Short Run Production Function And Its Short Run Cost Function Do
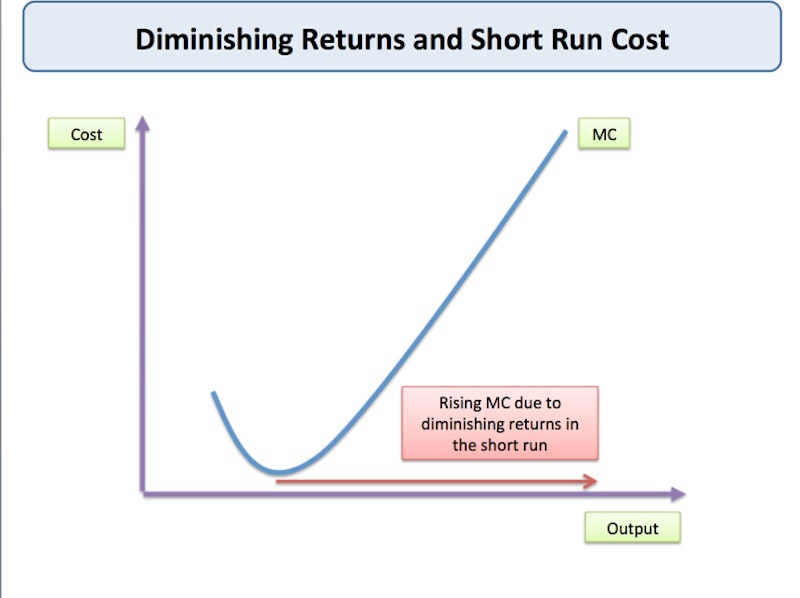
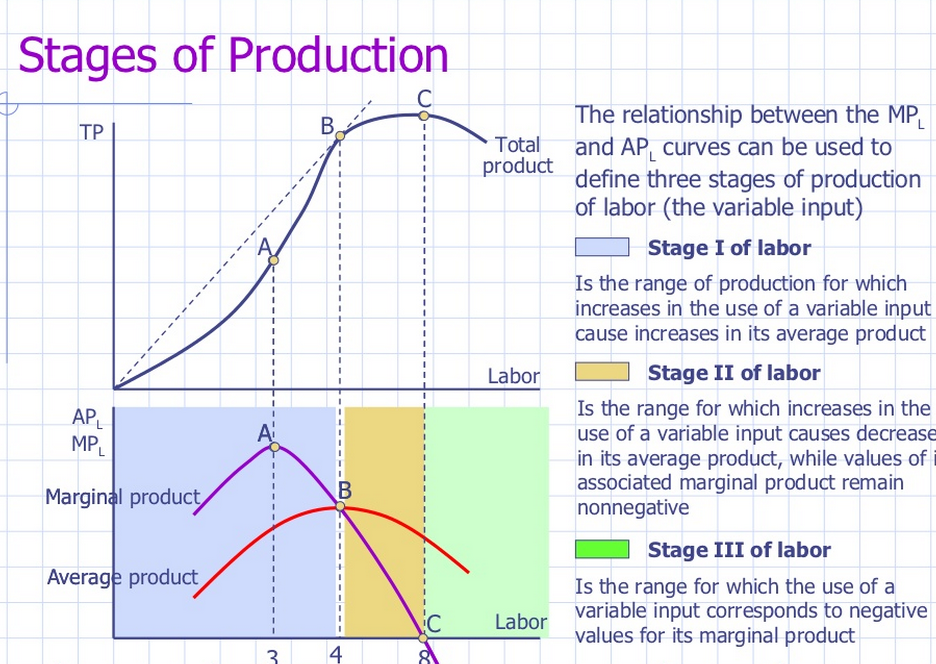
Production Function In The Short Run Reference Library Economics Equation 8.1. m p l = Δq Δl m p l = Δ q Δ l. in addition we can define the average product of a variable factor. it is the output per unit of variable factor. the average product of labor (apl), for example, is the ratio of output to the number of units of labor (q l). In this article we will discuss about the relation between short run costs and production. there is a close relation between production and cost in the short run since one is a mirror image of the other. since in the short run labour was considered to be the only variable factor, columns (1) and (2) of table 14.3 show the points on the production function for three and four units of labour.

Production Function Meaning And Types Tutor S Tips Introduction to production, costs, and industry structure; 7.1 explicit and implicit costs, and accounting and economic profit; 7.2 production in the short run; 7.3 costs in the short run; 7.4 production in the long run; 7.5 costs in the long run; key terms; key concepts and summary; self check questions; review questions; critical thinking. The short run production production assumes there is at least one fixed factor input. production functions. the production function relates the quantity of factor inputs used by a business to the amount of output that result. we use three measures of production and productivity: total product (total output). in manufacturing industries such as. We can decompose costs into fixed and variable costs. fixed costs are the costs of the fixed inputs (e.g., capital). because fixed inputs do not change in the short run, fixed costs are expenditures that do not change regardless of the level of production. whether you produce a great deal or a little, the fixed costs are the same. Then the production function can be interpreted as a function of l only. for example, if we have f(k;l)= k®l¯, then the short run production function is f(l;k)= k®l¯: to ¯nd the conditional labor demand, we invert the short run production function by solving x = f(l;k) for l. this gives us l(x;k), which does not depend.
Handout Short Run Production Theory Economic Investigations We can decompose costs into fixed and variable costs. fixed costs are the costs of the fixed inputs (e.g., capital). because fixed inputs do not change in the short run, fixed costs are expenditures that do not change regardless of the level of production. whether you produce a great deal or a little, the fixed costs are the same. Then the production function can be interpreted as a function of l only. for example, if we have f(k;l)= k®l¯, then the short run production function is f(l;k)= k®l¯: to ¯nd the conditional labor demand, we invert the short run production function by solving x = f(l;k) for l. this gives us l(x;k), which does not depend. In this course this is capital. variable costs are the costs of inputs that can be varied in the short run. in this course this is labor. total costs are the sum of fxed and variable costs: c = f vc. marginal cost is the extra cost for another unit of output: mc = dc dq where c is the total cost. dv c (b) in the short run mc = the marginal. Mathematically, marginal cost is the change in total cost divided by the change in output: \displaystyle mc=\delta tc \delta q m c = Δt c Δq. if the cost of the first widget is $32.50 and the cost of two widgets is $44, the marginal cost of the second widget is. $44 −$32.50 = $11.50 $ 44 − $ 32.50 = $ 11.50.
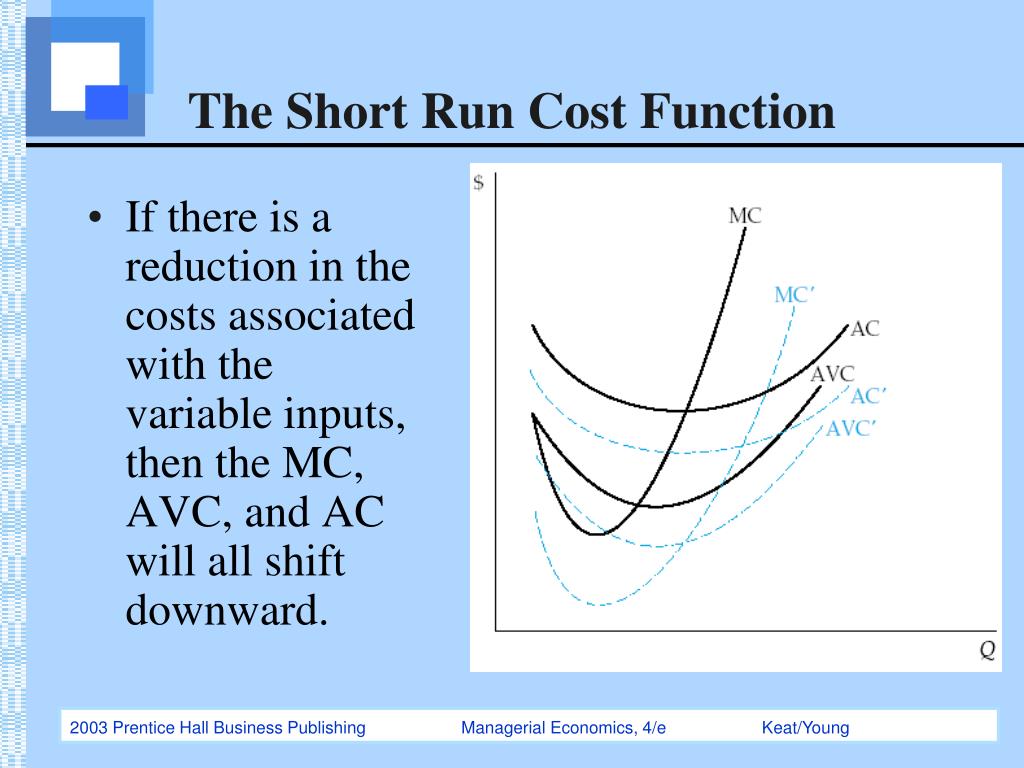
Ppt The Theory And Estimation Of Cost Powerpoint Presentation Free In this course this is capital. variable costs are the costs of inputs that can be varied in the short run. in this course this is labor. total costs are the sum of fxed and variable costs: c = f vc. marginal cost is the extra cost for another unit of output: mc = dc dq where c is the total cost. dv c (b) in the short run mc = the marginal. Mathematically, marginal cost is the change in total cost divided by the change in output: \displaystyle mc=\delta tc \delta q m c = Δt c Δq. if the cost of the first widget is $32.50 and the cost of two widgets is $44, the marginal cost of the second widget is. $44 −$32.50 = $11.50 $ 44 − $ 32.50 = $ 11.50.

Short Run And Long Run Production Analysis

Comments are closed.