Relay Logic Part 1 The Basics

Relay Logic Part 1 The Basics Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Relay logic circuit – examples and working. the working of a relay logic circuit can be explained through the given figures this figure shows a basic relay logic circuit. in this circuit, rung 1 contains one push button (initially off) and one control relay. rung 2 contains one push button (initially on) and one pilot lamp.
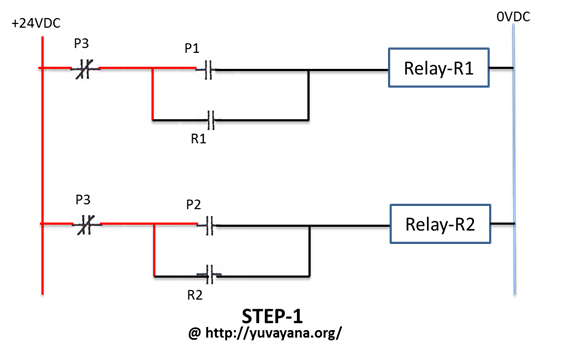
Basic Relay Logic Relay logic basically consists of relays wired up in a particular fashion to perform the desired switching operations. the circuit incorporates relays along with other components such as switches, motors, timers, actuators, contactors etc. the relay logic control works efficiently to perform basic on off operations by opening or closing the relay contacts but it involves a humongous wiring. Sometimes you will find relay contacts labeled identically to the coil (e.g. coil labeled cr5 and all contacts for that relay also labeled cr5) while other times you will find suffix numbers used to distinguish individual contacts within each relay from each other (e.g. coil labeled cr5 and its three contacts labeled cr5 1, cr5 2, and cr5 3). Relays are magnetic electromechanical devices with two primary purposes: to isolate different circuit voltages, and to form larger complex networks of logic to run machines without digital controllers. an electromechanical relay is an electrical switch actuated by an electromagnet coil. as switching devices, they exhibit simple “on” and. A relay logic circuit is an electrical network consisting of lines, or rungs, in which each line or rung must have continuity to enable the output device. a typical circuit consists of a number of rungs, with each rung controlling an output. this output is controlled by a combination of input or output conditions, such as input switches and.

Comments are closed.