Soil Porosity And Permeability

Explain The Difference Between Porosity And Permeability Reading: porosity and permeability. figure 1. a spring coming out of the shale near red creek. yes, that water is black! (photo: matt herod) as we’ve learned, groundwater is simply water that exists underground. however, there are still lots of misconceptions about how people envision groundwater. many envision large underground lakes and. Soil texture effects many other properties like structure, chemistry, and most notably, soil porosity, and permeability. soil porosity refers to the amount of pore, or open space between soil particles. pores are created by the contacts made between irregular shaped soil particles.
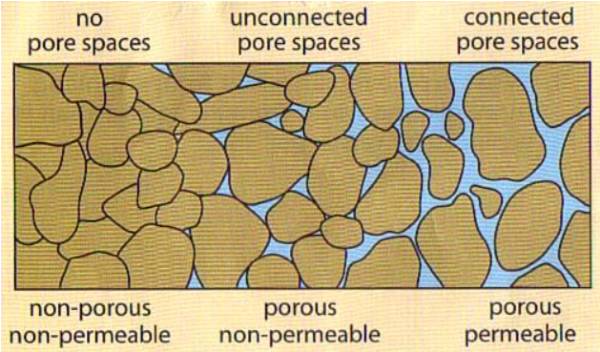
6 Major Difference Between Porosity And Permeability Explained 6–20 inches of water move through the soil per hour. rapid permeability includes textures of loamy sand and sand and soils with greater than 15 % gravel. soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. Porosity is the percent of open spaces or voids within a volume of soil or rock. the porosity of rocks describes the rocks' capacity to hold water. permeability is a physical property of soil and. Porosity. porosity is the amount of empty space in sediments or rocks. i n a soil or rock the porosity (empty space) exists between the grains of particles or minerals. in a material like gravel the grains are large and there is lots of empty space between them since they have angularity or spherical shape. however, in a material like a gravel. Expand collapse global location. 5.2: bulk density, porosity, particle density of soil. page id. anna r. schwyter & karen l. vaughan. university of wyoming via uw open education resources (oer) figure 1. illustration of the difference between bulk density and particle density by plant and soil science elibrary used with written consent.

Comments are closed.