Scalar Quantity And Vector Quantity Physics Infinity Learn
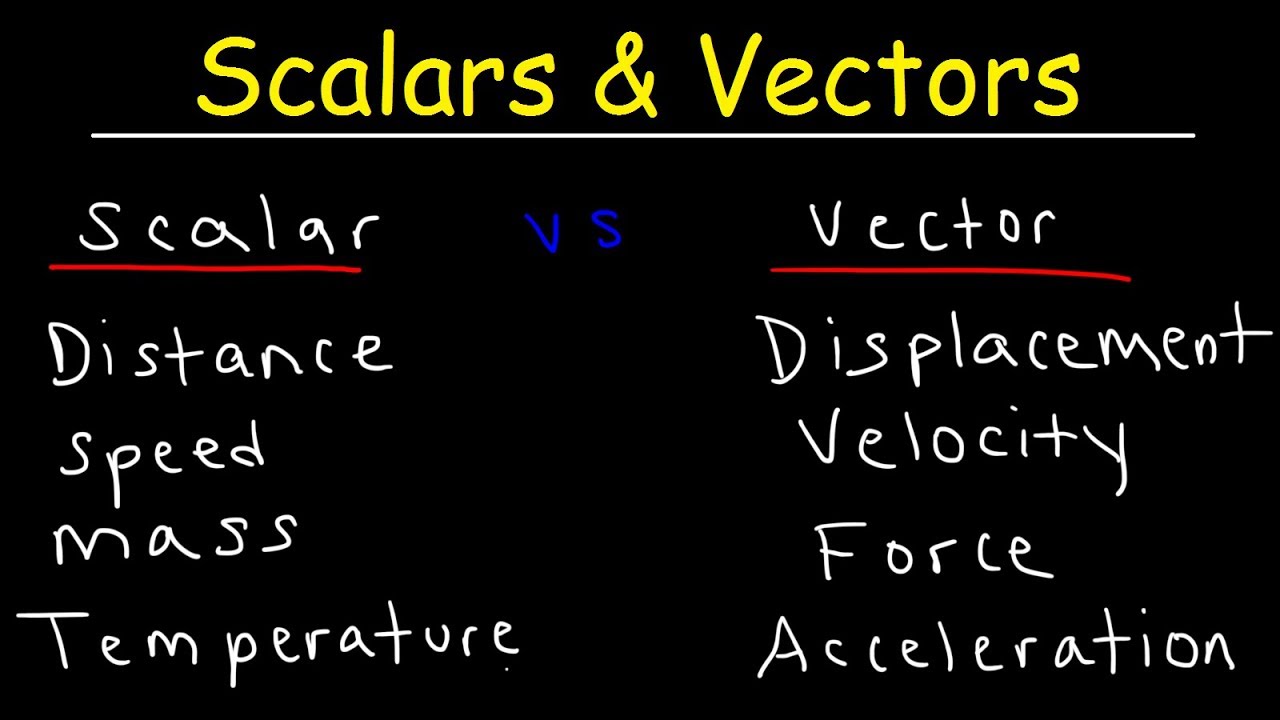
Scalar And Vector Definition Types Physical Quantities Physics The difference between scalar quantity and vector quantity is fundamental in understanding and describing the physical world. scalars give us the magnitude, and vectors provide magnitude with direction. this difference is crucial in physics, mathematics, and engineering, allowing for precise and accurate descriptions of natural phenomena. Speed, mass and temperature are examples of scalar quantity. what is vector quantity? a quantity that provides information on both magnitude and direction is a vector quantity. it is also called a two dimensional quantity. velocity, displacement, weight, acceleration, force are examples of vector quantity.

Scalar Quantity And Vector Quantity Physics Infinity Learn Youtube Vector quantity definition. a vector quantity is a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. examples of vector quantities are displacement, velocity, and force. scalar quantity examples: the length of a line the weight of a rock the temperature of a room. vector quantity examples: speed, voltage, current, resistance, capacitance. 🎯neet 2024 paper solutions with neet answer key: watch?v=fwxyzubp4m0&list=plmdfyqyshrjc4oswbsticoypgl0tjtgon&index=1📅🆓neet rank &. In mathematics and physics, a scalar is a quantity that only has magnitude (size), while a vector has both magnitude and direction. examples of scalar quantities include pure numbers, mass, speed, temperature, energy, volume, and time. examples of vector quantities include velocity, acceleration, momentum, displacement, and forces, such as. Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction. the remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities (distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration).

Vector Quantities Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Games In mathematics and physics, a scalar is a quantity that only has magnitude (size), while a vector has both magnitude and direction. examples of scalar quantities include pure numbers, mass, speed, temperature, energy, volume, and time. examples of vector quantities include velocity, acceleration, momentum, displacement, and forces, such as. Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone. vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction. the remainder of this lesson will focus on several examples of vector and scalar quantities (distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration). Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the difference between vector and scalar quantities. identify the magnitude and direction of a vector. explain the effect of multiplying a vector quantity by a scalar. describe how one dimensional vector quantities are added or subtracted. Equation 2.2.2 is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). if the scalar α is negative in the vector equation equation 2.2.1, then the magnitude | →b | of the new vector is still given by equation 2.2.2, but the direction of the new vector →b is antiparallel to the direction of →a .
Scalars And Vectors Physics Video Scalar Vs Vector Quantities Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: describe the difference between vector and scalar quantities. identify the magnitude and direction of a vector. explain the effect of multiplying a vector quantity by a scalar. describe how one dimensional vector quantities are added or subtracted. Equation 2.2.2 is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). if the scalar α is negative in the vector equation equation 2.2.1, then the magnitude | →b | of the new vector is still given by equation 2.2.2, but the direction of the new vector →b is antiparallel to the direction of →a .

Comments are closed.