Shaft Voltage

Shaft Voltage U Sh And Shaft Current I Sh On A Cross Section Of An Shaft voltage occurs in electric motors and generators due to leakage, induction, or capacitive coupling with the windings of the motor. it can occur in motors powered by variable frequency drives, as often used in heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. dc machines may have leakage current from the armature windings. Learn how to use the fluke mda 550 motor drive analyzer and a shaft voltage probe to measure and troubleshoot shaft voltage discharges that can damage bearings. see waveforms, events, and replay features of the analyzer.
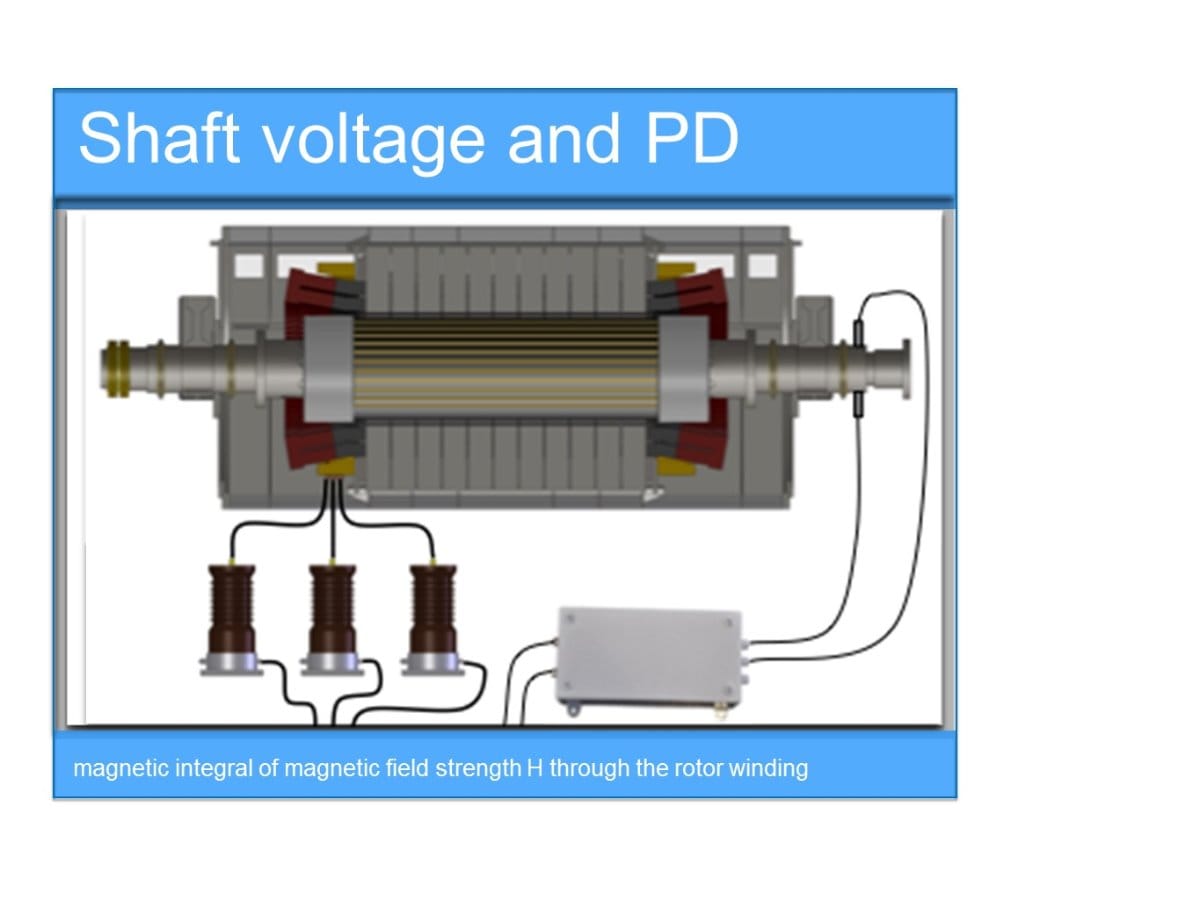
Shaft Voltage Static voltages produced on turbine shafts range from 1 v to 150 v. in one famous case, the shaft voltage on a high speed (20,000 to 30,000 rpm) turbine reached about 600 volts. the static. This paper puts into perspective the state of the art knowledge on bearing currents and diagnosis tools, which rely on shaft voltages and bearing currents phenomena. today, shaft signals measurements are progressively included in predictive health monitoring of large turbo and hydro generators. in addition, bearing fault diagnosis through shaft signals have recently gained some attention to. The turbine voltage of 0.2 volts is very safe while the 4.8 volts on unit #2 could indicate electrostatic voltage generation with possible gradual current pitting of the turbine bearings. figure 13. unit 2 shaft peak currents and voltages for one day. grounding brush currents = 2.2 and 6.7 amperes. “shaft voltage” in papers and articles can be sometimes confusing. references [26] and [27] distinguish clearly the “shaft end to end voltage” as the shaft voltage 𝑣 ℎ (i.e. the voltage between the two bearings along the motor shaft) and the “shaft to frame voltage” as the bearing voltage 𝑣𝑏 (i.e. the.

Shaft Voltage Bearing Currents And Testing The turbine voltage of 0.2 volts is very safe while the 4.8 volts on unit #2 could indicate electrostatic voltage generation with possible gradual current pitting of the turbine bearings. figure 13. unit 2 shaft peak currents and voltages for one day. grounding brush currents = 2.2 and 6.7 amperes. “shaft voltage” in papers and articles can be sometimes confusing. references [26] and [27] distinguish clearly the “shaft end to end voltage” as the shaft voltage 𝑣 ℎ (i.e. the voltage between the two bearings along the motor shaft) and the “shaft to frame voltage” as the bearing voltage 𝑣𝑏 (i.e. the. Capacitive shaft voltage, on the other hand, is present in all motors run by vfds, so all motors on drives are susceptible to capacitive edm current. how to test for shaft voltage measuring the shaft voltage on vfd driven motors provides you with valuable information to determine if there is a potential risk of bearing damage from electrical. Voltage pulses from a variable speed drive can couple from a motor’s stator to its rotor, causing a voltage to appear on the rotor shaft. when this rotor shaft voltage exceeds the insulating capacity of the bearing grease, flashover currents (sparking) can occur, causing pitting and fluting of the motor bearing race, damage that can cause a motor to fail prematurely.

Comments are closed.