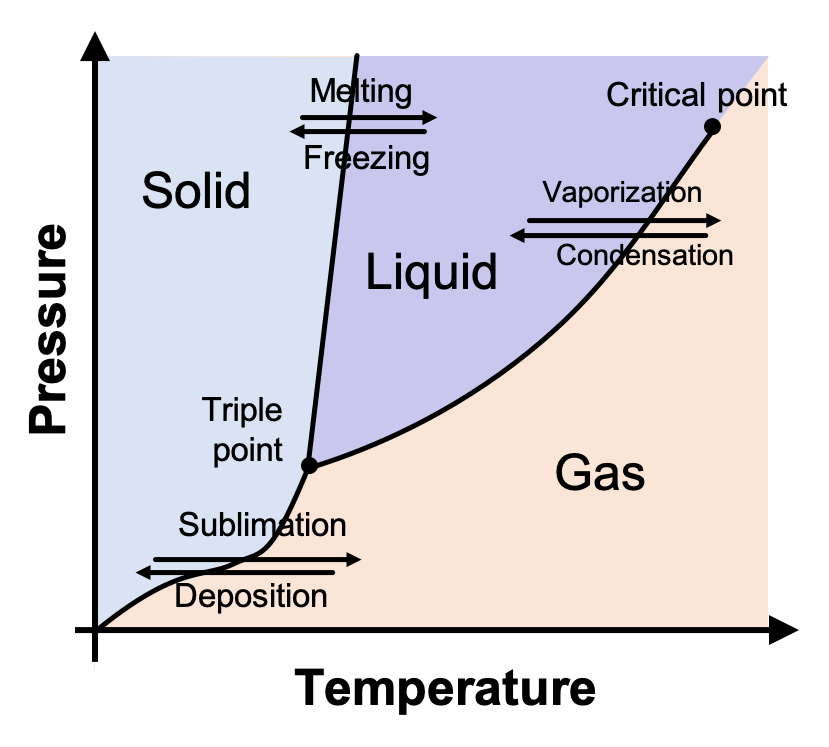
How To Read Phase Diagrams Chemistry Phase diagram. a phase diagram represents the various physical states or phases of matter at different pressures and temperatures. in other words, it summarizes the effect of pressure and temperature on the nature of a substance. a phase diagram is divided into three areas representing the substances’ solid, liquid, and gaseous phases [1 4]. A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in figure 11.5.1. figure 11.5.1. the physical state of a substance and its phase transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. to illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in figure 11.5.2.

Comments are closed.