Sfu Political Science Presents Democratic Backsliding Causes For

Sfu Political Science Presents Democratic Backsliding Causes For Defining backsliding. democratic backsliding and democratic erosion—which we use interchangeably—can be defined as “the state led debilitation or elimination of any of the political institutions that sustain an existing democracy” (bermeo reference bermeo 2016, 5). other scholars argue that backsliding can occur in any country. By studying cases of democratic backsliding, scholars reveal the process by which backsliding unfolds when and where it does. footnote 1 approaching the study of democratic backsliding from a different angle, we want to know how much backsliding, on average, can be attributed to certain causes. by analysing the full range of potential cases, we.
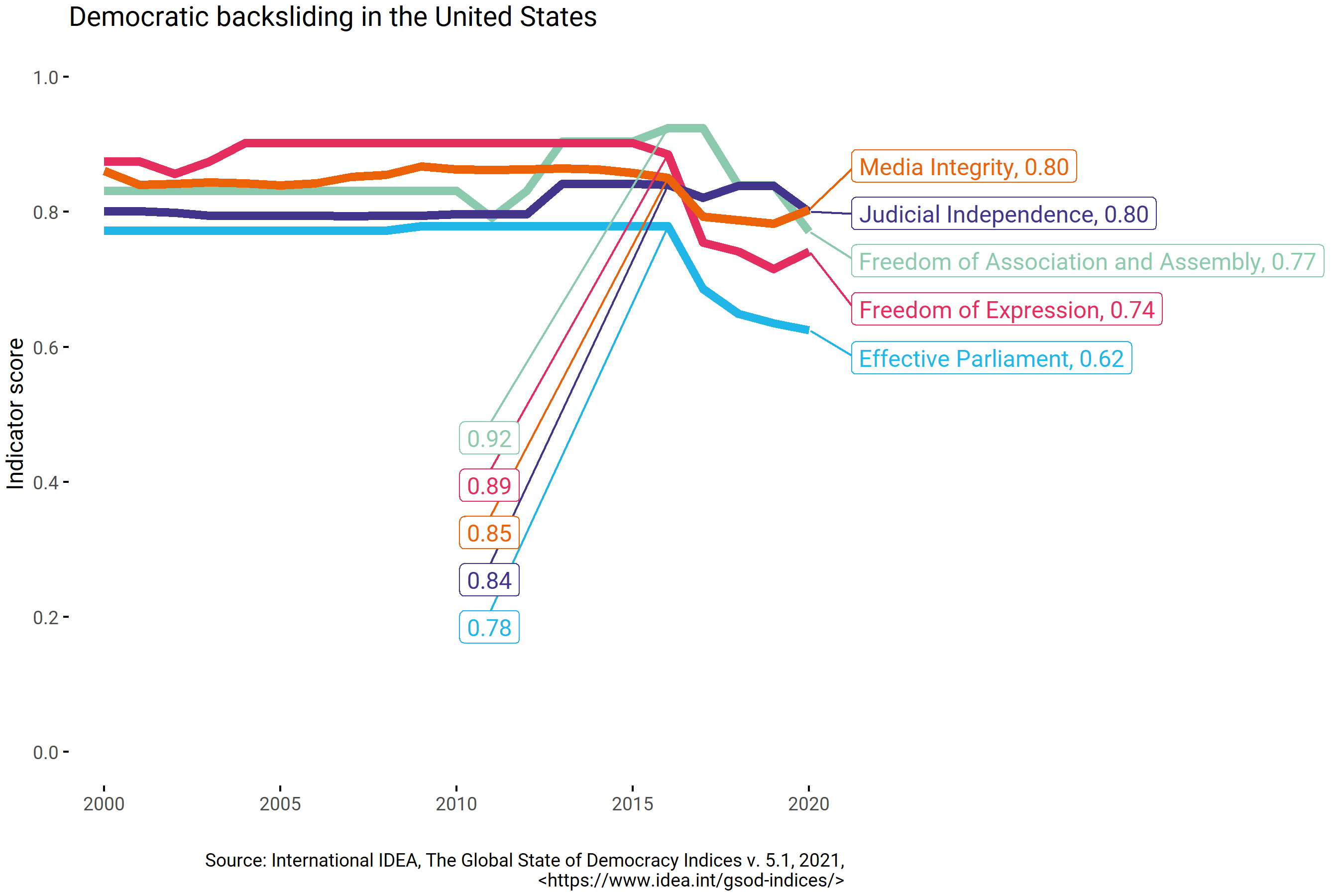
Explainer Democratic Backsliding International Idea Journalists seek surprising findings and tidy narratives, and the most confident voices often will receive the most attention. when highly publicized claims about political science research turn out to be unfounded, we collectively lose public trust. our point is not that we do not know anything about democratic progress and backsliding. Studying democratic backsliding as a multi dimensional process. to make the notion of democratic backsliding amenable to empirical study, it is necessary to start out by providing a clear understanding of the different dimensions of democracy that may come under attack during such processes. In a 2021 article in democratization about “when, where, and why” backsliding has occurred, the authors claim to have reviewed “over 100 working papers and recent articles on democratic backsliding published in 20 top political science journals.” 1 although definitions of backsliding abound, the one by nancy bermeo is the most cited and. After the enormous expansion of democracy that started in the 1980s and gained momentum after the end of the cold war, global levels of democracy have steadily declined since the mid 2000s. 6 central to this global democratic recession is democratic backsliding—processes of political change in which countries that enjoy a certain level of.

Comments are closed.