Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health The Bmj

Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health The Bmj Ana m valdes and colleagues discuss strategies for modulating the gut microbiota through diet and probiotics microbiome refers to the collective genomes of the micro organisms in a particular environment, and microbiota is the community of micro organisms themselves (box 1). approximately 100 trillion micro organisms (most of them bacteria, but also viruses, fungi, and protozoa) exist in the. Affiliations. 1 school of medicine, university of nottingham, city hospital, nottingham ng5 1pb, uk. 2 nihr nottingham biomedical research centre, nottingham, uk. 3 department of agricultural, food, and nutritional science and department of biological sciences, university of alberta, edmonton, canada. 4 department of computer science and.

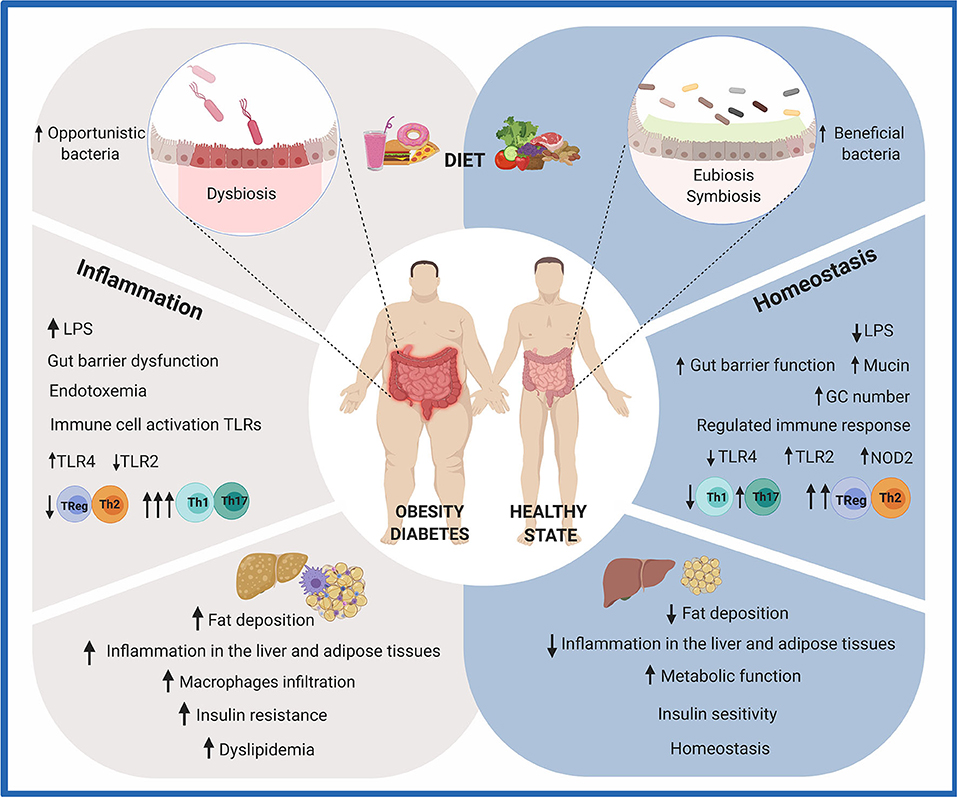
Pdf Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health Gut microbiota influences many areas of human health from innate immu nity to appetite and energy metabo lism. targeting the gut microbiome, with probiotics or dietary fibre, benefits human health and could potentially reduce obesity. drugs, food ingredients, antibiotics, and pesticides could all have adverse efects on the gut microbiota. The gut microbiota seems to play a role in the development and progression of obesity. most studies of overweight and obese people show a dysbiosis characterised by a lower diversity. germ free mice that receive faecal microbes from obese humans gain more weight than mice that receive microbes from healthy weight humans. Abstract. the microbial communities that colonize different regions of the human gut influence many aspects of health. in the healthy state, they contribute nutrients and energy to the host via the fermentation of nondigestible dietary components in the large intestine, and a balance is maintained with the host's metabolism and immune system. Accumulating evidence indicates that the gut microbiome is an important regulator of body weight, glucose and lipid metabolism, and inflammatory processes, and may thereby play a key role in the aetiology of obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. interindividual responsiveness to specific dietary interventions may be partially determined by differences in baseline gut microbiota.
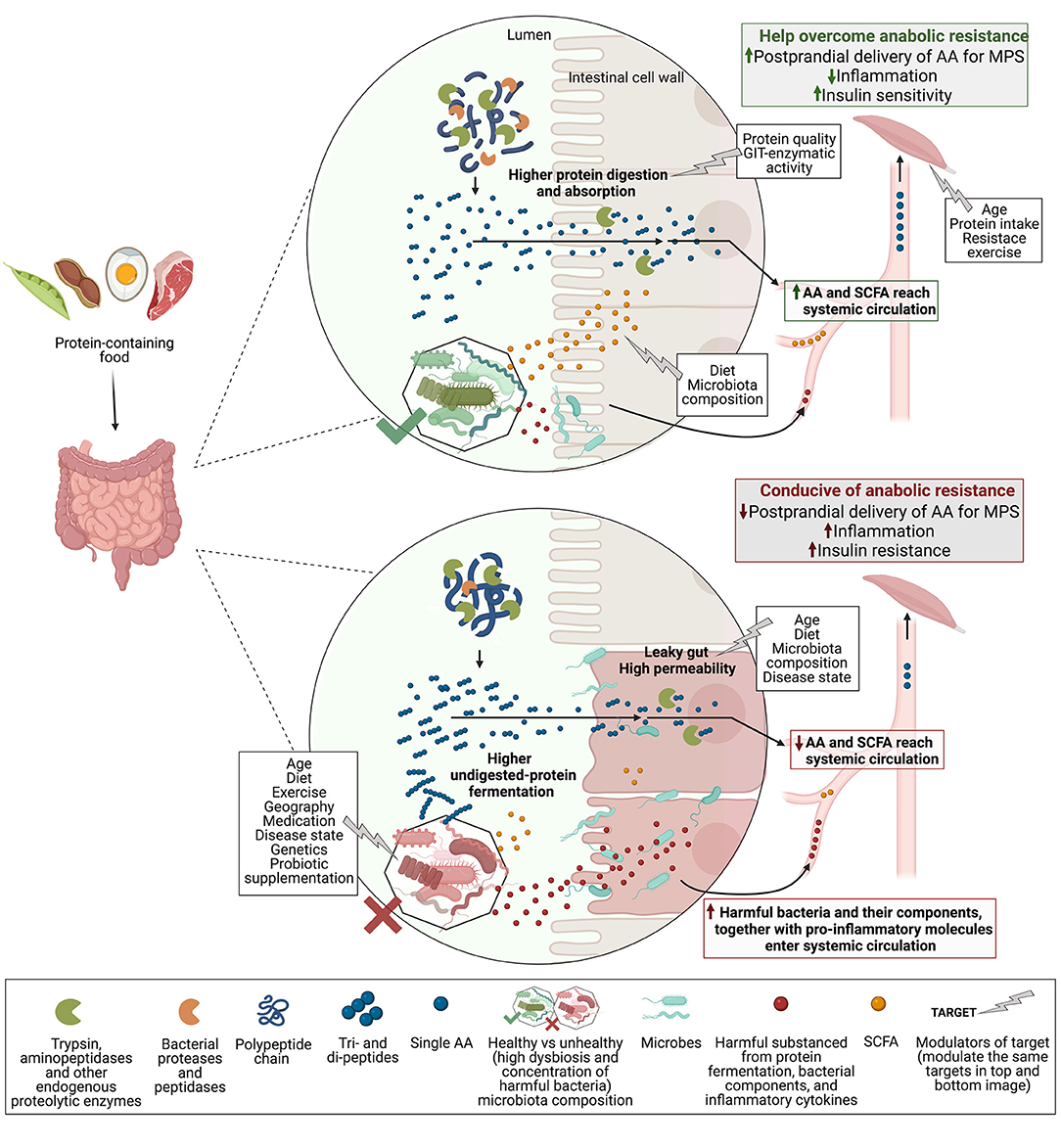
Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health Th Vrogue Co Abstract. the microbial communities that colonize different regions of the human gut influence many aspects of health. in the healthy state, they contribute nutrients and energy to the host via the fermentation of nondigestible dietary components in the large intestine, and a balance is maintained with the host's metabolism and immune system. Accumulating evidence indicates that the gut microbiome is an important regulator of body weight, glucose and lipid metabolism, and inflammatory processes, and may thereby play a key role in the aetiology of obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. interindividual responsiveness to specific dietary interventions may be partially determined by differences in baseline gut microbiota. The gut microbiota is now considered as one of the key elements contributing to the regulation of host health. virtually all our body sites are colonised by microbes suggesting different types of crosstalk with our organs. because of the development of molecular tools and techniques (ie, metagenomic, metabolomic, lipidomic, metatranscriptomic), the complex interactions occurring between the. Current understanding of the gut microbiota. in the last decade, several large scale projects, for example, the human microbiome project, have investigated the microbiota of a variety of bodily niches, including the skin as well as the oral, vaginal and nasal cavities.2 while some of these are relatively easy to access, the gi tract remains a challenging environment to sample, and to describe.

What Is The Microbiome Adc Education Practice Edition The gut microbiota is now considered as one of the key elements contributing to the regulation of host health. virtually all our body sites are colonised by microbes suggesting different types of crosstalk with our organs. because of the development of molecular tools and techniques (ie, metagenomic, metabolomic, lipidomic, metatranscriptomic), the complex interactions occurring between the. Current understanding of the gut microbiota. in the last decade, several large scale projects, for example, the human microbiome project, have investigated the microbiota of a variety of bodily niches, including the skin as well as the oral, vaginal and nasal cavities.2 while some of these are relatively easy to access, the gi tract remains a challenging environment to sample, and to describe.
Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Health Th Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.