Solidification Of Metals Solidification And Cooling

Solidification Of Metals Solidification And Cooling Youtube To further cool down the metal, spray cooling is used. when the metal is completely solidified, it can be cut into billets. this is a stationary, time invariant, process. the rate at which the metal enters and leaves the modeling domain does not vary with time, and neither does the location of the solidification front. This video covers the following topics in details:1. solidification of metals a. solidification of pure metals b. the solidification of most alloys c.
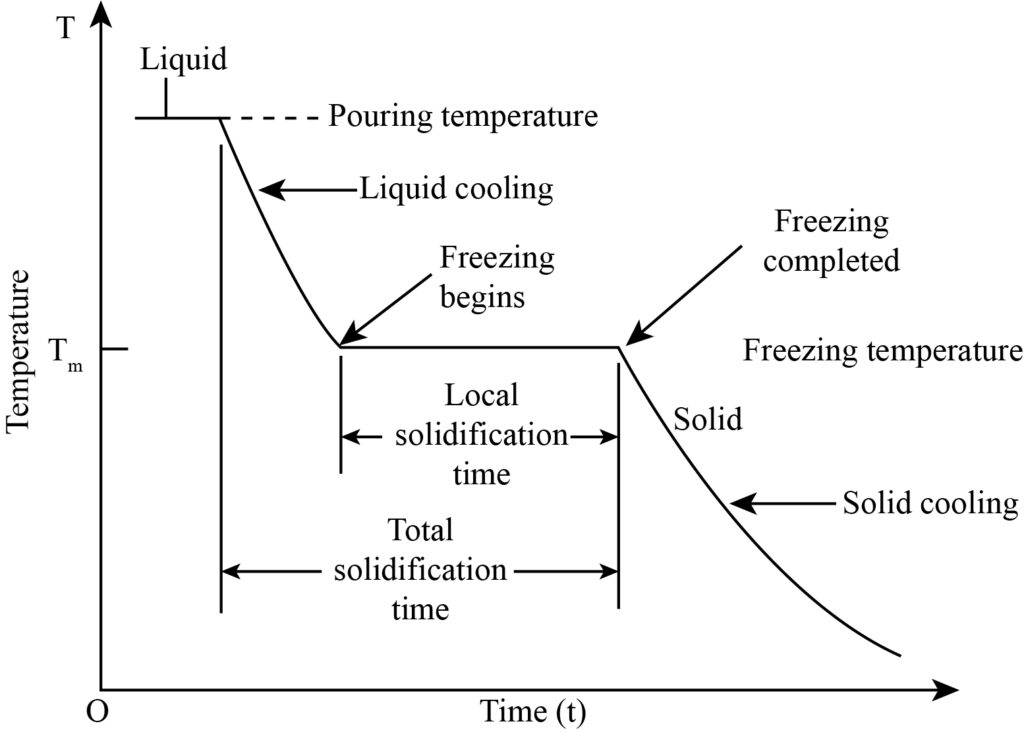
Solidification Of Metals Bartleby The process consists of introducing the liquid metal of appropriate composition into the mould effecting its solidification under controlled conditions of cooling, pouring, etc. to obtain the desired cast structure [3, 4]. a molten metal has a viscosity which is about one twentieth of the corresponding solid. 5 | cooling and solidification of metal for smaller values of Δt, the transition becomes sharper, and the model gives confidence that the metal is completely solidified before the strand is cut. figure 2: the fraction of solid phase for Δt = 75 k shows a gradual transition between the liquid and solid phase. Ated from its environment. in general, solidification is by heterogeneous nucleation, either on impurity particles or wherever the liquid comes into contact. ith the container surface. the velocity v of the transformation front is related to the dier. solid atom jumps and the solid jumps: v exp. q. Cooling and solidification of metal. which ramps the . dt. parameter down to 25 . k. these results are shown in figure 3. the point of complete solidification moves slightly as the transition zone is made smaller. as the transition zone becomes smaller, a finer mesh is needed, otherwise the model might not converge.

Solidification Of Pure Metal Cooling Curve Gibb S Phase Rule Ated from its environment. in general, solidification is by heterogeneous nucleation, either on impurity particles or wherever the liquid comes into contact. ith the container surface. the velocity v of the transformation front is related to the dier. solid atom jumps and the solid jumps: v exp. q. Cooling and solidification of metal. which ramps the . dt. parameter down to 25 . k. these results are shown in figure 3. the point of complete solidification moves slightly as the transition zone is made smaller. as the transition zone becomes smaller, a finer mesh is needed, otherwise the model might not converge. The outside of the mold is cooled and the metal solidifies as it flows through. when the metal leaves the mold, it is completely solidified on the outside, but still liquid inside. the metal will continue to cool and eventually solidify completely, at which point it can be cut into sections. this model is simplified somewhat by not computing. Solidification and cooling shrinkage. concepts and laws. methods of measurement. solidification and cooling shrinkage during casting. solidification shrinkage during ingot casting. solidification and cooling shrinkage during continuous casting. thermal stress and crack formation during solidification and cooling processes. summary. exercises.

Cooling Curve Phase Diagram The outside of the mold is cooled and the metal solidifies as it flows through. when the metal leaves the mold, it is completely solidified on the outside, but still liquid inside. the metal will continue to cool and eventually solidify completely, at which point it can be cut into sections. this model is simplified somewhat by not computing. Solidification and cooling shrinkage. concepts and laws. methods of measurement. solidification and cooling shrinkage during casting. solidification shrinkage during ingot casting. solidification and cooling shrinkage during continuous casting. thermal stress and crack formation during solidification and cooling processes. summary. exercises.

Comments are closed.