Relationships Between A Firms Short Run Costs Of Production

Relationships Between A Firm S Short Run Costs Of Production Youtube The short run production function. a firm uses factors of production to produce a product. the relationship between factors of production and the output of a firm is called a production function our first task is to explore the nature of the production function. consider a hypothetical firm, acme clothing, a shop that produces jackets. This lesson focuses on just the per unit cost curves, their shapes, and the relationships between them. as you will see, the marginal cost curve, itself shap.
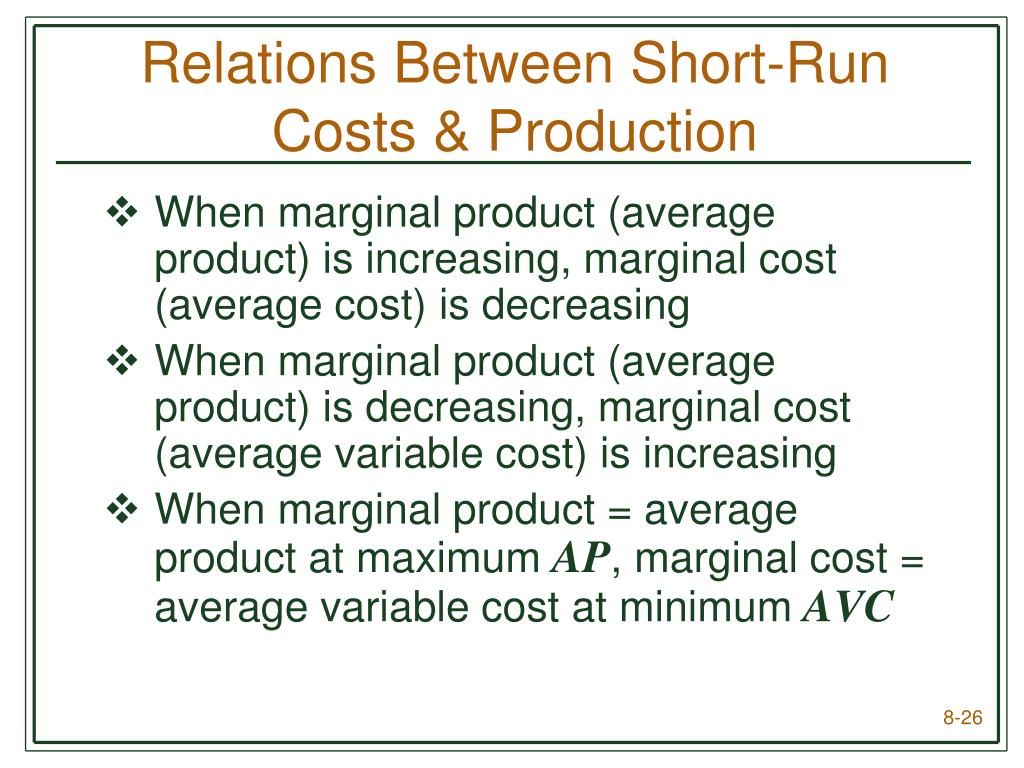
Ppt Chapter 8 Production And Cost In The Short Run Powerpoint Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs analyze short run costs in terms of fixed cost and variable cost we’ve explained that a firm’s total cost of production depends on the quantities of inputs the firm uses to produce its output and the cost of those inputs to the firm. At zero production, the fixed costs of $160 are still present. as production increases, we add variable costs to fixed costs, and the total cost is the sum of the two. graphically shows the relationship between the quantity of output produced and the cost of producing that output. we always show the fixed costs as the vertical intercept of the. Analyze short run costs in terms of fixed cost and variable cost. we’ve explained that a firm’s total cost of production depends on the quantities of inputs the firm uses to produce its output and the cost of those inputs to the firm. the firm’s production function tells us how much output the firm will produce with given amounts of inputs. Introduction to production, costs, and industry structure; 7.1 explicit and implicit costs, and accounting and economic profit; 7.2 production in the short run; 7.3 costs in the short run; 7.4 production in the long run; 7.5 costs in the long run; key terms; key concepts and summary; self check questions; review questions; critical thinking.

Chapter 8 Production Cost In The Short Run Ppt Download Analyze short run costs in terms of fixed cost and variable cost. we’ve explained that a firm’s total cost of production depends on the quantities of inputs the firm uses to produce its output and the cost of those inputs to the firm. the firm’s production function tells us how much output the firm will produce with given amounts of inputs. Introduction to production, costs, and industry structure; 7.1 explicit and implicit costs, and accounting and economic profit; 7.2 production in the short run; 7.3 costs in the short run; 7.4 production in the long run; 7.5 costs in the long run; key terms; key concepts and summary; self check questions; review questions; critical thinking. Since by definition capital is fixed in the short run, our production function becomes. q = f[l,k−]orq = f[l] q = f [l, k −] or q = f [l] this equation simply indicates that since capital is fixed, the amount of output (e.g., trees cut down per day) depends only on the amount of labor employed (e.g., number of lumberjacks working). Chapter 7.3 – costs in the short run. by the end of this section, you will be able to: understand the relationship between production and costs. understand that every factor of production has a corresponding factor price. analyze short run costs in terms of total cost, fixed cost, variable cost, marginal cost, and average cost.

Ppt Chapter 20 The Costs Of Production Powerpoint Presentation Free Since by definition capital is fixed in the short run, our production function becomes. q = f[l,k−]orq = f[l] q = f [l, k −] or q = f [l] this equation simply indicates that since capital is fixed, the amount of output (e.g., trees cut down per day) depends only on the amount of labor employed (e.g., number of lumberjacks working). Chapter 7.3 – costs in the short run. by the end of this section, you will be able to: understand the relationship between production and costs. understand that every factor of production has a corresponding factor price. analyze short run costs in terms of total cost, fixed cost, variable cost, marginal cost, and average cost.

Comments are closed.