Producer And Consumer Surplus Worksheets

Consumer Producer Surplus Worksheet A Level Economics Teaching This series of slides aids students in defining and calculating consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total economic surplus. . if you have difficulty accessing this content due to a disability, please contact us at 314 444 4662 or [email protected]. find more economics and personal finance resources. If you still buy the good but at the higher price, your consumer surplus falls. the store's producer surplus increases, they are getting a higher price at the same cost. if you draw a rightward shift of the demand curve you will see both market consumer surplus and market producer surplus rise, resulting in an increase in economic surplus.
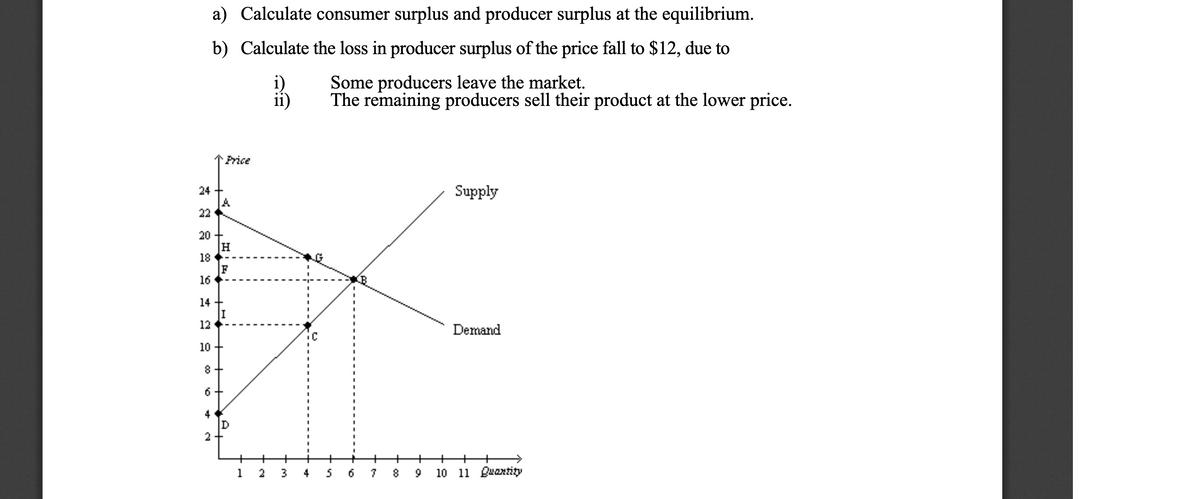
Consumer And Producer Surplus Worksheet Consumerandproducersurplus (1).notebook 11 february 08, 2016 mar 2412:34 pm while each of the people below value the bottle of water differently, they each pay the same price, $2.50. consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay. Consumer and producer surplus interactive practice. new interactive practice tool: how are consumers and producers affected by changes in market prices? this set of interactive questions helps students identify changes in consumer and producer surplus on a supply and demand graph. deadweight loss is also illustrated. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Determine the consumer and producer’s surplus at equilibrium. sketch the graph of the situation and shade and label the p.s. and c.s. on the graph. answers: 1) consumer’s surplus is $24,000 each month 2) demand of 65 dozen golf balls, gives p.s. of $507 3) equilibrium point (25,5) c.s. = $312.50 and p.s. is about $41.67.
Consumer And Producer Surplus Worksheet Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Determine the consumer and producer’s surplus at equilibrium. sketch the graph of the situation and shade and label the p.s. and c.s. on the graph. answers: 1) consumer’s surplus is $24,000 each month 2) demand of 65 dozen golf balls, gives p.s. of $507 3) equilibrium point (25,5) c.s. = $312.50 and p.s. is about $41.67. Consumer surplus in a small setting. consumer surplus and market demand. consumer surplus. willingness to pay. micro chapter 7 willingness to pay (wtp) 4 1 willingness to pay and marginal benefiit. solving for maximum willingness to pay for insurance. microeconomics i maximum willingness to pay for a membership i two part pricing. 7.7. consumer surplus (cs), producer surplus (ps) and the effects of a per unit tax. demand: p = 240 6qd supply: p = 120 4qs. answering 7.71 and 7.72 graph two different diagrams. 7.71 calculate consumer surplus and producer surplus at the market equilibrium. 7.72 now a new per unit tax of 20 is introduced.

Solution Unit 5 Worksheet Consumer And Producer Surplus Studypool Consumer surplus in a small setting. consumer surplus and market demand. consumer surplus. willingness to pay. micro chapter 7 willingness to pay (wtp) 4 1 willingness to pay and marginal benefiit. solving for maximum willingness to pay for insurance. microeconomics i maximum willingness to pay for a membership i two part pricing. 7.7. consumer surplus (cs), producer surplus (ps) and the effects of a per unit tax. demand: p = 240 6qd supply: p = 120 4qs. answering 7.71 and 7.72 graph two different diagrams. 7.71 calculate consumer surplus and producer surplus at the market equilibrium. 7.72 now a new per unit tax of 20 is introduced.
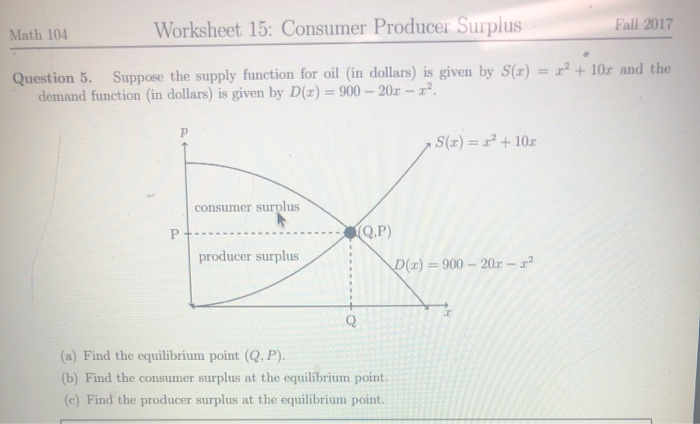
Worksheet 15 Consumer Producer Surplus Math 104 Fall Chegg

Comments are closed.