Segment 2 Risk Assessment In Prostate Cancer
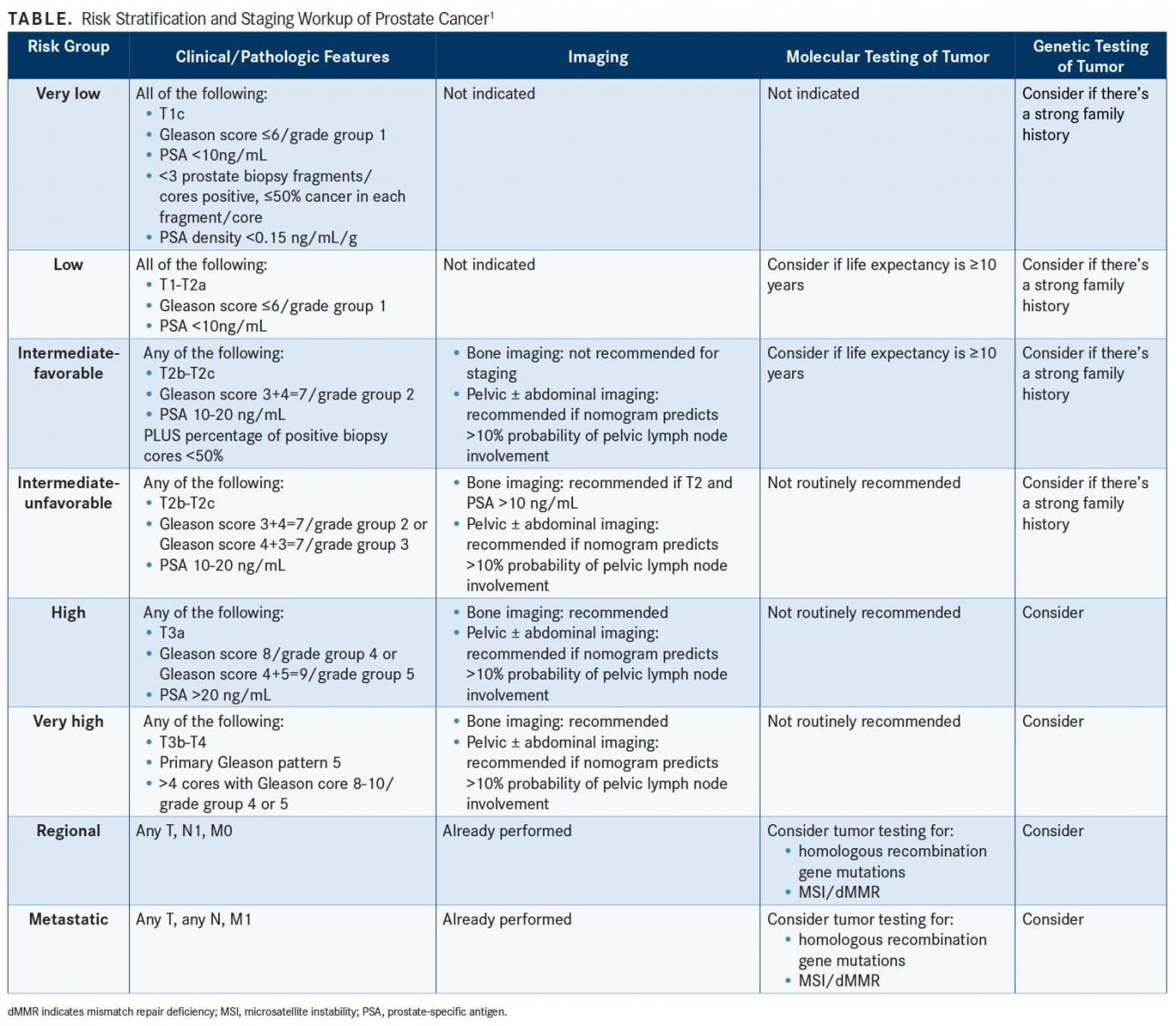
Nccn Prostate Cancer Guidelines Emphasize Risk Stratification Capra score is equal to the sum of the individual variables: . 1 1 1 0 0 = 3 . patient one has a capra score equal to 3. example patient two: a 48 year old man with a psa of 15.2, a gleason score of 4 3, and stage t1c prostate cancer involving 5 of 10 cores (50%) would have a score of 6. The original prostate cancer prevention trial (pcpt) prostate cancer risk calculator (pcptrc) posted in 2006 was developed based upon 5519 men in the placebo group of the prostate cancer prevention trial. all of these 5519 men initially had a prostate specific antigen (psa) value less than or equal to 3.0 ng ml and were followed for seven years.

Ppt Management Of Prostate Cancer Post Prostatectomy Powerpoint It is an accurate tool in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. in pi rads v2.1 clinically significant cancer is defined on pathology as: gleason score ≥ 7 including 3 4 with prominent but not predominant gleason 4 component and or. tumor volume > 0.5cc and or. extraprostatic extension (epe). The cancer of the prostate risk assessment (capra) score is graded on a scale of 1 to 10 on the basis of points assigned to the age at diagnosis, psa level at diagnosis, gleason score, clinical. In closing, as templated structured reporting becomes more common, it should also be applied to multiparametric mri staging of prostate cancer. mehralivand et al showed that epe results could be improved by incorporating clinical risk features such as tumor grade, serum prostate specific antigen level, and age into the risk assessment. Clinicians should provide an individualized risk estimate of post treatment prostate cancer recurrence to patients with prostate cancer. (clinical principle) the selection of a management strategy for clinically localized prostate cancer is preference sensitive and very often based on patients’ interpretation of the balance between treatment.

Segment 2 Risk Assessment In Prostate Cancer Youtube In closing, as templated structured reporting becomes more common, it should also be applied to multiparametric mri staging of prostate cancer. mehralivand et al showed that epe results could be improved by incorporating clinical risk features such as tumor grade, serum prostate specific antigen level, and age into the risk assessment. Clinicians should provide an individualized risk estimate of post treatment prostate cancer recurrence to patients with prostate cancer. (clinical principle) the selection of a management strategy for clinically localized prostate cancer is preference sensitive and very often based on patients’ interpretation of the balance between treatment. Studies were included on meeting the criteria of 1) population—patients with suspected prostate cancer or on active surveillance for prostate cancer; 2) index tests—pi rads v2 categorization using prebiopsy bpmri or mpmri of the prostate; 3) comparator—ie no requirements; 4) outcome—detection rates of cspca or all pca for each pi rads. The nccn guidelines for prostate cancer address staging and risk assessment after a prostate cancer diagnosis and include management options for localized, regional, and metastatic disease. recommendations for disease monitoring and treatment of recurrent disease are also included. the nccn prostate cancer panel meets annually to reevaluate and.

Emerging Concepts In The Treatment Of Prostate Cancer Studies were included on meeting the criteria of 1) population—patients with suspected prostate cancer or on active surveillance for prostate cancer; 2) index tests—pi rads v2 categorization using prebiopsy bpmri or mpmri of the prostate; 3) comparator—ie no requirements; 4) outcome—detection rates of cspca or all pca for each pi rads. The nccn guidelines for prostate cancer address staging and risk assessment after a prostate cancer diagnosis and include management options for localized, regional, and metastatic disease. recommendations for disease monitoring and treatment of recurrent disease are also included. the nccn prostate cancer panel meets annually to reevaluate and.

Comments are closed.