Profit Maximization And Perfect Competition 2 Summary A Level

Profit Maximization And Perfect Competition 2 Summary A Level Figure 1 shows total revenue, total cost and profit using the data from table 1. the vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit, for example, at q = 60, tr = 240 and tc = 165. the difference is 75, which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. the firm doesn’t make a profit at every level of output. Figure 2. market price. the equilibrium price of raspberries is determined through the interaction of market supply and market demand at $4.00. since a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, it can sell whatever quantity it wishes at the market determined price. marginal cost, the cost per additional unit sold, is calculated by dividing.
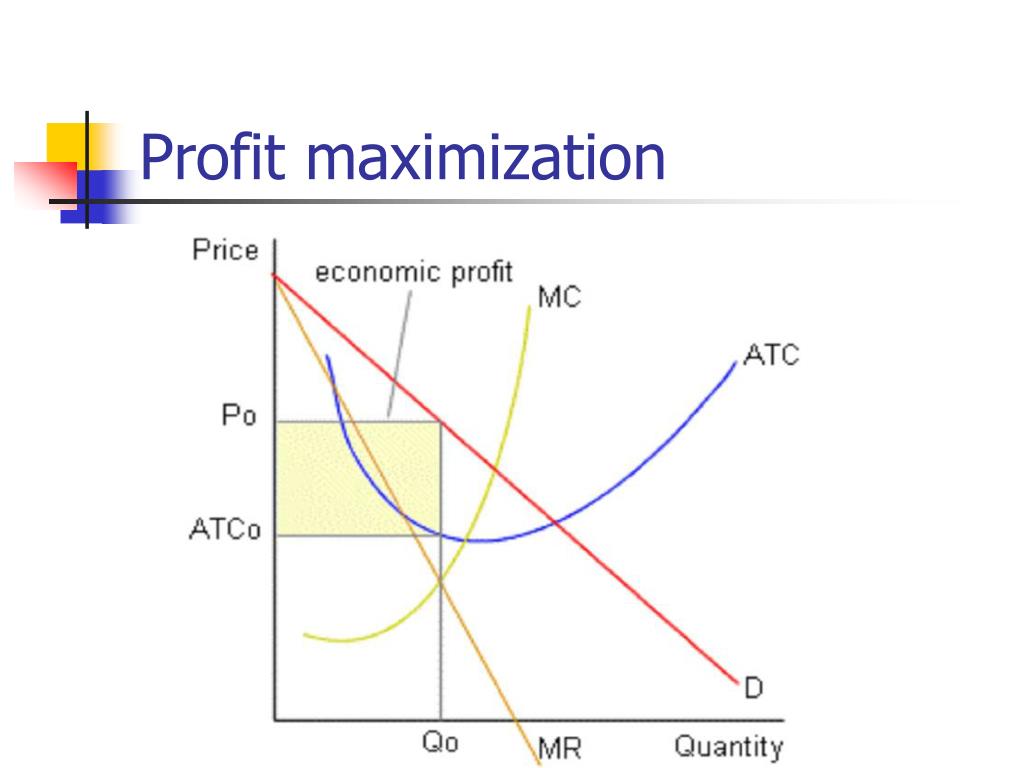
Ppt Chapter 9 вђ Profit Maximization Powerpoint Presentation Free 2. price takers: firm has no influence over the price of the good. takes it as given. i agents are aware of the fact that their decisions will not affect prices. b. selby ec 311 perfect competition 2 25. Profit maximisation in perfect competition. in perfect competition, the same rule for profit maximisation still applies. the firm maximises profit where mr=mc (at q1). for a firm in perfect competition, demand is perfectly elastic, therefore mr=ar=d. this gives a firm normal profit because at q1, ar=ac. profit maximisation in the real world. Profit maximization means increasing profits by the business firms using a proper strategy to equal marginal revenue and marginal cost. this theory forms the basis of many economic theories. it is present in a monopoly and perfect competition market. the profit maximization formula depends on profit = total revenue – total cost. This state either reflects profit maximisation or minimize losses. a producer can attain equilibrium level under the following two situations: perfect competition: in the market conditions of perfect competition, a price is fixed by the industry which has to be accepted by all firms. any quantity of the commodity can be sold at this price.
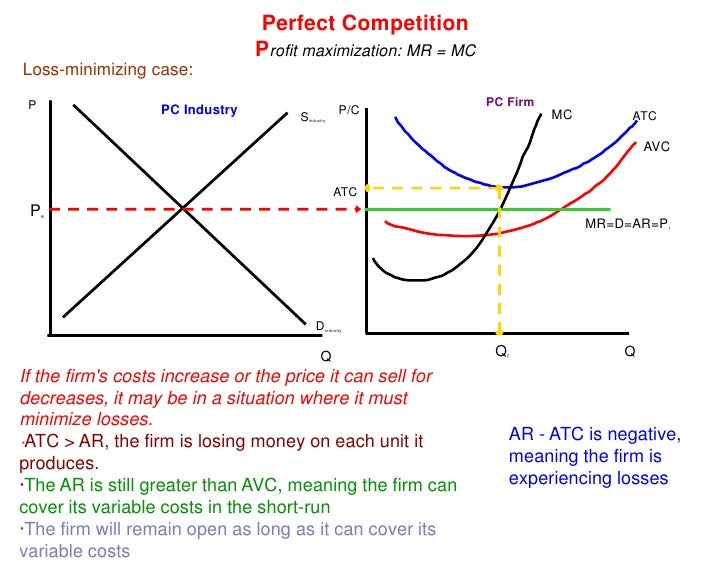
Unit 2 3 2 Perfect Competition Profit maximization means increasing profits by the business firms using a proper strategy to equal marginal revenue and marginal cost. this theory forms the basis of many economic theories. it is present in a monopoly and perfect competition market. the profit maximization formula depends on profit = total revenue – total cost. This state either reflects profit maximisation or minimize losses. a producer can attain equilibrium level under the following two situations: perfect competition: in the market conditions of perfect competition, a price is fixed by the industry which has to be accepted by all firms. any quantity of the commodity can be sold at this price. A price level that generates economic profit at the price level p = $10 unit, the firm has adjusted its plant size so that smc2 = lmc =10. at the profit maximizing level of output, q = 200, the firm earns an economic profit equal to $600 each time period ch11: perfect competition 22. Perfect competition. this is an updated revision presentation on the market structure perfect competition. students should be able to: understand the assumptions of perfect competition and be able to explain the behaviour of firms in this market structure. understand the significance of firms as price takers in perfectly competitive markets.

Comments are closed.