Producers And Consumers

Understanding The Producer And Consumer Philosophy By Arnav Gupta Learn the difference between producers and consumers in biology, with examples of photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs, and heterotrophs. find out how producers use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to produce food and how consumers depend on producers or other consumers for energy. Learn the difference between producers and consumers in science, and see examples of each in different food chains and webs. producers make their own food, while consumers eat it, and they are all part of a circle of life.
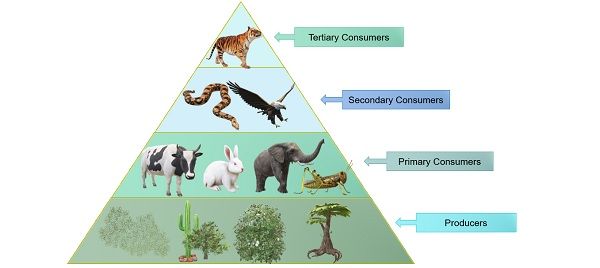
Consumer Examples Biology Learn what producers and consumers are and how they create and buy goods and services in a society's economy. find out how industries, jobs, and wealth are related to producers and consumers. Learn what producers and consumers are and how they interact in the economy. watch a video, make a bookmark, and sing a song to understand the basics of economics. The general concept is the same in biology, but the specifics are somewhat different. in biology, producers and consumers refer to living organisms. while producers manufacture their own food, consumers get their food from producers either directly or indirectly. let’s have a detailed look at each of these groups of organisms. Learn how producers, consumers, and decomposers form the food chain in different ecosystems. find out the trophic levels, examples, and facts about food chains and webs.

Consumer And Producers Examples Kids The general concept is the same in biology, but the specifics are somewhat different. in biology, producers and consumers refer to living organisms. while producers manufacture their own food, consumers get their food from producers either directly or indirectly. let’s have a detailed look at each of these groups of organisms. Learn how producers, consumers, and decomposers form the food chain in different ecosystems. find out the trophic levels, examples, and facts about food chains and webs. The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the next one is the secondary consumer. Consumers the next trophic levels are made up of animals that eat producers. these organisms are called consumers. consumers can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also.

Consumer Biology Britannica The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the next one is the secondary consumer. Consumers the next trophic levels are made up of animals that eat producers. these organisms are called consumers. consumers can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also.

Comments are closed.