Sedimentary Environments
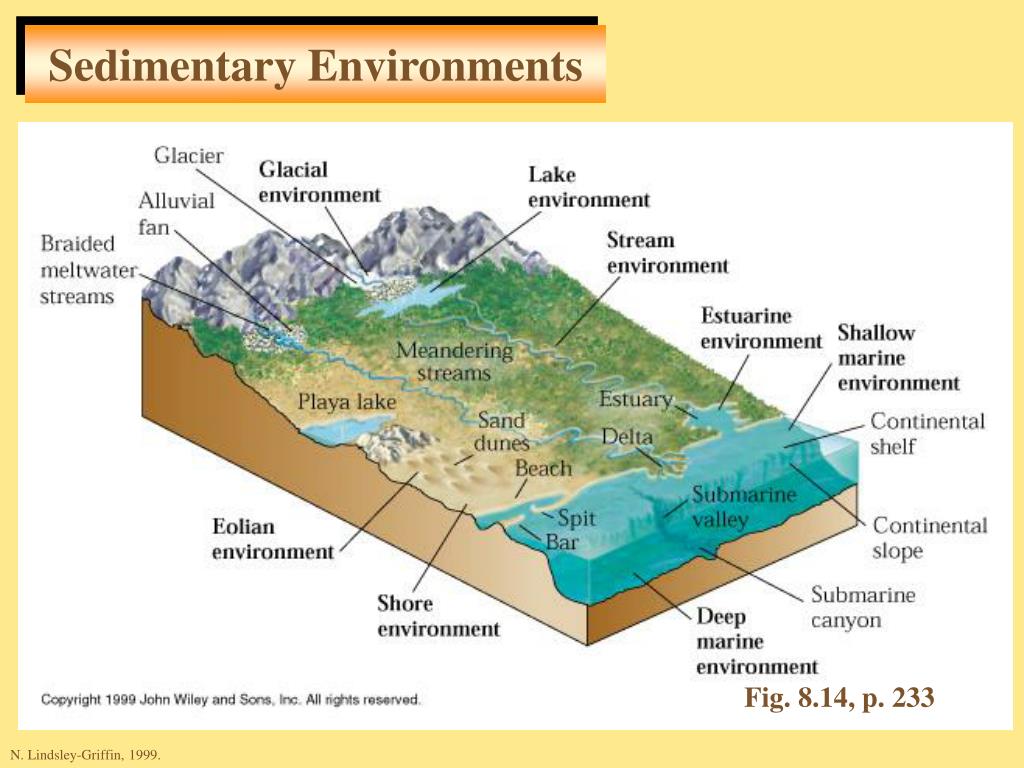
Ppt Sediments And Sedimentary Rocks Powerpoint Presentation Free The sedimentary environment is the specific depositional setting of a particular sedimentary rock and is unique in terms of physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. the physical features of a sedimentary environment include water depth and the velocity and persistence of currents. chemical characteristics of an environment include. Sediments accumulate in a wide variety of environments, both on the continents and in the oceans. some of the more important of these environments are illustrated in figure 6.3.1 6.3. 1. figure 6.3.1 6.3. 1 some of the important depositional environments for sediments and sedimentary rocks. table 6.4 provides a summary of the processes and.
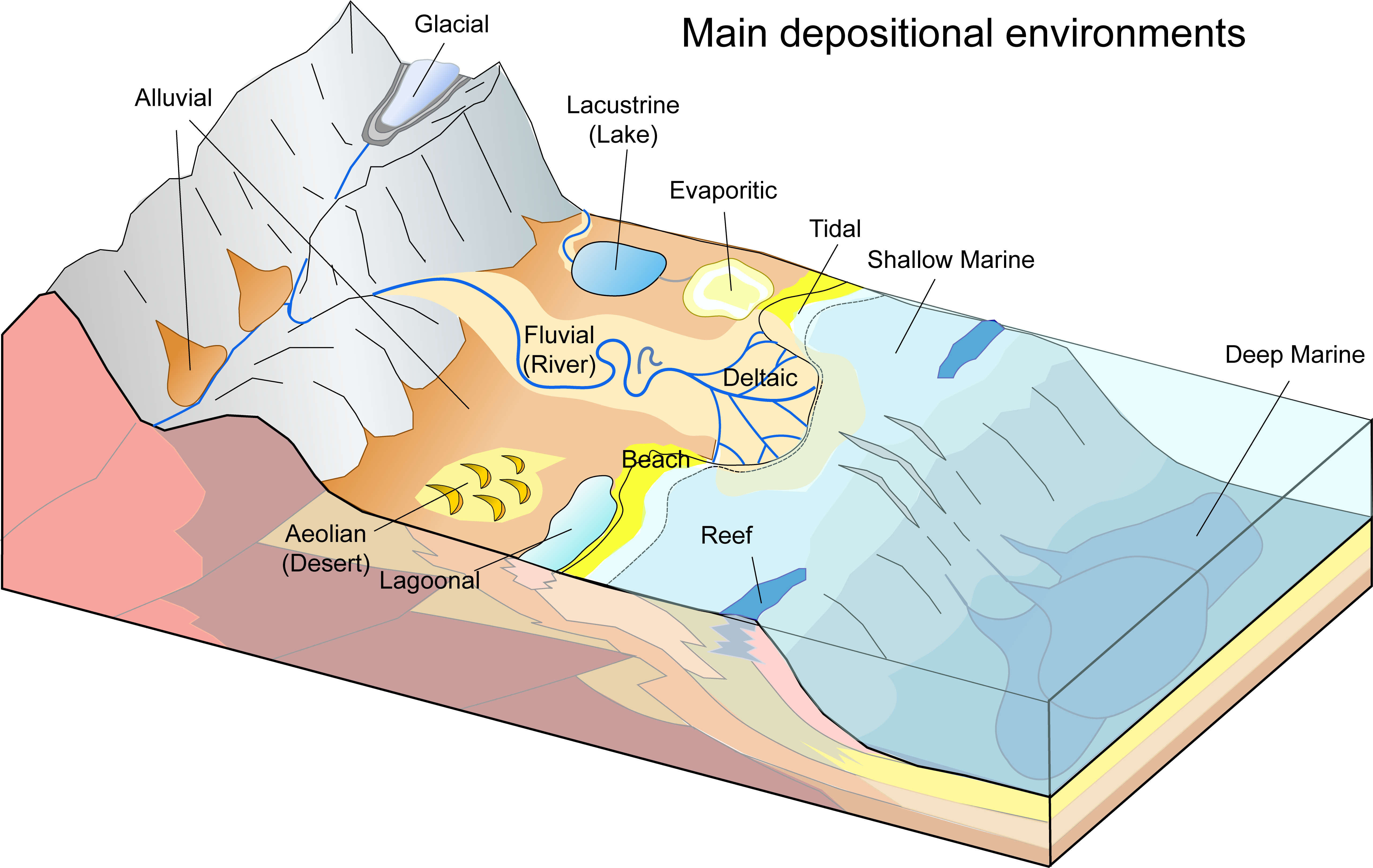
Chapter 2 Earth Materials The Story Of Earth An Observational Guide With failing sea level, the opposite may occur. so, sedimentary facies vary both laterally and vertically (geographically and temporally). this page titled 7.6: sedimentary environments and facies is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by via that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. Depositional environment. in geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. Sand. cementation. sedimentary rock, rock formed at or near earth’s surface by the accumulation and lithification of sediment (detrital rock) or by the precipitation from solution at normal surface temperatures (chemical rock). sedimentary rocks are the most common rocks exposed on earth’s surface but are only a minor constituent of the. The lithologic characteristics, sedimentary structures, processes, and knowledge of fossils gained in previous chapters can be used as a powerful tool for interpreting depositional environments. this chapter provides an overview of the major clastic and carbonate environments and the characteristics and processes that can be expected in each.

Amazing Geology Depositional Environments Where Sediments Accumul Sand. cementation. sedimentary rock, rock formed at or near earth’s surface by the accumulation and lithification of sediment (detrital rock) or by the precipitation from solution at normal surface temperatures (chemical rock). sedimentary rocks are the most common rocks exposed on earth’s surface but are only a minor constituent of the. The lithologic characteristics, sedimentary structures, processes, and knowledge of fossils gained in previous chapters can be used as a powerful tool for interpreting depositional environments. this chapter provides an overview of the major clastic and carbonate environments and the characteristics and processes that can be expected in each. Organic sedimentary rocks, also called biologic sedimentary rocks, form from the accumulation of plant or animal debris. coal : forms from compressed plant matter, typically in swamp environments. oil shale : contains significant amounts of organic material (kerogen) that can produce oil upon heating. Learn about sedimentary rocks, one of the three main types of rocks, formed from erosion, weathering, dissolution, precipitation, and lithification. explore examples of detrital and chemical sedimentary rocks, and how they relate to sedimentary environments.

9 4 Depositional Environments And Sedimentary Basins вђ Physical Geology Organic sedimentary rocks, also called biologic sedimentary rocks, form from the accumulation of plant or animal debris. coal : forms from compressed plant matter, typically in swamp environments. oil shale : contains significant amounts of organic material (kerogen) that can produce oil upon heating. Learn about sedimentary rocks, one of the three main types of rocks, formed from erosion, weathering, dissolution, precipitation, and lithification. explore examples of detrital and chemical sedimentary rocks, and how they relate to sedimentary environments.
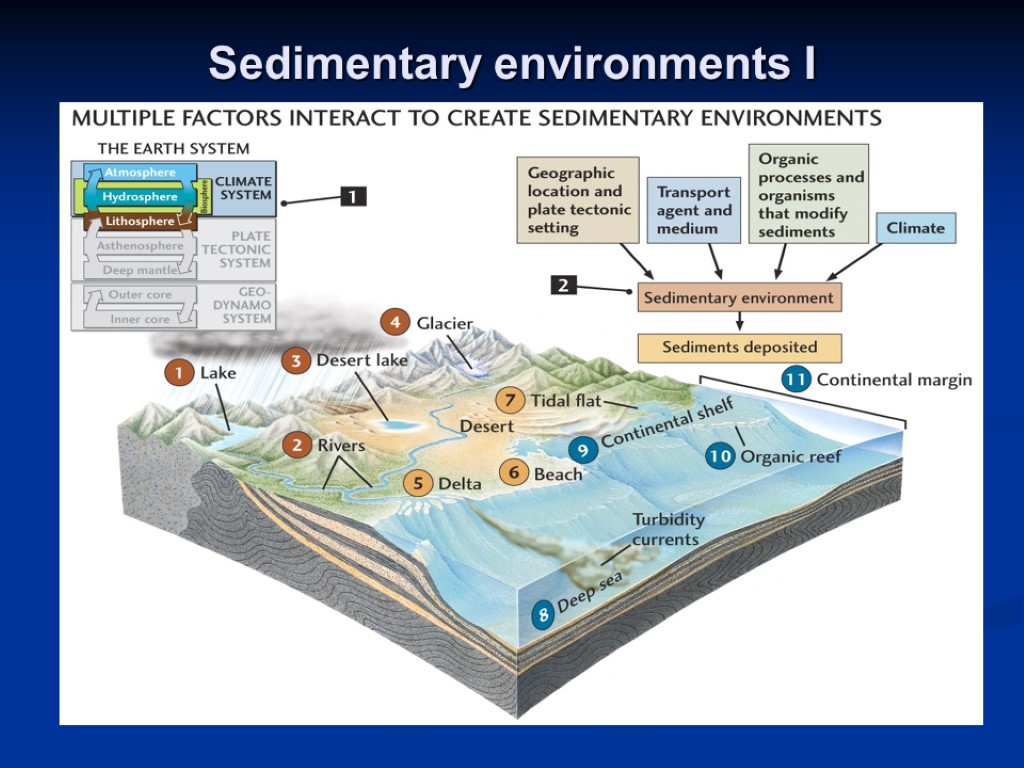
Why Is Sedimentary Rock Important

Comments are closed.