Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes What Are The Key Differences Technology
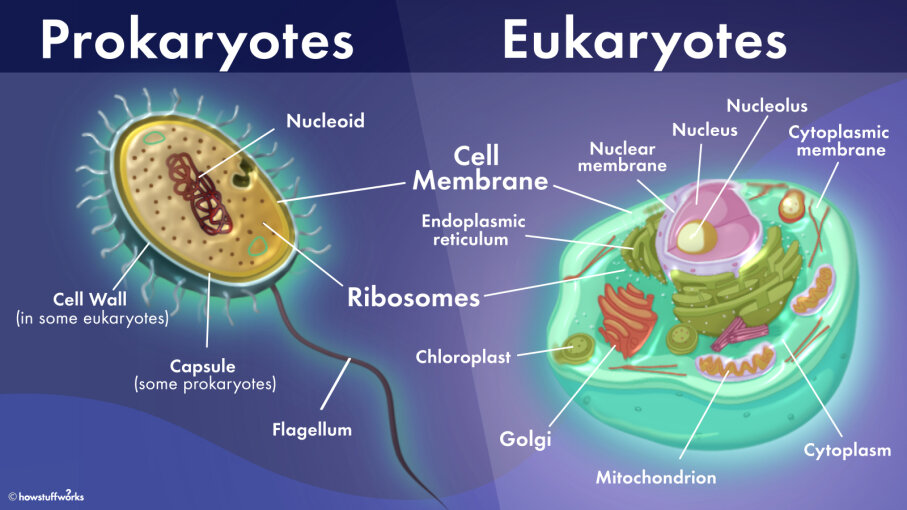
Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Simple Scientists believe that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes around 2.7 billion years ago. the primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. the nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. Prokaryotic cells are unicellular, while eukaryotic cells may be multicellular. a prokaryotic cell has a single haploid (n) chromosome, while eukaryotes have multiple, paired, diploid (2n) chromosomes. both types of cells have ribosomes, but eukaryotic ribosomes are larger. prokaryotic chromosomes are circular or linear.

Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes What Are The Key Differences Technology Every living organism falls into one of two groups: eukaryotes or prokaryotes. cellular structure determines which group an organism belongs to. in this video, we explore what prokaryotes and eukaryotes are and outline the differences between the two. The general characteristics of prokaryotic cells are listed below: in general, prokaryotes range in size from 0.1 to 5.0 µm and are considerably smaller than eukaryotic cells. the shape of prokaryotes ranges from cocci, bacilli, spirilla, and vibrio. however, prokaryotic cells with modifications of these shapes are also found in nature. The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells has to do with the little stuff doing parts of the cell, called organelles. prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's dna. though more primitive than eukaryotes, prokaryotic bacteria are the most diverse and. Another major difference between bacterial dna and eukaryotic dna is that bacterial dna has no introns, whereas eukaryotic dna does. a key genetic difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes typically contain two copies of each gene and are, thus, genetically diploid. eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells (created with biorender.

Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells has to do with the little stuff doing parts of the cell, called organelles. prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's dna. though more primitive than eukaryotes, prokaryotic bacteria are the most diverse and. Another major difference between bacterial dna and eukaryotic dna is that bacterial dna has no introns, whereas eukaryotic dna does. a key genetic difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes typically contain two copies of each gene and are, thus, genetically diploid. eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells (created with biorender. Typically, prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. prokaryotic cells usually have a size of 0.1 to 5 micrometres, whereas eukaryotic cells have a size of 10 to 100 micrometres. eukaryotic cells contain a distinct nucleus, whereas prokaryotic cells do not. eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles such as the golgi apparatus. 02 17 2011. prokaryotic cell. a eukaryotic cell (left) has membrane enclosed dna, which forms a structure called the nucleus (located at center of the eukaryotic cell; note the purple dna enclosed.

Prokaryotic Cells Vs Eukaryotic Cells Typically, prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. prokaryotic cells usually have a size of 0.1 to 5 micrometres, whereas eukaryotic cells have a size of 10 to 100 micrometres. eukaryotic cells contain a distinct nucleus, whereas prokaryotic cells do not. eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles such as the golgi apparatus. 02 17 2011. prokaryotic cell. a eukaryotic cell (left) has membrane enclosed dna, which forms a structure called the nucleus (located at center of the eukaryotic cell; note the purple dna enclosed.

Comments are closed.