Solution Definition Essential Properties 9 Types Examples
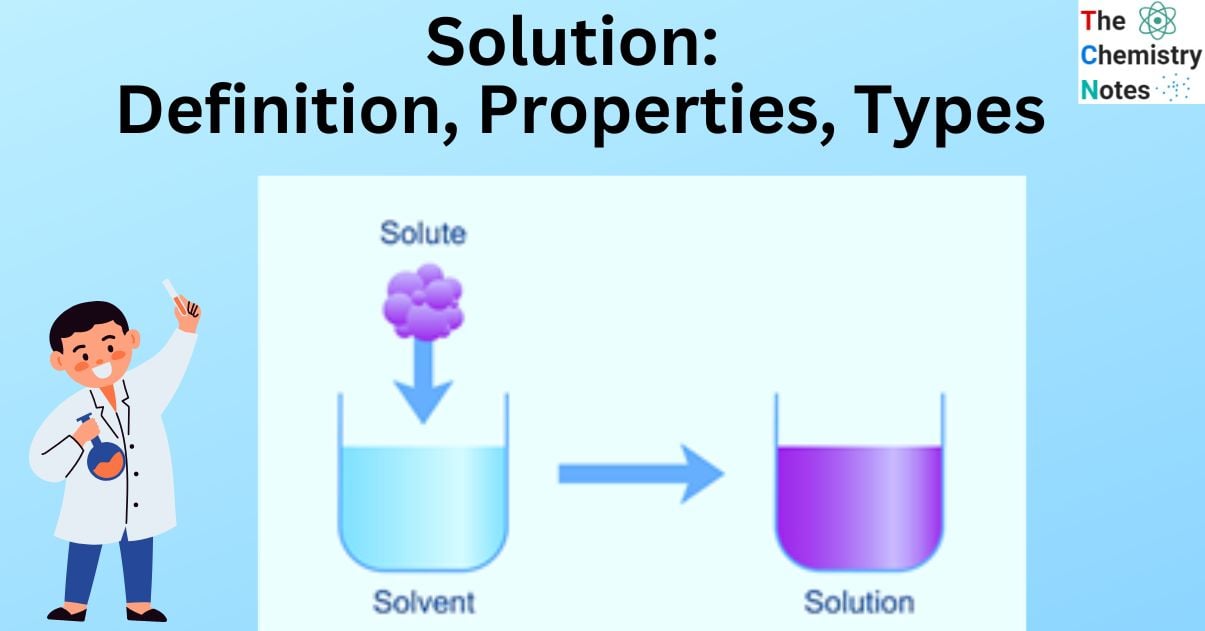
Solution Definition Essential Properties 9 Types Examples Solid liquid solutions are solutions in which the solutes are solid and the solvent is liquid. for example, 1. sucrose (table sugar) dissolved in water (sugar is the solute; water is the solvent) 2. table salt, sodium chloride (nacl), or any other salt that dissolves in water to create an electrolyte. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm. common examples of solutions are sugar in water and salt in water solutions, soda water, etc. in a solution, all the components appear as a single phase. there is particle homogeneity i.e. particles are evenly distributed.

Solution Definition Essential Properties 9 Types Examples A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. a solution is formed of two components: the solute and the solvent. the substance dissolved in the solution is called the solute, whereas the component in which the solute is dissolved is known as a solvent. in this article, we will learn about solutions and their types in detail. A solution is a homogeneous mixture comprising smaller component s called solute s of small molecules or ions comparable in size to the molecules of a larger component called the solvent. for example, nacl dissolved in water is a solution. the solute is almost uniformly distributed in the solvent, making a homogeneous mixture. 13.1: the solution process. solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances whose components are uniformly distributed on a microscopic scale. the component present in the greatest amount is the solvent, and the components present in lesser amounts are the solute (s). the formation of a solution from a solute and a solvent is a. As a result, depending on the physical states of the solute and solvent, there are nine different types of solutions: solid liquid solutions. liquid liquid solutions. gas liquid solutions. solid liquid solution: most solids dissolve in one liquid or the other to form homogeneous mixtures called solid liquid solutions.
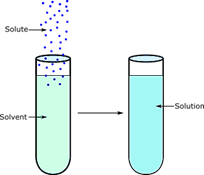
Solution Definition Essential Properties 9 Types Examples 13.1: the solution process. solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances whose components are uniformly distributed on a microscopic scale. the component present in the greatest amount is the solvent, and the components present in lesser amounts are the solute (s). the formation of a solution from a solute and a solvent is a. As a result, depending on the physical states of the solute and solvent, there are nine different types of solutions: solid liquid solutions. liquid liquid solutions. gas liquid solutions. solid liquid solution: most solids dissolve in one liquid or the other to form homogeneous mixtures called solid liquid solutions. Examples of solutions include air, sugar water, steel, saltwater, pancake syrup, and natural gas. examples of solutions. air is an example of a gaseous solution (gas gas). the air we breathe exists in roughly these proportions, and because it is a solution, every sample will nearly match every other sample: 78% nitrogen (. A solution is a homogeneous type of mixture of two or more substances. a solution has two parts: a solute and a solvent. the solute is the substance that dissolves, and the solvent is the majority.

Solution Definition Essential Properties 9 Types Examples Examples of solutions include air, sugar water, steel, saltwater, pancake syrup, and natural gas. examples of solutions. air is an example of a gaseous solution (gas gas). the air we breathe exists in roughly these proportions, and because it is a solution, every sample will nearly match every other sample: 78% nitrogen (. A solution is a homogeneous type of mixture of two or more substances. a solution has two parts: a solute and a solvent. the solute is the substance that dissolves, and the solvent is the majority.

Comments are closed.