Production Function Definition Economics Formula Types

Production Function Definition Economics Formula Types The general production function formula is: q= f (k, l), here q is the output quantity, l is the labor used, and. k is the capital invested for the production of the goods. the f is a mathematical function depending upon the input used for the desired output of the production. for example, it means if the equation is re written as: q= k l for. In economics, a production function gives the technological relation between quantities of physical inputs and quantities of output of goods. the production function is one of the key concepts of mainstream neoclassical theories, used to define marginal product and to distinguish allocative efficiency, a key focus of economics.

Production Function Definition Economics Formula Types The production of all goods and services is carried out using certain inputs. these inputs include the labour, capital and raw materials used in producing the given good or service. the production function expresses the use of these inputs to produce the output in a mathematical and graphical form. it is a key concept in economics which is used. Production function: mathematical equation that tells how much output a firm can produce with given amounts of inputs. short run: period of time during which at least one or more of the firm’s inputs is fixed. variable inputs: factors of production that a firm can easily increase or decrease in a short period of time. In economics, a production function relates physical output of a production process to physical inputs or factors of production. it is a mathematical function that relates the maximum amount of output that can be obtained from a given number of inputs – generally capital and labor. the production function, therefore, describes a boundary or. Definitions. consider the production function given by. y = f (x1, x2, xn) = f (x) (25) where y is output and x is the vector of inputs x1 xn. the rate at which the amount of output, y, increases as all inputs are increased proportionately is called the degree of returns to scale for the production function f(x).

Production Function Meaning And Types Tutor S Tips In economics, a production function relates physical output of a production process to physical inputs or factors of production. it is a mathematical function that relates the maximum amount of output that can be obtained from a given number of inputs – generally capital and labor. the production function, therefore, describes a boundary or. Definitions. consider the production function given by. y = f (x1, x2, xn) = f (x) (25) where y is output and x is the vector of inputs x1 xn. the rate at which the amount of output, y, increases as all inputs are increased proportionately is called the degree of returns to scale for the production function f(x). The production function in economics is a function that relates the output a firm can produce to specific inputs, and therefore measures the efficiency of production. there are different inputs. The production function can thus answer a variety of questions. it can, for example, measure the marginal productivity of a particular factor of production (i.e., the change in output from one additional unit of that factor). it can also be used to determine the cheapest combination of productive factors that can be used to produce a given output.
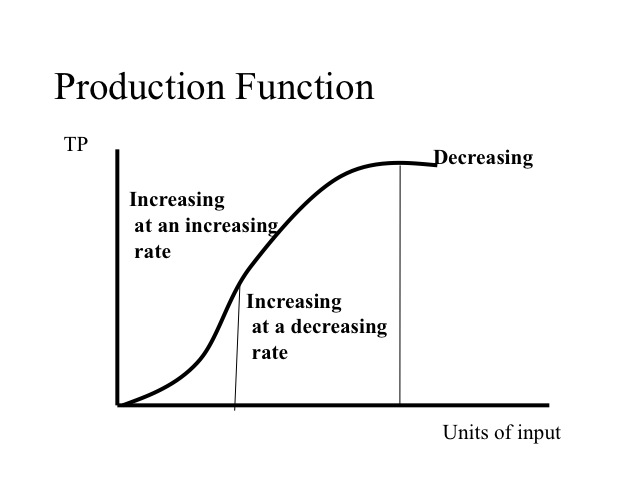
Econ 150 Microeconomics The production function in economics is a function that relates the output a firm can produce to specific inputs, and therefore measures the efficiency of production. there are different inputs. The production function can thus answer a variety of questions. it can, for example, measure the marginal productivity of a particular factor of production (i.e., the change in output from one additional unit of that factor). it can also be used to determine the cheapest combination of productive factors that can be used to produce a given output.
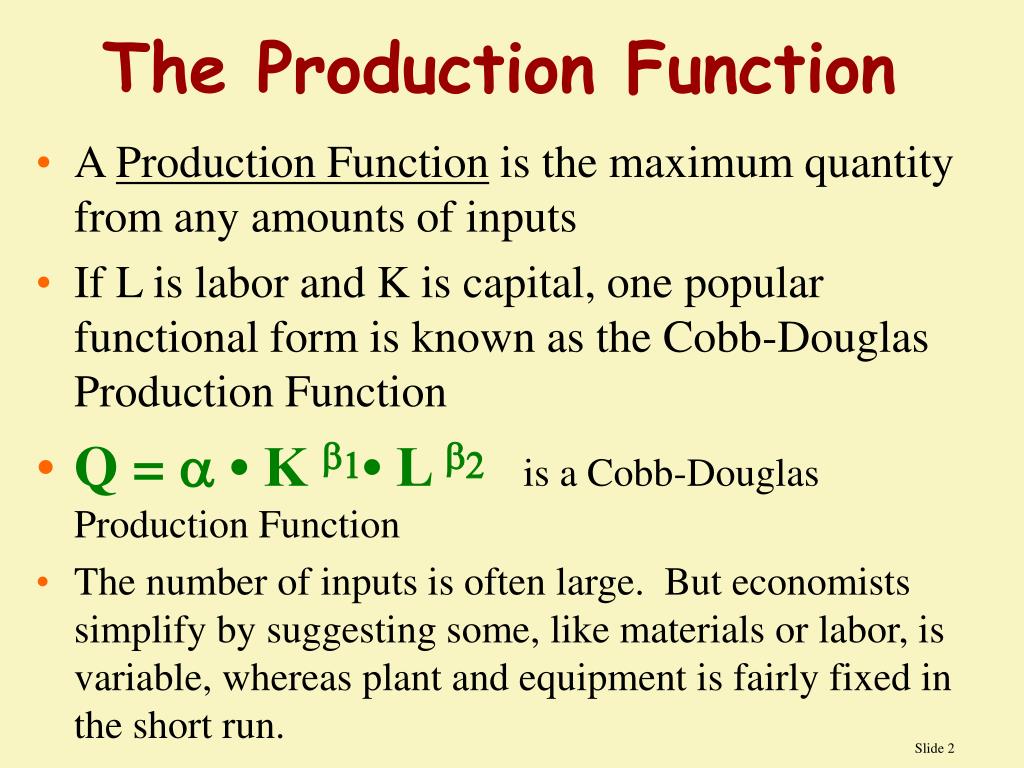
Ppt Production Economics Chapter 6 Powerpoint Presentation Free

Comments are closed.