Ppt Theories Of Consumer Behaviour Andrew Egesa Academia Edu

Ppt Theories Of Consumer Behaviour Andrew Egesa Academia Edu 1. consumption theory: theory of the consumer we assume there are two goods x and y with givens prices px and py. the consumer has income i. the consumer’s budget constraint in a simple world simply describes possible expenditure now, or in some fixed period of time (e.g. this week). Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. download free ppt. download free pdf. theory of consumer behaviour.
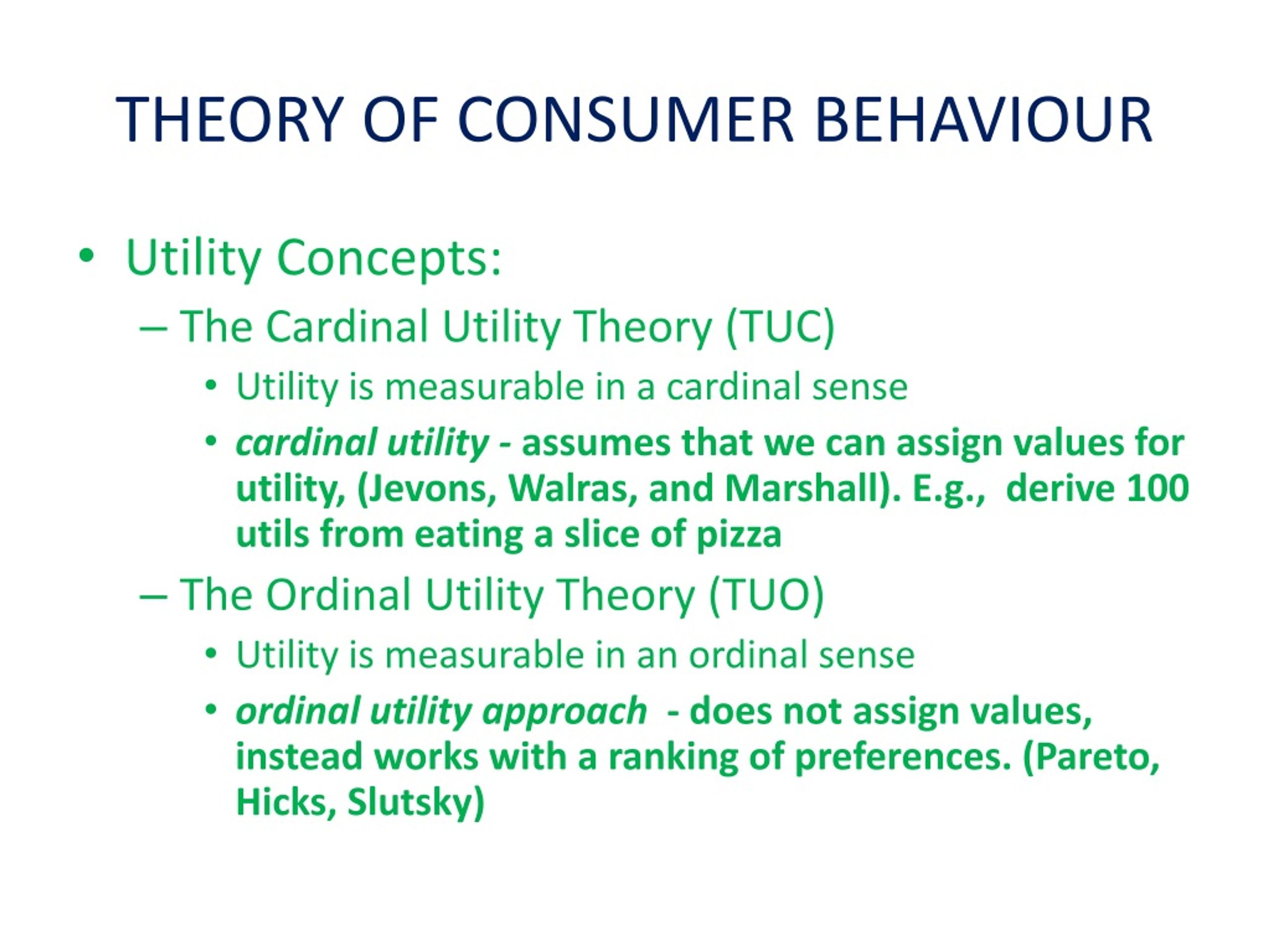
Ppt Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Powerpoint Presentation Free The most widely used prescriptive models are the theory of reasoned action27 and the theory of planned behaviour.28 figure 1.2: cognitive consumer behaviour models (source: adapted from (fawcett and downs 1992, moital 2007)) analytic cognitive models the theory of buyer behaviour howard developed the first consumer decision model in 1963.29. The document discusses theories of consumer behavior and choice. it covers: 1) the cardinal and ordinal approaches to measuring utility, with the cardinal approach assigning numeric values to utility and the ordinal only ranking preferences. 2) concepts of total utility, marginal utility, and the law of diminishing marginal utility. This document discusses consumer behavior theory and its significance for business. it covers key concepts like utility, total utility, marginal utility, and the law of diminishing marginal utility. consumer behavior theory describes how consumers make purchasing decisions by maximizing utility within a budget. understanding factors that influence consumer satisfaction and loyalty can help. Consumer behaviour is the study of how individual customers, groups or organizations select, buy, use, and dispose ideas, goods, and services to satisfy their needs and wants. it refers to the actions of the consumers in the marketplace and the underlying motives for those actions. the study of consumer behaviour assumes that the consumers are.

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free This document discusses consumer behavior theory and its significance for business. it covers key concepts like utility, total utility, marginal utility, and the law of diminishing marginal utility. consumer behavior theory describes how consumers make purchasing decisions by maximizing utility within a budget. understanding factors that influence consumer satisfaction and loyalty can help. Consumer behaviour is the study of how individual customers, groups or organizations select, buy, use, and dispose ideas, goods, and services to satisfy their needs and wants. it refers to the actions of the consumers in the marketplace and the underlying motives for those actions. the study of consumer behaviour assumes that the consumers are. 1 chapter 5 theory of consumer behavior. 2 learning objectives explain the concept of utility and basic assumptions underlying consumer preferences define the concept of indifference curves and explain the properties of indifference curves and maps construct a consumer’s budget line and explain how to rotate or shift the line when prices or. 1991. lea, tarpy & webley. the model considers that: (1) economic behaviour is subjected to a twofold causation, which means certain types of economic behaviour determine the course of affairs in this matter. at the same time, the economy, as a social reality, exerts a major influence in human behaviour.

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free 1 chapter 5 theory of consumer behavior. 2 learning objectives explain the concept of utility and basic assumptions underlying consumer preferences define the concept of indifference curves and explain the properties of indifference curves and maps construct a consumer’s budget line and explain how to rotate or shift the line when prices or. 1991. lea, tarpy & webley. the model considers that: (1) economic behaviour is subjected to a twofold causation, which means certain types of economic behaviour determine the course of affairs in this matter. at the same time, the economy, as a social reality, exerts a major influence in human behaviour.

Comments are closed.