Solution Solving Simultaneous Linear Differential Equations By Using

Solution Solving Simultaneous Linear Differential Equations By Using Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): the scheme for solving an ordinary differential equation using laplace transforms. one transforms the initial value problem for \(y(t)\) and obtains an algebraic equation for \(y(s)\). solve for \(y(s)\) and the inverse transform gives the solution to the initial value problem. After differentiating (1) (1) with respect to t t, and substituting in expressions for y y and dy dt d y d t, i got a second order equation and solved it to get the general solution for x x as: (3) x = ae4t be−3t (3) x = a e 4 t b e − 3 t. after this, if i differentiate this expression and use it in (1) (1), i get the general solution.

Solution Solving Simultaneous Linear Differential Equations By Using We get the following system: (s 1 1 s) ⋅(x¯ y¯) =(2 1 s2 1 s s2 1) (s 1 1 s) ⋅ (x ¯ y ¯) = (2 1 s 2 1 s s 2 1) then you will have to multiply the left hand side with. (s 1 1 s)−1 (s 1 1 s) − 1. from the left, then inverse transform the expression. share. cite. follow. answered jul 23, 2014 at 14:36. I. =complete solution is: c.f. p.icase iii: when p.i =1. take the lowest degree term common from to get an expressi. n. f the. orm in the denominator and take it to numerator to become2. expandusing bi. omial theorem up to nth degree as (n 1)th deriv. following expansions will be useful to expand. However, the solution to a certain class of system of simultaneous equations does always converge using the gauss seidel method. this class of system of equations is where the coefficient matrix \(\lbrack a\rbrack\) in \(\lbrack a\rbrack\lbrack x\rbrack = \lbrack c\rbrack\) is diagonally dominant, that is. Cramer’s rule for solving a system of two equations. for the system of equations {a1x b1y = k1 a2x b2y = k2, {a 1 x b 1 y = k 1 a 2 x b 2 y = k 2, the solution (x, y) (x, y) can be determined by. notice that to form the determinant d, we use take the coefficients of the variables.
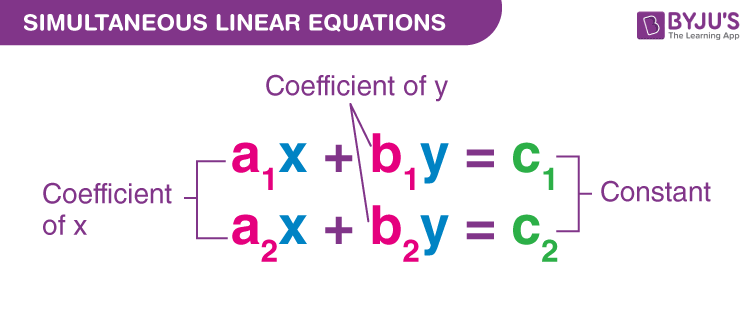
Simultaneous Linear Equations Definition And Examples However, the solution to a certain class of system of simultaneous equations does always converge using the gauss seidel method. this class of system of equations is where the coefficient matrix \(\lbrack a\rbrack\) in \(\lbrack a\rbrack\lbrack x\rbrack = \lbrack c\rbrack\) is diagonally dominant, that is. Cramer’s rule for solving a system of two equations. for the system of equations {a1x b1y = k1 a2x b2y = k2, {a 1 x b 1 y = k 1 a 2 x b 2 y = k 2, the solution (x, y) (x, y) can be determined by. notice that to form the determinant d, we use take the coefficients of the variables. One of the most popular techniques for solving simultaneous linear equations is the gaussian elimination method. the approach is designed to solve a general set of n equations and n unknowns. a11x1 a12x2 a13x3 … a1nxn = b1 a21x1 a22x2 a23x3 … a2nxn = b2 ⋮ ⋮ an1x1 an2x2 an3x3 … annxn = bn. 4.3.1 numerical or symbolic linear equations with solve or linsolve the maxima functions solve, linsolve, and linsolve by lu can be used for linear equations. linear equations containing symbolic coefcients can be solved by solve and linsolve. for example the pair of equations. ax by=c;dx ey=f.

Simultaneous Linear Equations Solver Solved Examples Cuemath One of the most popular techniques for solving simultaneous linear equations is the gaussian elimination method. the approach is designed to solve a general set of n equations and n unknowns. a11x1 a12x2 a13x3 … a1nxn = b1 a21x1 a22x2 a23x3 … a2nxn = b2 ⋮ ⋮ an1x1 an2x2 an3x3 … annxn = bn. 4.3.1 numerical or symbolic linear equations with solve or linsolve the maxima functions solve, linsolve, and linsolve by lu can be used for linear equations. linear equations containing symbolic coefcients can be solved by solve and linsolve. for example the pair of equations. ax by=c;dx ey=f.

Comments are closed.